Cholinergic Receptors
Summary
TLDRThis lecture explores cholinergic receptors, focusing on their subtypes, locations, and physiological effects when stimulated. It differentiates between nicotinic and muscarinic receptors, with a deeper dive into muscarinic receptors (M1, M2, M3) that influence various organs. Activation of M1 leads to increased cognition and digestive processes, M2 slows heart rate, and M3 stimulates glands and smooth muscles, impacting functions like tear production, digestion, and urination. The lecture also discusses the side effects of excessive receptor stimulation (DUMBELLS), such as bradycardia and bronchoconstriction, highlighting the parasympathetic nervous system's role in rest and digest responses.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cholinergic receptors are classified into two subtypes: nicotinic and muscarinic, which are activated by acetylcholine (ACH).
- 😀 The parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest) is activated when acetylcholine binds to these receptors, leading to physiological effects like pupil constriction and digestive processes.
- 😀 Nicotinic receptors are found in two main types: Nicotinic N (nerve) and Nicotinic M (muscle), each with distinct functions in neurotransmission and muscle contraction.
- 😀 Muscarinic receptors have five subtypes: M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5, with most pharmacological effects related to M1, M2, and M3.
- 😀 M1 receptors are located in the brain and stomach, where they enhance cognition and memory, and stimulate the release of HCl and pepsinogen in the stomach.
- 😀 M2 receptors are found in the heart, and their activation results in the slowing of heart rate and decreased atrial contraction force.
- 😀 M3 receptors are the most widespread, found in glands and smooth muscles. They regulate glandular secretions and smooth muscle contraction.
- 😀 Glandular effects of M3 stimulation include increased secretion of saliva, tears, digestive enzymes, insulin, and mucus.
- 😀 Smooth muscle effects of M3 stimulation include pupil constriction, bronchoconstriction, accommodation of the lens, peristalsis in the digestive tract, and bladder contraction.
- 😀 Agonizing cholinergic receptors (activating them) may lead to side effects collectively known as 'DUMBELS,' which include diarrhea, drooling, urinary output, meiosis (pupil constriction), bradycardia, emesis (vomiting), and lacrimation (tearing).
Q & A
What are cholinergic receptors and where are they located in the body?
-Cholinergic receptors are receptors that are activated by acetylcholine (ACH). These receptors are found in the parasympathetic nervous system and are located in various organs such as the eye, mouth, lungs, heart, pancreas, GI tract, and bladder.
What is the main difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems in terms of receptor activation?
-The sympathetic nervous system primarily uses norepinephrine to activate adrenergic receptors, while the parasympathetic nervous system uses acetylcholine to activate cholinergic receptors. The parasympathetic system promotes rest and digestion, contrasting with the 'fight or flight' response of the sympathetic system.
What are the two main subtypes of cholinergic receptors?
