Pengaruh kekuatan ion
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explains the relationship between ionic strength and potentiometric measurements, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a constant ionic strength for accurate results. The script covers how ionic strength influences the activity coefficient, which in turn affects the linear relationship between cell potential and analyte concentration. Practical examples demonstrate the calculation of ionic strength in solutions like NaCl and MgCl2. The use of Ionic Strength Adjusters (ISA), such as NaCl, is explored as a method to stabilize ionic strength, ensuring reliable measurements, especially when using ion-selective electrodes for concentration determination.
Takeaways
- 😀 Quantitative analysis aims to determine the concentration of an analyte in a sample, not just the sample itself.
- 😀 In potentiometry, the primary measurement is the cell potential, which is related to the analyte's activity in the solution.
- 😀 The relationship between activity and concentration is expressed as: activity = activity coefficient × concentration.
- 😀 The linear relationship between cell potential and the logarithm of concentration holds true only if the activity coefficient is constant.
- 😀 The activity coefficient depends on the ionic strength of the solution.
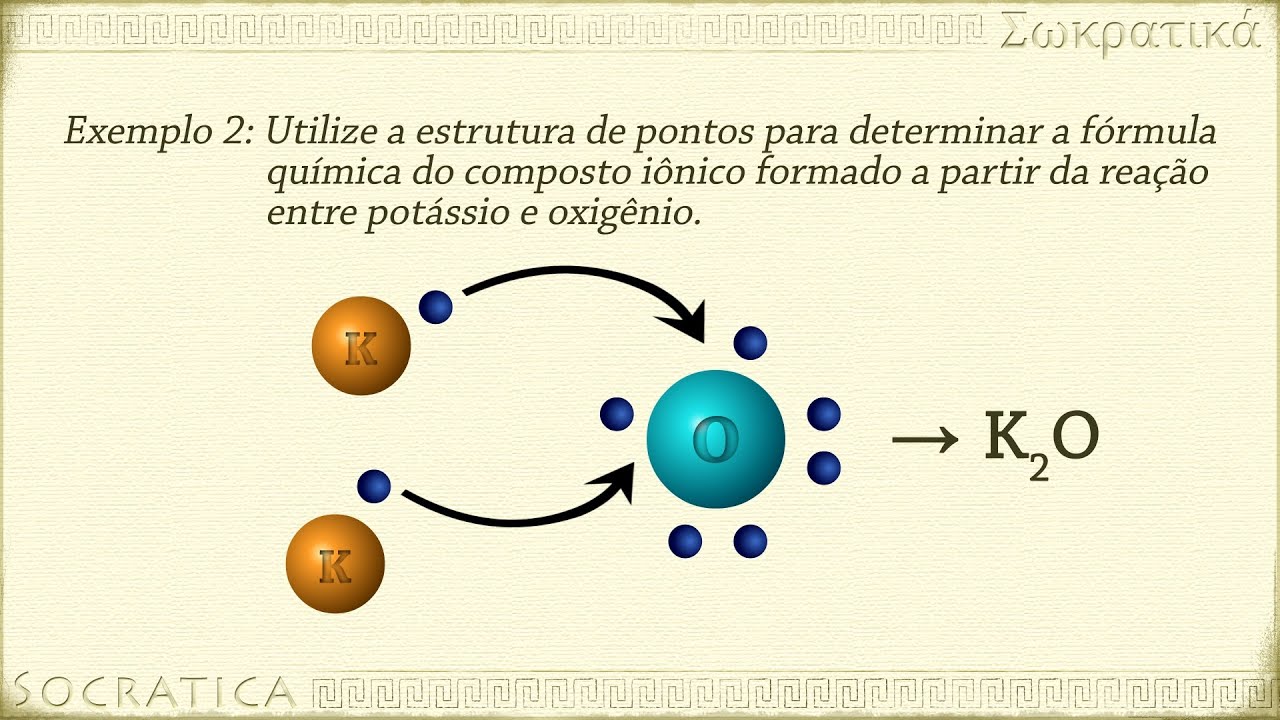
- 😀 Ionic strength (I) is calculated as half the sum of the concentration of each ion multiplied by the square of its charge.
- 😀 For NaCl (0.1 M), the ionic strength is 0.1, while for MgCl2 (0.1 M), the ionic strength is 0.3.
- 😀 Mixing NaCl (0.1 M) and MgCl2 (0.1 M) results in a total ionic strength of 0.4.
- 😀 To maintain a constant activity coefficient, the ionic strength must remain constant, which can be achieved by adding an ionic strength adjuster (ISA).
- 😀 Adding NaCl as an ISA can help ensure that the ionic strength remains constant, leading to more reliable potentiometric measurements.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of quantitative analysis in potentiometry?
-The primary goal of quantitative analysis in potentiometry is to determine the concentration of an analyte in a sample, not just its presence.
What does the cell potential in potentiometry relate to?
-In potentiometry, the cell potential is related to the activity of the analyte in solution, and this relationship can be described using a mathematical equation.
How is activity related to concentration in potentiometry?
-Activity is related to concentration through the equation: activity = activity coefficient × concentration. The activity coefficient depends on factors like ionic strength.
What is the relationship between cell potential and concentration?
-The relationship between cell potential and concentration is linear only if the activity coefficient is constant, which happens when the ionic strength remains constant.
What role does ionic strength play in potentiometric measurements?
-Ionic strength affects the activity coefficient, which in turn impacts the cell potential. For consistent results, the ionic strength must be constant during measurements.
What is the equation for calculating ionic strength?
-Ionic strength is calculated as: Ionic strength = 1/2 × Σ (concentration of ion i × charge of ion i^2), where the sum is over all ions present in the solution.
How do we calculate ionic strength for NaCl and MgCl2 solutions?
-For a 0.1 M NaCl solution, the ionic strength is 0.1, while for a 0.1 M MgCl2 solution, the ionic strength is 0.3. If both are mixed, the total ionic strength is the sum of the individual ionic strengths, which in this case would be 0.4.
What is an ionic strength adjuster (ISA), and why is it used?
-An ionic strength adjuster (ISA) is used to maintain a constant ionic strength in a solution, which helps stabilize the activity coefficient and ensures accurate potentiometric measurements.
What should be added as an ISA when measuring magnesium ion concentration?
-To maintain constant ionic strength, NaCl can be added as an ISA, ensuring that the ionic strength remains at 0.1 M in each measuring flask.
What are the key requirements for compounds used as ionic strength adjusters?
-Compounds used as ionic strength adjusters must be soluble in the solution and have a very small selectivity coefficient, meaning they should not interfere with the analyte being measured (e.g., Na+ ions should not affect the Mg2+ ion selective electrode).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)