Masih berpikir bahwa hipotesis statistik itu membingungkan? | Statistika
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the basics of hypothesis testing. It introduces the concept of a hypothesis as a temporary answer based on relevant theories and empirical data. The video differentiates between research and statistical hypotheses, focusing on testing whether findings from a sample apply to a population. It covers key topics like the significance of statistical differences, types of errors (Type I and Type II), and testing methods such as T-tests. The video concludes with steps for hypothesis testing, including formulating hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and calculating statistical values.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Hypothesis is a temporary answer to a research problem, based on relevant theory and empirical facts.
- 📊 Research hypothesis involves the entire population, while statistical hypothesis focuses on the sample to generalize to the population.
- 👕 An example of a research hypothesis: There is a tendency for new students to choose size L clothes.
- ✏️ Statistical hypothesis example: There is a significant difference between pre-test and post-test exam scores after applying a new teaching method.
- 📉 Statistical significance indicates whether observed differences in data are likely due to chance or not, based on tests like t-tests or z-tests.
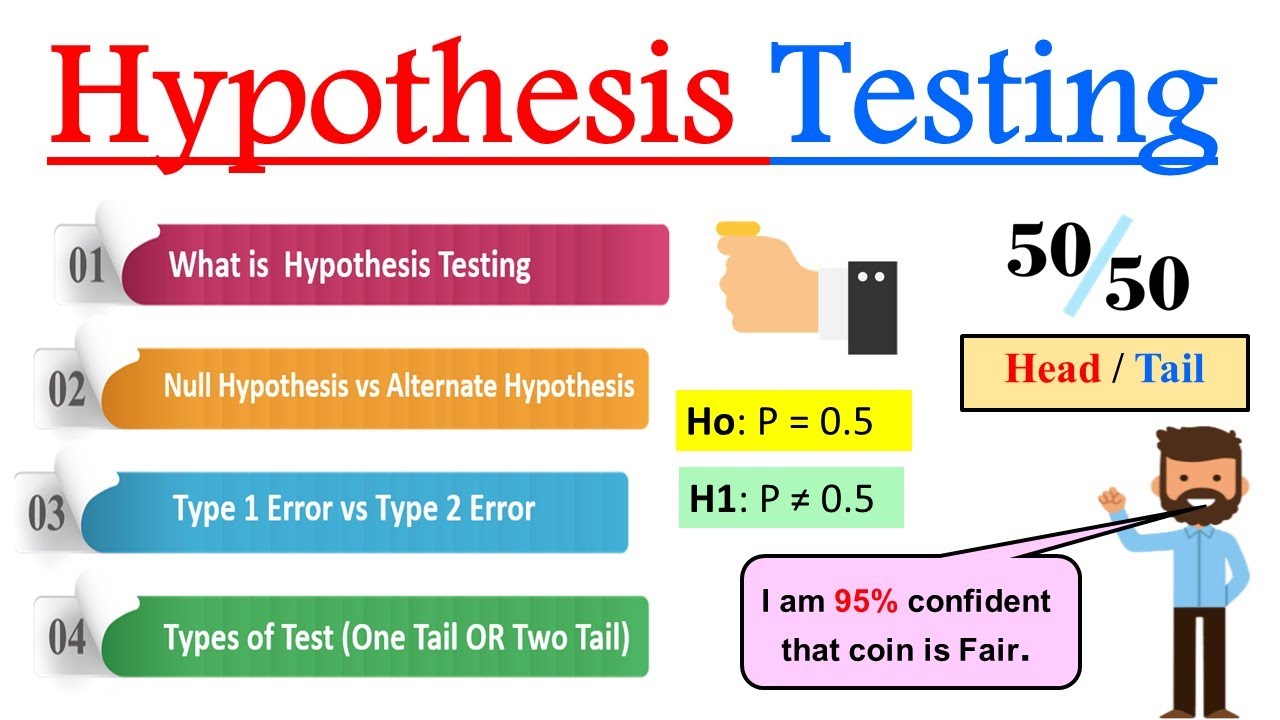
- ⚖️ Null hypothesis (H0) states there is no difference or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) suggests a difference or relationship exists.
- 🚫 Type I error occurs when H0 is rejected even though it is true (false positive), while Type II error occurs when H0 is not rejected even though it is false (false negative).
- 🎯 The level of significance (alpha) indicates the probability of making a Type I error, commonly set at 5%.
- 📐 Testing hypotheses often involves calculating statistical values and comparing them to critical values to decide whether to reject or accept H0.
- 📊 Hypothesis tests can use graphical methods like scatterplots to explore relationships and correlations between variables.
Q & A
What is a hypothesis in research?
-A hypothesis is a temporary answer to a research problem. It is based on relevant theories but supported by empirical facts, meaning it still needs to be tested.
What is the difference between a research hypothesis and a statistical hypothesis?
-A research hypothesis refers to a statement about a population, often based on empirical data. In contrast, a statistical hypothesis is tested using sample data to make inferences about the population.
What is an example of a research hypothesis?
-One example is the tendency of new students to choose size 'L' for clothing. Another example could be the difference in exam scores before and after a new teaching method is applied.
What does 'significant' mean in hypothesis testing?
-In hypothesis testing, 'significant' refers to whether an observed difference or relationship is unlikely to have occurred by chance. For instance, if exam scores before and after applying a method differ significantly, it indicates that the difference is statistically meaningful.
What are the two types of hypotheses in statistical testing?
-The two types of hypotheses are the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (H1). H0 usually states no effect or no difference, while H1 indicates the presence of an effect or difference.
What is a Type I error in hypothesis testing?
-A Type I error occurs when the null hypothesis (H0) is rejected even though it is true. The probability of making this error is denoted by Alpha (α), often set at 5%.
What is a Type II error in hypothesis testing?
-A Type II error happens when the null hypothesis (H0) is not rejected when it is actually false. The probability of making this error is denoted by Beta (β).
Why do researchers focus more on Type I errors?
-Researchers typically focus more on minimizing Type I errors because rejecting a true null hypothesis can lead to incorrect conclusions about the research findings.
How can hypothesis tests be used with sample data?
-Hypothesis tests use sample data to draw conclusions about a population. For instance, if a sample from two classes shows a difference in average exam scores, a hypothesis test can determine if the difference is statistically significant for the entire population.
What are the steps to perform a hypothesis test?
-The steps include formulating the hypotheses (H0 and H1), selecting the significance level (usually 5%), choosing the appropriate statistical test, calculating the test statistic, comparing the result to the critical value or p-value, and making a conclusion.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics ? | Introduction to Hypothesis Testing

Uji Hipotesis: Lemma Neyman - Pearson (Kuasa Uji)

NULL AND ALTERNATIVE HYPOTHESES || HYPOTHESIS TESTING || STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Q4

Hypothesis Testing and The Null Hypothesis, Clearly Explained!!!

Pengujian Hipotesis Part 1

An Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)