Identifying Appropriate Rejection Region for a given Level of Significance
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Teacher IE explains the concept of critical values, significance levels, hypothesis testing, and rejection regions. Students learn how to determine critical values using z-scores and t-distributions, as well as how to identify rejection regions for different tests (one-tailed, two-tailed) based on population variance. The lesson includes examples like testing the mean weight of bananas against a company's claim and finding critical values using tables. Additionally, students are taught to visualize rejection regions using standard normal curves. Activities are provided for practice and application of the concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Critical values are used in hypothesis testing to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis based on the test statistic.
- 😀 The Z-distribution is applied when the population standard deviation is known or when sample sizes are large.
- 😀 T-distribution is used when the population standard deviation is unknown or for smaller sample sizes, and it requires degrees of freedom for calculations.
- 😀 The rejection region represents areas on the test distribution where values indicate rejection of the null hypothesis.
- 😀 The standard normal curve is essential in visualizing areas under the curve for critical values and rejection regions.
- 😀 For a left-tailed test, the rejection region is located to the left of the critical value; for a right-tailed test, it's located to the right.
- 😀 Two-tailed tests involve critical values on both ends of the curve, with the rejection regions on both sides.
- 😀 The level of significance (α) defines the sensitivity of the test and influences where the critical values fall on the distribution.
- 😀 Example scenarios, like the banana weight problem, illustrate how to identify hypotheses, the test type, and rejection regions based on given data.
- 😀 Interactive activities in the lesson help students practice shading the standard normal curve and identifying critical values and rejection regions for various test types.
- 😀 To determine the critical value, use Z or T tables based on the type of test (one-tailed or two-tailed) and the significance level (α).
Q & A
What is the critical value in hypothesis testing?
-The critical value is a point on the test distribution that is compared to the test statistic to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It depends on the type of test, significance level, and whether it's a one-tailed or two-tailed test.
When should a z-distribution be used in hypothesis testing?
-A z-distribution should be used when the population standard deviation is known or when the sample size is large. It is typically applied when the sample distribution is normal or close to normal.
What is the difference between a z-test and a t-test?
-A z-test is used when the population standard deviation is known or for large samples, while a t-test is used when the population standard deviation is unknown and typically for smaller samples. The t-distribution accounts for the sample size by using degrees of freedom.
What is a rejection region in hypothesis testing?
-The rejection region, also known as the critical region, represents the area of values in a test distribution where we reject the null hypothesis. It is determined by the critical value and the significance level.
How do you determine the critical value for a z-distribution?
-The critical value for a z-distribution can be determined by using a standard normal distribution table. It depends on the type of test (one-tailed or two-tailed) and the level of significance (alpha).
What is the significance of the level of significance (alpha) in hypothesis testing?
-The level of significance (alpha) defines the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis. It is the probability of committing a Type I error, i.e., rejecting a true null hypothesis. Common values are 0.05, 0.01, and 0.10.
What is the formula for calculating degrees of freedom in a t-test?
-The degrees of freedom in a t-test is calculated as the sample size minus one (n - 1). This value is used to determine the critical t-value from the t-distribution table.
How do you perform a hypothesis test using a one-tailed test?
-In a one-tailed test, you determine the critical value based on the direction of the hypothesis (left-tailed or right-tailed). The rejection region will be on one side of the mean, and you compare the test statistic to the critical value to decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
What is the role of a t-distribution table in hypothesis testing?
-A t-distribution table is used to find critical t-values based on the sample's degree of freedom and the level of significance. It is particularly useful when the population standard deviation is unknown and the sample size is small.
How is the critical value used in a two-tailed hypothesis test?
-In a two-tailed hypothesis test, the critical values are determined based on half of the significance level (alpha/2) for both tails of the distribution. The rejection region is located on both sides of the mean, and both critical values are compared to the test statistic.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

ILLUSTRATING THE REJECTION REGION || STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Q4

