How to prepare the perfect Gram stain - Gram staining procedure
Summary
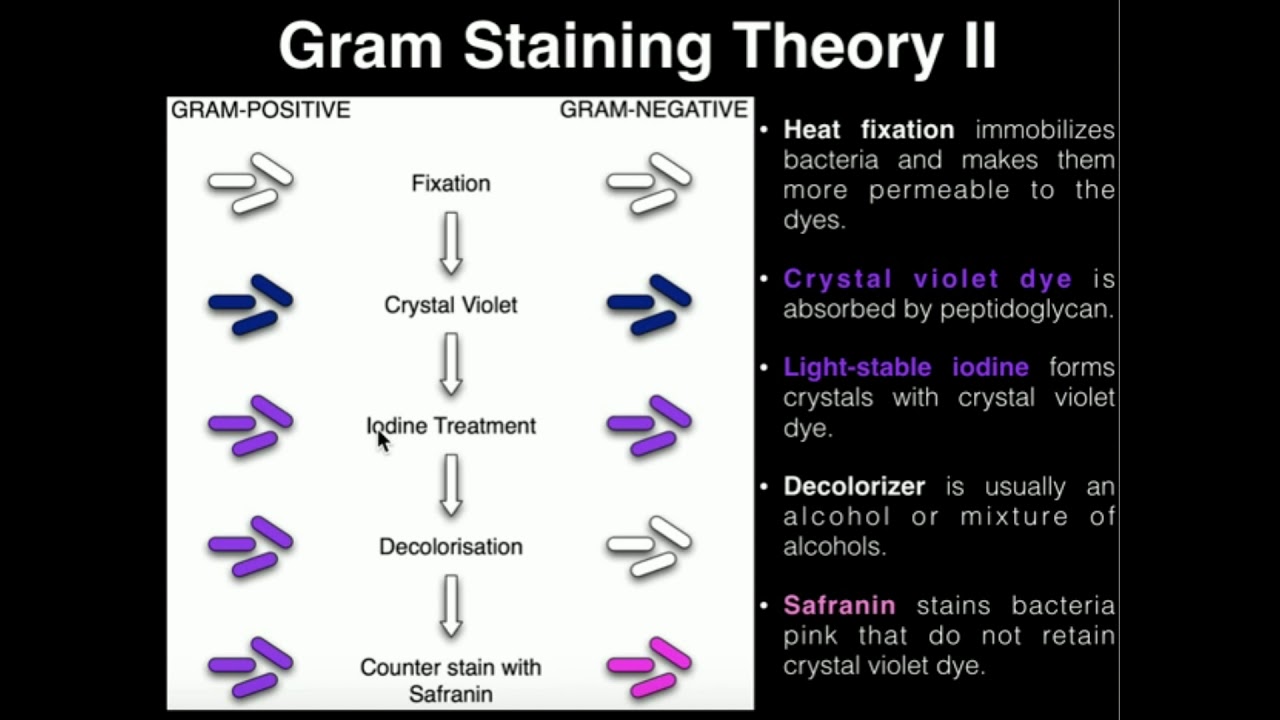
TLDRThe Gram stain, developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, is a vital microbiological technique used to differentiate bacteria into two categories: gram-positive and gram-negative. It involves a series of steps including staining with crystal violet, iodine, decolorizing with alcohol, and counterstaining with saffron or carbol fuchsin. Gram-positive bacteria appear blue-purple, while gram-negative bacteria turn pink-red. The technique helps identify bacterial shapes (cocci, rods, or spirals) and is essential for diagnosing infections. Proper technique is crucial, as over or under-decolorization can lead to inaccurate results.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Gram stain was developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884 and is used to differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- 😀 The Gram stain provides two critical features: the gram reaction (color) and the morphology (shape) of bacterial cells.
- 😀 Bacterial cells can have three common shapes: spherical, rod, or corkscrew. These shapes are important in identifying bacteria.
- 😀 The Gram stain works by differentiating bacteria based on the structure of their cell walls, specifically the peptidoglycan layer.
- 😀 Gram-positive bacteria stain dark blue or purple because they have a thick peptidoglycan layer that retains the primary dye.
- 😀 Gram-negative bacteria stain pink or red due to their thin peptidoglycan layer, which allows the dye to be washed away during decolorization.
- 😀 Proper technique involves using sterile saline or water to prepare the slide and distributing the cells evenly for accurate results.
- 😀 Methanol is used to fix bacterial cells to the slide, ensuring they don't wash off during the staining process and preserving cell morphology.
- 😀 Decolorization is a critical step that uses alcohol and acetone to extract lipids from the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria, leading to dye loss.
- 😀 Saffranin is used as a counterstain to color the gram-negative bacteria pink or red, while gram-positive bacteria retain their initial crystal violet stain.
- 😀 To avoid errors, it’s essential to stop decolorization at the right time, as over-decolorization or under-decolorization can lead to false results.
- 😀 After staining, the slide should be dried gently, either by air-drying or blotting with lint-free paper, to avoid removing the smear.
Q & A
Who developed the Gram stain and when?
-The Gram stain was developed by Hans Christian Gram, a Danish botanist and pharmacology teacher, in 1884.
What does the Gram stain help to distinguish between?
-The Gram stain is used to distinguish between gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial cells.
What are the two main features observed in the Gram stain?
-The two main features observed in the Gram stain are the gram reaction (color of the cell) and the cell morphology (shape of the cell).
What are the three main shapes of bacterial cells?
-The three main shapes of bacterial cells are spherical, rod-shaped, and corkscrew-shaped.
What is the importance of knowing the bacterial cell type causing an infection?
-Knowing the type of bacterial cell causing an infection is critical to determining the appropriate treatment for the patient.
How does the Gram stain differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
-The Gram stain differentiates bacteria based on the structure of their cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer that retains the primary dye, while gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer that loses the primary dye during the decolorization step.
What is the role of the methanol fixation in the Gram stain process?
-Methanol fixation is used to fix the bacterial cells to the slide, preventing them from washing off during staining. It also helps preserve the morphology of the cells.
Why is heat fixation not recommended for Gram staining?
-Heat fixation is not recommended because it can distort the cells, increase cell debris, and may lead to inaccurate Gram reactions.
What happens during the decolorization step in the Gram stain process?
-During decolorization, the alcohol-acetone mixture removes lipids from the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria, making their walls permeable and causing them to lose the purple dye. In contrast, gram-positive bacteria's thicker cell walls retain the dye.
What is the counterstain used in the Gram stain, and what is its purpose?
-The counterstain used is saffron or carbol fuchsin. It stains gram-negative bacteria pink to red, allowing for differentiation from gram-positive bacteria, which retain the initial crystal violet stain.
Why is over-decolorization or under-decolorization a concern in the Gram stain?
-Over-decolorization can lead to false gram-negative results, while under-decolorization can result in false gram-positive results, both of which compromise the accuracy of the test.
What is the magnification achieved when using the oil immersion objective in the Gram stain?
-The oil immersion objective, when used with the high-power objective lens (100x), results in an overall magnification of 1000x.
What is the purpose of the Gram Stain Advanced kit offered by Hardy Diagnostics?
-The Gram Stain Advanced kit from Hardy Diagnostics offers improved staining formulations that produce bright, vivid colors, even for bacteria that are difficult to stain, ensuring superior results.
How can the quality of the Gram stain and technique be tested?
-The quality of the Gram stain and technique can be tested using Hardy Diagnostics' quality control slides, which are pre-inoculated and methanol-fixed with both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)