Pembagian Kelas IP Address
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the basics of IP address classification, an essential concept for building computer networks. It covers the definition of an IP address, its structure, and its conversion from binary to decimal. The video details five IP address classes (A, B, C, D, E) and their specific ranges, usage, and purposes. It highlights how to determine the class of an IP address based on its first octet, and how these classes are used in different network scales, from large to small. It also provides practical examples and clarifies that IP address classes do not impact network speed.
Takeaways
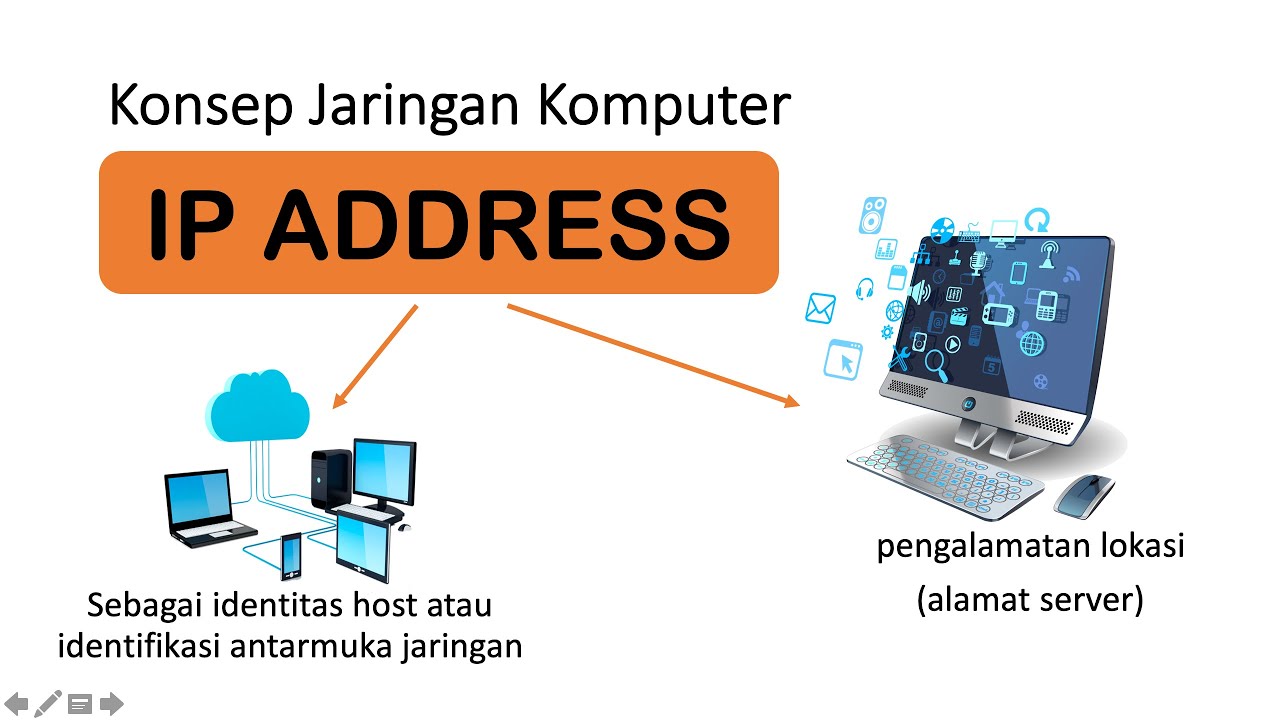
- 😀 An IP address is a unique identifier for devices connected to a network, ensuring no two devices have the same address.
- 😀 IP addresses can be compared to home addresses, where each device on a network has a unique 'address' to distinguish it from others.
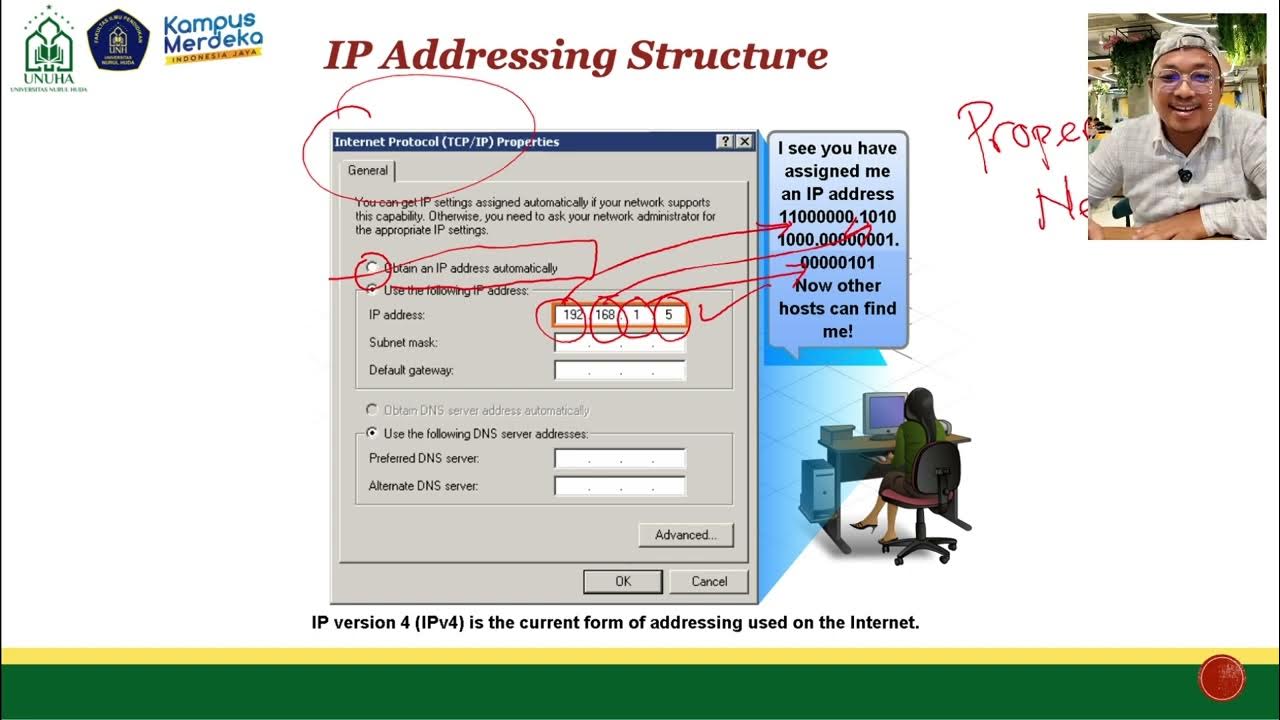
- 😀 An IP address consists of 32 binary digits (bits) grouped into 4 octets, each containing 8 bits, often written in decimal format for easier readability.
- 😀 The decimal format of an IP address ranges from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255, making it easier for humans to remember compared to binary format.
- 😀 There are five main classes of IP addresses: Class A, B, C, D, and E. Each class is used for different network sizes and purposes.
- 😀 Class A IP addresses range from 1.0.0.0 to 126.0.0.0, typically used for large networks, with a network ID in the first octet.
- 😀 Class B IP addresses range from 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255, used for medium-sized networks with the network ID in the first two octets.
- 😀 Class C IP addresses range from 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255, used for small networks, with the network ID in the first three octets.
- 😀 Class D IP addresses (used for multicast) range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255, while Class E addresses are reserved for research purposes and range from 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
- 😀 The first octet of a Class A IP address always starts with a 0 in binary, Class B with 10, Class C with 110, Class D with 1110, and Class E with 1111, helping classify the addresses.
- 😀 The address 127.0.0.1 is a special 'localhost' address used by devices to communicate with themselves, regardless of whether they are connected to a network.
- 😀 IP addresses from Class D and E are not used for general public networks. Classes A, B, and C are meant for standard networking purposes, while others serve specific functions like research and multicast.
Q & A
What is an IP address?
-An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It ensures that devices can communicate with each other over the network. An IP address can be thought of as the address of a house, where each device has its own unique address.