-The two main subtypes of cholinergic receptors are nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Nicotinic receptors are further divided into nicotinic nerve (Nn) and nicotinic muscle (Nm) receptors, while muscarinic receptors are classified into M1, M2, and M3 subtypes.
What is the role of nicotinic receptors in the nervous and muscular systems?
-Nicotinic nerve (Nn) receptors are involved in transmitting electrical impulses across synapses between neurons, while nicotinic muscle (Nm) receptors are located at neuromuscular junctions and are responsible for muscle contraction when acetylcholine binds to them.
What is the primary function of M1 muscarinic receptors?
-M1 muscarinic receptors are primarily found in the brain and stomach. In the brain, they enhance cognition and memory, while in the stomach, they stimulate the release of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and pepsinogen to aid digestion.
What effect does activation of M2 muscarinic receptors have on the heart?
-Activation of M2 muscarinic receptors in the heart leads to inhibition, slowing down the heart rate and reducing atrial contraction force, contributing to a more relaxed state.
How do M3 muscarinic receptors affect glands and smooth muscles?
-M3 muscarinic receptors play a role in both glands and smooth muscles. In glands, activation increases secretions such as saliva, tears, mucus, digestive enzymes, and insulin. In smooth muscles, it causes contraction in organs like the bladder, bronchioles, and GI tract, as well as pupil constriction and lens accommodation.
What are the physiological effects of agonizing muscarinic receptors, often referred to as 'DUMBBELS'?
-When muscarinic receptors are agonized, they can cause a series of effects known as 'DUMBBELS': Diarrhea, Urinary output, Miosis (pupil constriction), Bronchoconstriction, Bradycardia (slow heart rate), Emesis (vomiting), and Lacrimation (tearing).
What is the role of M3 receptors in the digestive system?
-M3 muscarinic receptors in the digestive system stimulate peristalsis in the GI tract, promoting the movement and breakdown of food. They also enhance the secretion of digestive enzymes from glands such as the pancreas and promote mucus production in the stomach.
Why are M4 and M5 muscarinic receptors less emphasized in this lecture?
-M4 and M5 muscarinic receptors are primarily found in the brain, and their role is not directly relevant to the pharmacology of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is why they were less emphasized in this lecture. The focus was placed on M1, M2, and M3 receptors, which have more widespread physiological effects in the body.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Agonistas Colinérgicos (parte 1 - receptores) | Aula 9 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide
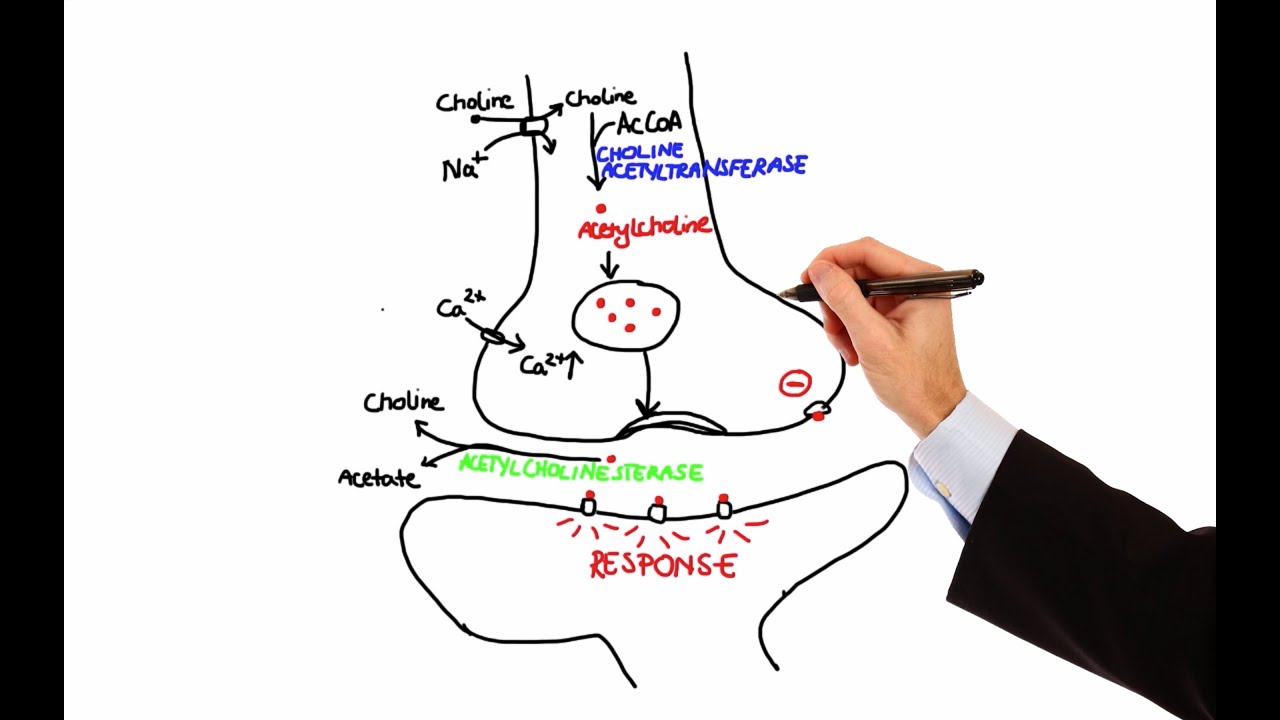
Pharmacology - CHOLINERGIC DRUGS (MADE EASY)

Cholinergic agonists || Mechanism, actions, side effects & uses

Agonistas Colinérgicos (Diretos/Muscarínicos) | Aula 10 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide

TRANSMISSÃO COLINÉRGICA - AULA NEUROFISIOLOGIA #3

قیمت 4بخش2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
