Torque Converter, How does it work?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the workings of the torque converter in automatic transmission vehicles. It showcases how this component isolates the engine from the transmission, preventing stalling during braking, and multiplies torque to improve acceleration. The video covers the roles of the pump, turbine, reactor, and one-way clutch, detailing their fluid mechanics and interaction. It also discusses the role of the lock-up clutch in enhancing energy efficiency. The torque converter’s brilliant design ensures smooth driving and efficient power transfer, making it essential for modern automatic transmissions.
Takeaways
- 😀 An automatic transmission car eliminates the need for manual gear shifting and clutch pedal operation, thanks to the torque converter.
- 😀 The torque converter isolates the engine from the transmission during braking to prevent mechanical failure or engine stalling.
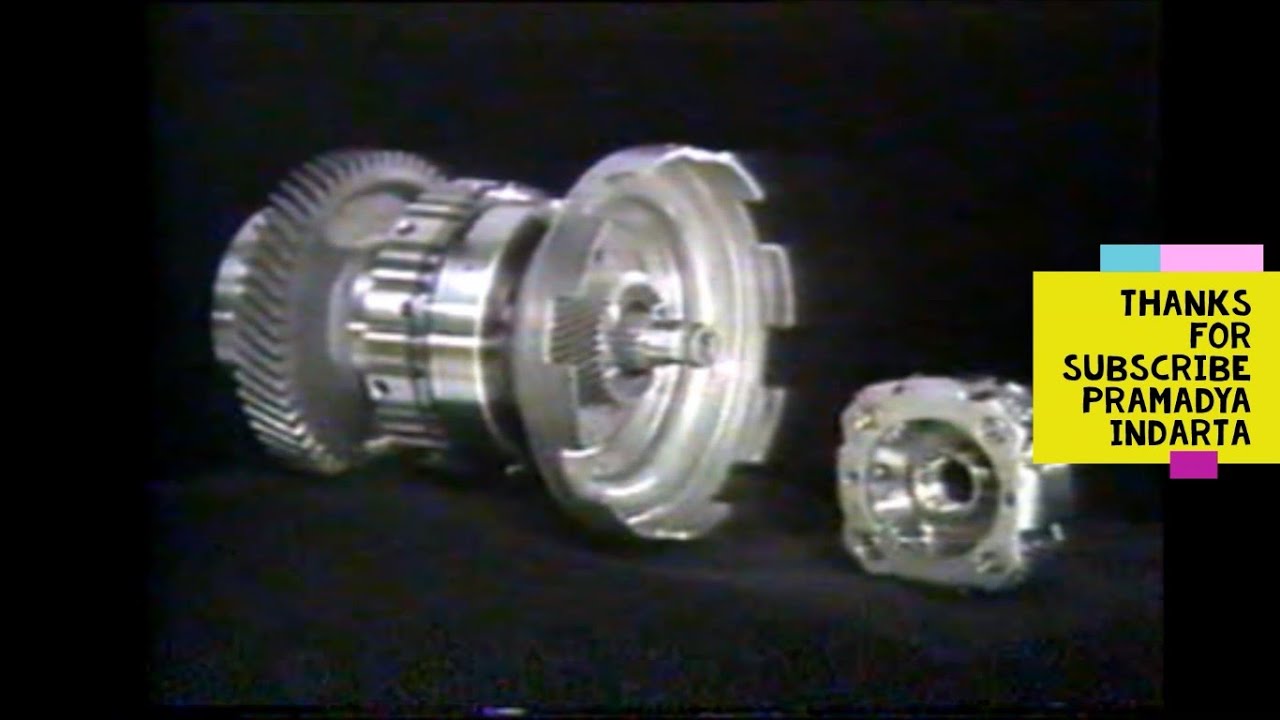
- 😀 The torque converter consists of a pump and turbine immersed in transmission fluid, which transfers engine power to the transmission.
- 😀 A fluid flywheel configuration allows the pump and turbine to work together, with energy transferred via transmission fluid.
- 😀 The reactor in a torque converter helps direct fluid from the turbine back to the pump, ensuring efficient operation even during sudden stops.
- 😀 The torque converter can multiply torque at the vehicle's start, increasing the vehicle's initial power when needed.
- 😀 A one-way clutch in the reactor helps to prevent the reactor from spinning in the opposite direction, assisting in torque multiplication.
- 😀 As the vehicle speed increases, the torque converter gradually reduces torque multiplication and the reactor starts spinning in the same direction as the pump and turbine.
- 😀 The turbine blades are curved to absorb the maximum amount of fluid energy, but without a reactor, energy losses would harm the torque converter's efficiency.
- 😀 Modern torque converters use a lock-up clutch to eliminate energy loss due to fluid friction, making the system more efficient during normal operation.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the torque converter in an automatic transmission vehicle?
-The torque converter isolates the engine rotation from the transmission during braking and transfers power to the transmission during normal driving conditions, ensuring smooth vehicle operation.
How does the torque converter help prevent the engine from stalling when braking?
-The torque converter acts as a motion isolator, allowing the engine to keep running while the transmission and drive wheels stop during braking, preventing the engine from stalling.
What is the basic configuration of a simplified torque converter?
-A simplified torque converter consists of a pump and a turbine immersed in transmission fluid, where the pump is connected to the engine and the turbine is connected to the transmission. The fluid transfers motion and power between the pump and turbine.
What role does the reactor play in a torque converter?
-The reactor helps in efficiently redirecting the fluid from the turbine back to the pump, improving the torque converter's performance, especially in terms of torque multiplication during the vehicle’s start.
Why is the torque converter considered to multiply torque?
-The torque converter multiplies torque by utilizing the reactor, which redirects fluid from the turbine back to the pump, increasing pressure and thus amplifying the torque delivered to the transmission when the vehicle starts moving.
What causes the turbine to rotate at a slower speed than the pump in a torque converter?
-The turbine rotates slower than the pump due to energy losses in the fluid that connects them. These losses occur as the fluid transfers power between the pump and turbine.
How does the torque converter’s one-way clutch work with the reactor?
-The one-way clutch in the reactor allows the reactor to rotate only in one direction, preventing it from spinning in the opposite direction, which helps in directing fluid flow in a way that increases the pump’s efficiency and torque multiplication.
Why are the turbine blades in a torque converter curved?
-The turbine blades are curved to absorb the maximum energy from the fluid, allowing the fluid to leave in the opposite direction of the pump's rotation, which is necessary for optimal power transfer and torque conversion.
What is the role of the lock-up clutch in modern torque converters?
-The lock-up clutch in modern torque converters locks the turbine to the pump, eliminating fluid friction and energy loss, allowing both components to turn at the same speed during normal operation.
Why is the actual configuration of a torque converter more complex than the simplified model?
-The actual configuration is more complex to ensure efficient operation, with the pump and turbine aligned along the crankshaft centerline and a bearing used to center the turbine, which isn't required in the simplified version.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)