Jenis-jenis pengujian hipotesis: Uji Beda Rata-rata (Uji z dan Uji t)
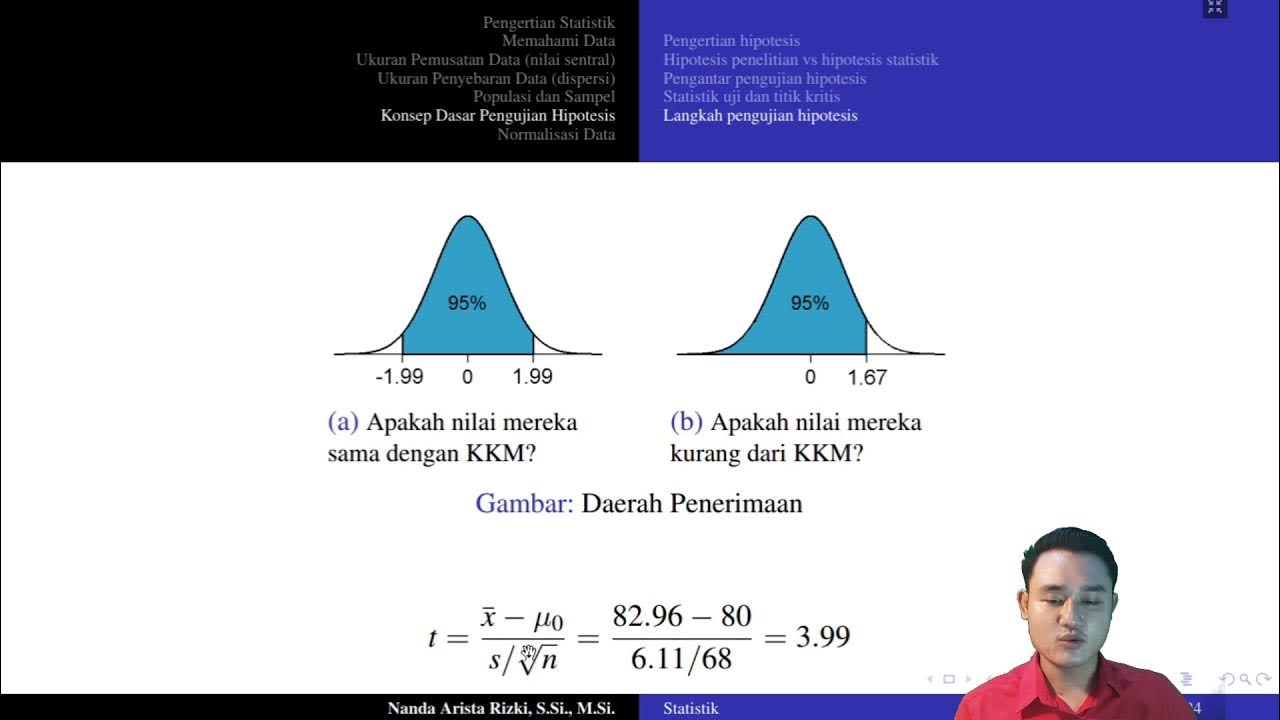
Masih berpikir bahwa hipotesis statistik itu membingungkan? | Statistika

Uji Hipotesis: Lemma Neyman - Pearson (Kuasa Uji)

Uji Hipotesis part 2 (Prosedur Pengujian Hipotesis, Statistik Uji, Wilayah Tolak/ Kritis)
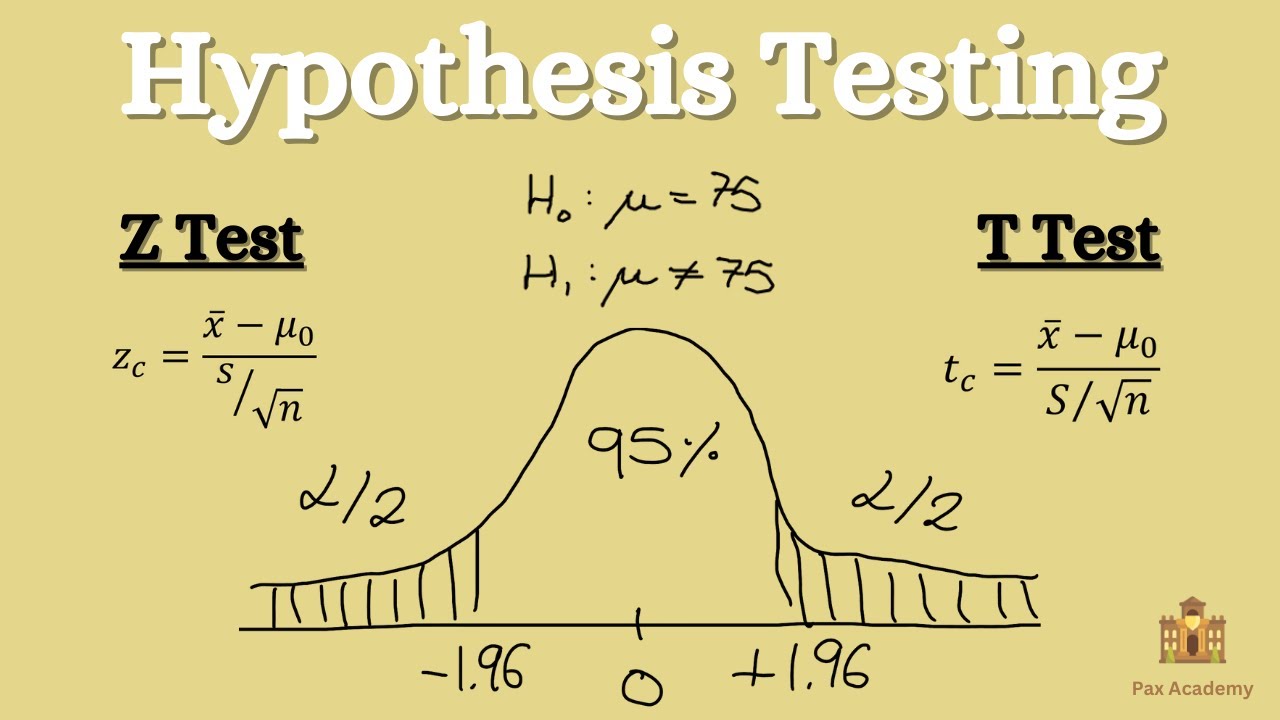
Hypothesis Testing - Z test & T test
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
