How Do AC and DC Generators Work? // HSC Physics
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working principles of generators, focusing on how mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy via Faraday's Law of Induction. It covers both AC and DC generators, highlighting their structural differences, such as the use of slip rings in AC generators and split ring commutators in DC generators. The video also delves into how these generators produce alternating and direct currents, and how factors like rotational speed affect frequency and amplitude. A comparison of both types of generators, alongside their applications and limitations, is also provided.
Takeaways
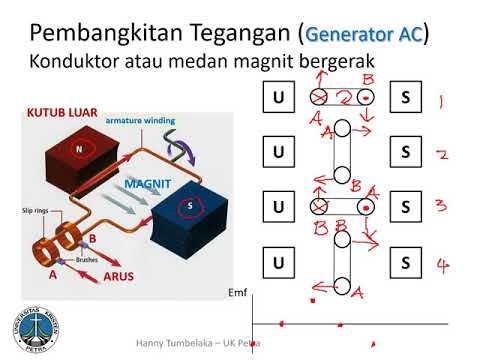
- 😀 A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, using Faraday's law of induction.
- 😀 The structure of a generator is similar to that of a DC motor, with a coil rotating inside a magnetic field.
- 😀 AC generators produce alternating current (AC), while DC generators produce direct current (DC).
- 😀 AC generators use slip ring commutators to produce alternating current, where the current direction reverses every half rotation of the coil.
- 😀 The frequency of AC generated is proportional to the rotational speed of the coil.
- 😀 Lenz's law helps determine the direction of the induced current in a generator, opposing the changing magnetic flux.
- 😀 The induced current in an AC generator changes direction every half revolution of the coil.
- 😀 The magnetic flux in an AC generator changes sinusoidally as the coil rotates, leading to a corresponding sinusoidal EMF.
- 😀 DC generators use split ring commutators to maintain unidirectional current flow in the external circuit, ensuring the current does not reverse direction.
- 😀 The direction of current in a DC generator remains constant, even though the current within the coil reverses during each revolution.
- 😀 The rotational speed of the generator affects both the frequency and amplitude of the induced EMF and current produced.
Q & A
What is the main function of a generator?
-A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using Faraday's law of induction to induce electromotive force (emf) and produce current.
How does the structure of a generator resemble a DC motor?
-The structure of a generator is similar to a simple DC motor in that it consists of multiple turns of a coil inside a magnetic field. This coil rotates within the magnetic field to produce electrical energy.
What is the difference between an AC generator and a DC generator?
-An AC generator produces alternating current (AC) by using slip ring commutators, while a DC generator produces direct current (DC) by using split ring commutators.
What role do slip rings play in an AC generator?
-In an AC generator, slip rings are used to ensure that the current produced alternates. They maintain constant contact with the brushes and allow the current to reverse direction every 180 degrees of coil rotation.
How does Lenz's Law apply to the operation of a generator?
-Lenz's Law states that the induced current will oppose the change in magnetic flux that caused it. This principle is applied in generators to determine the direction of the induced current based on the coil’s rotation.
How does the rotation speed of the coil affect the frequency of the current produced?
-The frequency of the alternating current (AC) in a generator is directly proportional to the speed at which the coil rotates. A faster rotation results in a higher frequency of the alternating current.
Why does the direction of current reverse in an AC generator?
-The direction of current reverses in an AC generator because the coil rotates 180 degrees, causing a reversal in the movement of the coil within the magnetic field, and the induced current alternates to oppose the change in magnetic flux.
How does the induced emf behave as the coil rotates in the magnetic field?
-The induced emf in a generator changes sinusoidally as the coil rotates. The emf reaches its peak when the rate of flux change is the greatest and is zero when the coil is aligned parallel to the magnetic field.
What is the key difference in the commutators between a DC generator and an AC generator?
-The key difference is that a DC generator uses split ring commutators, which maintain a unidirectional current, while an AC generator uses slip ring commutators that allow the current to alternate.
Why can't DC generators be used with transformers?
-DC generators produce unidirectional current, which does not fluctuate, making it incompatible with transformers. Transformers require alternating current (AC), which changes direction to induce a magnetic field for voltage conversion.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)