What is the role of an IP address in a computer network?
-The role of an IP address in a computer network is to provide a unique identifier to each device. This allows devices like computers, servers, phones, and printers to communicate with each other, ensuring that data is sent to the correct location.
Why is it easier for humans to remember IP addresses in decimal format rather than binary?
-Humans find it easier to remember numbers in decimal format rather than binary because decimal numbers are more familiar and shorter. Binary numbers are long and consist of only 1s and 0s, making them harder to recall.
How are binary IP addresses converted to decimal format?
-A binary IP address is divided into four 8-bit sections, known as octets. Each octet is then converted to its decimal equivalent. For example, the binary '00000000' is 0 in decimal, and '11111111' is 255 in decimal.
What are the five classes of IP addresses, and what is their purpose?
-The five classes of IP addresses are Class A, B, C, D, and E. Classes A, B, and C are used for general network communication, with A for large networks, B for medium networks, and C for small networks. Class D is used for multicast, and Class E is reserved for research and development.
What defines an IP address as belonging to Class A?
-An IP address is considered to belong to Class A if its first octet is between 1 and 126. Additionally, in binary, the first bit of the first octet is always 0, making it distinct from other classes.
How do we determine if an IP address belongs to Class B?
-An IP address belongs to Class B if its first octet is between 128 and 191. In binary, the first two bits of the first octet are '10', differentiating it from other classes.
What is the range of IP addresses for Class C, and how are they structured?
-Class C IP addresses have a first octet between 192 and 223. In binary, the first three bits of the first octet are '110'. Class C is typically used for smaller networks.
What are the main uses for Class D and Class E IP addresses?
-Class D IP addresses are used for multicast, which involves sending data to multiple recipients simultaneously. Class E IP addresses are reserved for research and experimentation and are not used in public networks.
What is the significance of the IP address '127.0.0.1'?
-'127.0.0.1' is known as the 'localhost' address, which points to the device itself. It is used to test the networking stack of a computer or device, ensuring it can communicate internally without connecting to a network.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Apa itu IP Address? | Tutorial Belajar Online Lengkap CISCO CCNA 200-301 Part 3

IP Addresses Explained | Cisco CCNA 200-301
Konsep Dasar IP Address Komputer

30 Menit Belajar IP Address dan Cara Menghitung IP Address | Seri Jaringan Komputer

Jaringan Komputer dan Internet (JKI) | Materi Informatika Fase D Kelas 8 BAB 5 | Kurikulum Merdeka
Pertemuan 5 - IP Address
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
