TRANSMISSÃO COLINÉRGICA - AULA NEUROFISIOLOGIA #3
Summary
TLDRIn this video, neuroscientist Bruno explains cholinergic neurotransmission, covering the synthesis, metabolism, and activity of acetylcholinesterase. He delves into its importance in various body systems, including the central and autonomic nervous systems. The video discusses the roles of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors, highlighting their different types and physiological effects, such as muscle contraction and attention modulation. Bruno also explores the role of acetylcholine in memory, sleep, and wakefulness, alongside its peripheral effects like vasodilation and heart rate regulation. The video aims to simplify complex neurobiological concepts for better understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cholinergic neurotransmission is crucial in both the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), influencing various bodily functions.
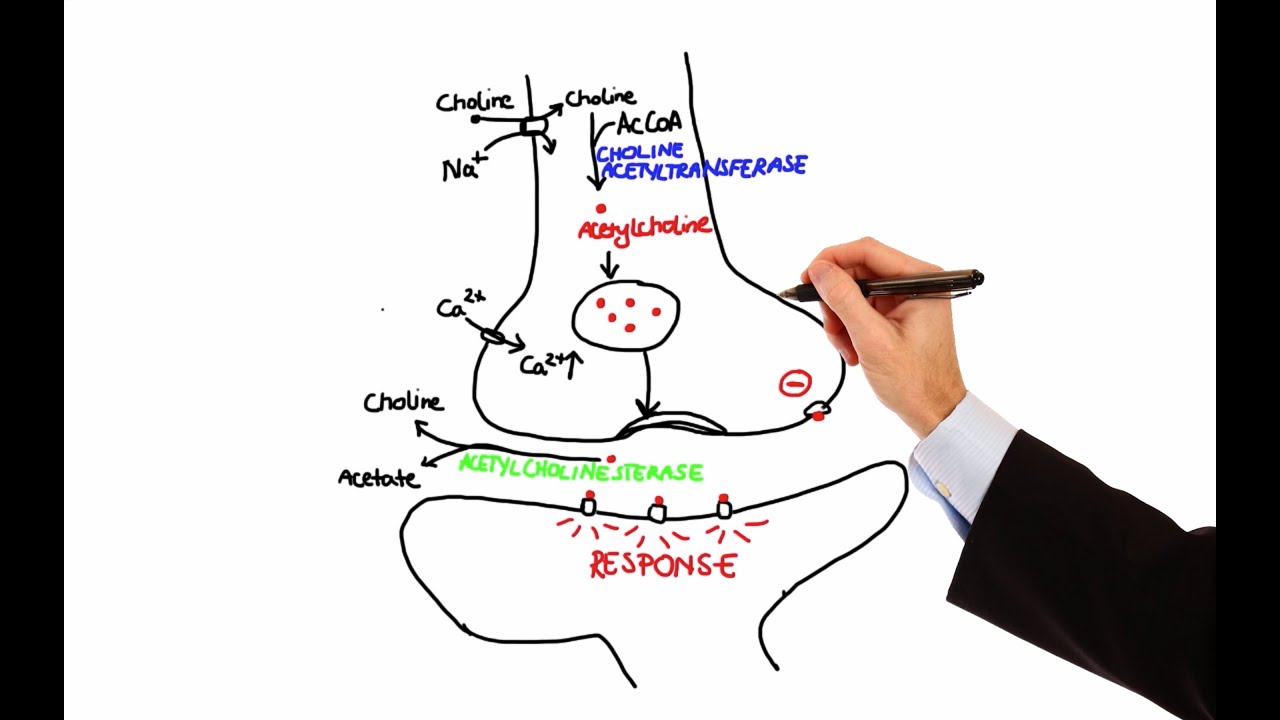
- 😀 Acetylcholine is synthesized using choline from different sources, including enzymatic breakdown and transport, as well as acetyl-CoA produced via glycolysis.
- 😀 Acetylcholine is stored in synaptic vesicles, and its release is triggered by calcium influx during action potentials.
- 😀 Once released, acetylcholine acts on post-synaptic receptors, influencing ionotropic (nicotinic) and metabotropic (muscarinic) receptors.
- 😀 Nicotinic receptors are ion channels that mediate skeletal muscle contraction, particularly in the neuromuscular junction.
- 😀 Muscarinic receptors are G-protein coupled receptors that modulate various functions, such as heart rate, smooth muscle contraction, and neural plasticity.
- 😀 Muscarinic M1 receptors play a role in memory, attention, and analgesia, primarily in the CNS.
- 😀 Muscarinic M2 receptors regulate the cardiovascular system, slowing down heart rate and promoting parasympathetic actions.
- 😀 Muscarinic M3 receptors are involved in smooth muscle contraction, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and bladder.
- 😀 The cholinergic system modulates critical functions like attention, learning, sleep-wake cycles, and memory, with acetylcholine influencing neural plasticity and cognitive processes.
Q & A
What is cholinergic neurotransmission?
-Cholinergic neurotransmission refers to the transmission of signals in the nervous system involving acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. It is crucial in both the central nervous system and the autonomic nervous system, as well as in neuromuscular junctions.
How is acetylcholine synthesized in the body?
-Acetylcholine is synthesized in the body from choline, which can be derived from various sources such as the breakdown of phosphatidylcholine or directly through the action of acetyl-CoA, which is produced via glycolysis. The synthesis involves the enzyme choline acetyltransferase.
What role does acetylcholinesterase play in neurotransmission?
-Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft into acetic acid and choline, thus terminating the signal transmission and preventing overstimulation of the postsynaptic receptors.
What happens to acetylcholine after it is released into the synaptic cleft?
-Once released, acetylcholine can bind to postsynaptic receptors, such as nicotinic and muscarinic receptors, to transmit the signal. It can also interact with presynaptic receptors to modulate the feedback loop and may be broken down by acetylcholinesterase.
What are the two main types of cholinergic receptors, and how do they differ?
-The two main types of cholinergic receptors are nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. Nicotinic receptors are ionotropic and directly mediate ion channel opening, while muscarinic receptors are metabotropic, working through G-proteins to modulate intracellular signaling.
What is the role of muscarinic receptors in the body?
-Muscarinic receptors, which are G-protein coupled, play a key role in processes such as muscle contraction, heart rate regulation, vasodilation, and the modulation of brain activity related to attention and memory.
What are the functions of nicotinic receptors in the nervous system?
-Nicotinic receptors mediate the transmission of signals at neuromuscular junctions, promoting muscle contraction, and they are also involved in autonomic ganglia, influencing the firing of post-ganglionic neurons.
How does acetylcholine affect the cardiovascular system?
-In the cardiovascular system, acetylcholine acts on muscarinic receptors, particularly the M2 type, to slow down the heart rate by inducing hyperpolarization and reducing conduction speed in the heart.
What is the relationship between acetylcholine and the central nervous system?
-In the central nervous system, acetylcholine is involved in regulating states of wakefulness, learning, memory, and attention. It plays a significant role in processes such as plasticity, development, and neural activation.
How does acetylcholine impact muscle function?
-Acetylcholine is essential for muscle function as it binds to nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction, promoting depolarization of muscle fibers and enabling both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

TRANSMISSÃO ADRENÉRGICA - AULA NEUROFISIOLOGIA #4
Pharmacology - CHOLINERGIC DRUGS (MADE EASY)

Agonistas Colinérgicos (Diretos/Muscarínicos) | Aula 10 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide
AP Biology Unit 3: Cellular Energetics Complete Review

How Donepezil works in Alzheimer's disease | Mechanism and side effects
Folic Acid Metabolism | Folate Cycle
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)