Respon imun bawaan: Proses Inflamasi
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the body's innate immune system, focusing on its non-specific defense mechanisms. It explains the two main categories of immune defense: external and internal. External defense involves barriers like skin and mucus, while internal defense engages the immune system, which actively attacks invaders like bacteria. The video further explains inflammation, its purpose, and the role of immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils in fighting infections. It details how these cells trigger the immune response, activating proteins and cytokines to protect the body. The information aims to help viewers understand complex immune processes in a straightforward way.
Takeaways
- 😀 The body's immune defense system is divided into external and internal components.
- 😀 External defense includes anatomical barriers such as skin, mucous membranes, and physical activities like sneezing or coughing.
- 😀 Internal defense involves the immune system, which actively attacks and eliminates pathogens.
- 😀 The immune system is divided into innate and adaptive components, with innate immunity being nonspecific and the first line of defense.
- 😀 Inflammation is the body’s response to foreign invaders or tissue damage, with the goal of neutralizing threats and promoting healing.
- 😀 Inflammation triggers the recruitment of phagocytes and plasma proteins to the site of infection or damage.
- 😀 Key players in inflammation include neutrophils, macrophages, and other white blood cells (leukocytes), which consume pathogens and clean up debris.
- 😀 Cytokines, produced by immune cells, play a vital role in coordinating the immune response by signaling other immune cells to act.
- 😀 The process of phagocytosis involves immune cells engulfing and breaking down pathogens like bacteria.
- 😀 The inflammatory response also involves the dilation of blood vessels to allow immune cells to reach the affected area more efficiently.
Q & A
What are the two main types of body defense systems discussed in the transcript?
-The two main types of body defense systems discussed are the external defense system and the internal defense system. The external system includes physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, while the internal system involves the immune response activated by immune cells like macrophages.
What does the external defense system include?
-The external defense system includes anatomical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes, as well as secretions like lysosomes, hydrochloric acid (HCL) in the stomach, and activities like sneezing and cilia movement.
How does the external defense system work passively?
-The external defense system works passively by weakening or neutralizing invaders, such as bacteria, without actively attacking them. For example, HCL in the stomach does not directly kill bacteria but creates an environment that prevents bacterial survival.
What is the role of macrophages in the immune response?
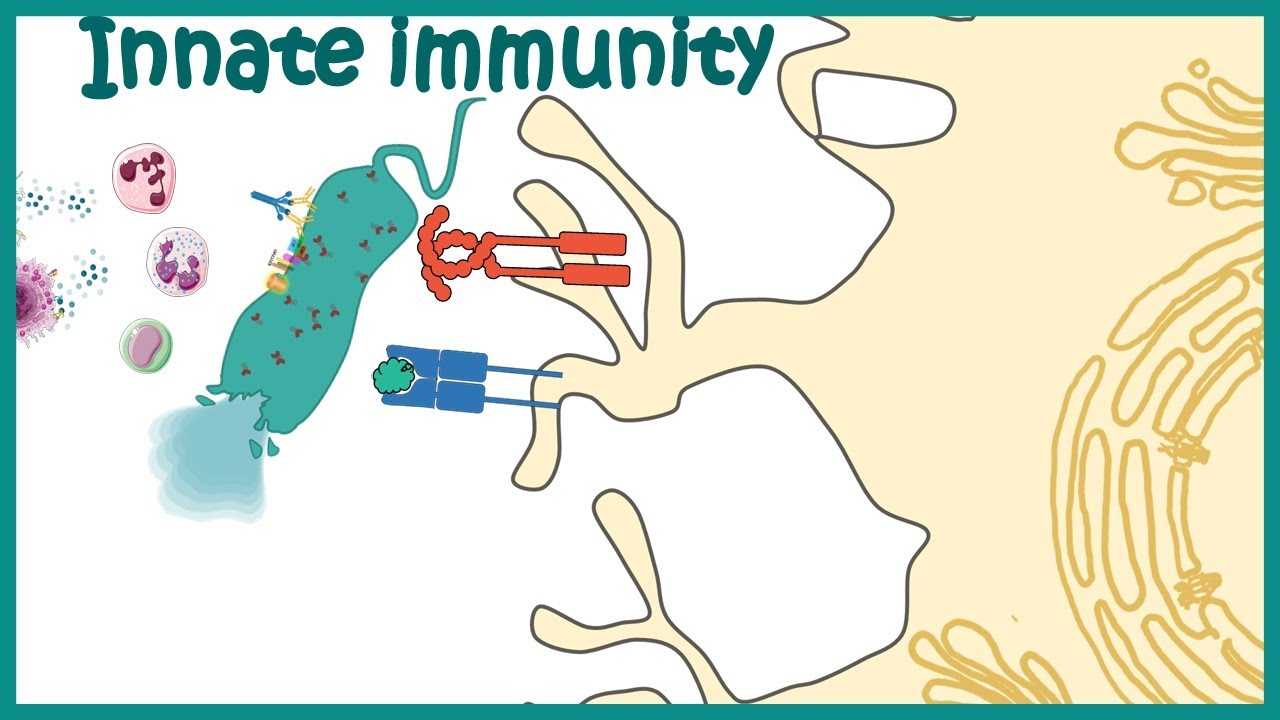
-Macrophages are immune cells that play a key role in phagocytosis, where they engulf and digest foreign invaders like bacteria. They also release cytokines to recruit other immune cells to the site of infection.
What is inflammation (informasi), and why does it occur?
-Inflammation is the body's response to foreign invasion or tissue damage. It occurs to recruit immune cells and plasma proteins to the affected area to help destroy invaders, clear debris, and initiate tissue healing.
What are cytokines, and how do they function in the immune response?
-Cytokines are signaling proteins released by immune cells like macrophages. They help coordinate the immune response by attracting other immune cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, to the site of infection or injury.
What happens during the process of phagocytosis?
-During phagocytosis, immune cells like macrophages engulf and digest foreign invaders, such as bacteria. The bacteria are broken down inside the cell, and the process helps to clear the infection and prepare for healing.
How does the body ensure that immune cells reach the site of infection?
-The body increases the permeability of blood vessels in the affected area, allowing immune cells like neutrophils and monocytes to migrate from the bloodstream into the tissue. This process is facilitated by cytokines and other signaling molecules.
What are neutrophils and monocytes, and what role do they play in inflammation?
-Neutrophils and monocytes are types of white blood cells that play important roles in the immune response. They are attracted to the site of infection by cytokines, where they help to clear pathogens and debris, aiding in the resolution of inflammation.
How does the immune system distinguish between foreign invaders and normal tissue?
-The immune system recognizes foreign invaders, such as bacteria, by detecting changes in the tissue or the presence of molecules that are not normally found in the body. Damaged tissue is often seen as foreign, prompting an immune response to remove or repair it.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Apa itu Sistem Imun ?

(209) Inflammation, B cells and Antibodies

Sistem pertahanan tubuh non spesifik eksternal. sistem pertahanan tubuh lapis pertama. biologi SMA

Basics of IMMUNOLOGY I Lecture 1 I Immune system I Immunity I CSIRNET I UPSC I NEET I GATE I IITJAM
Innate immune system (detailed overview)

Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh : (1) Pertahanan Eksternal dan Internal BIOLOGI 11 SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
