Evolution of Mobile Standards [1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G]
Summary
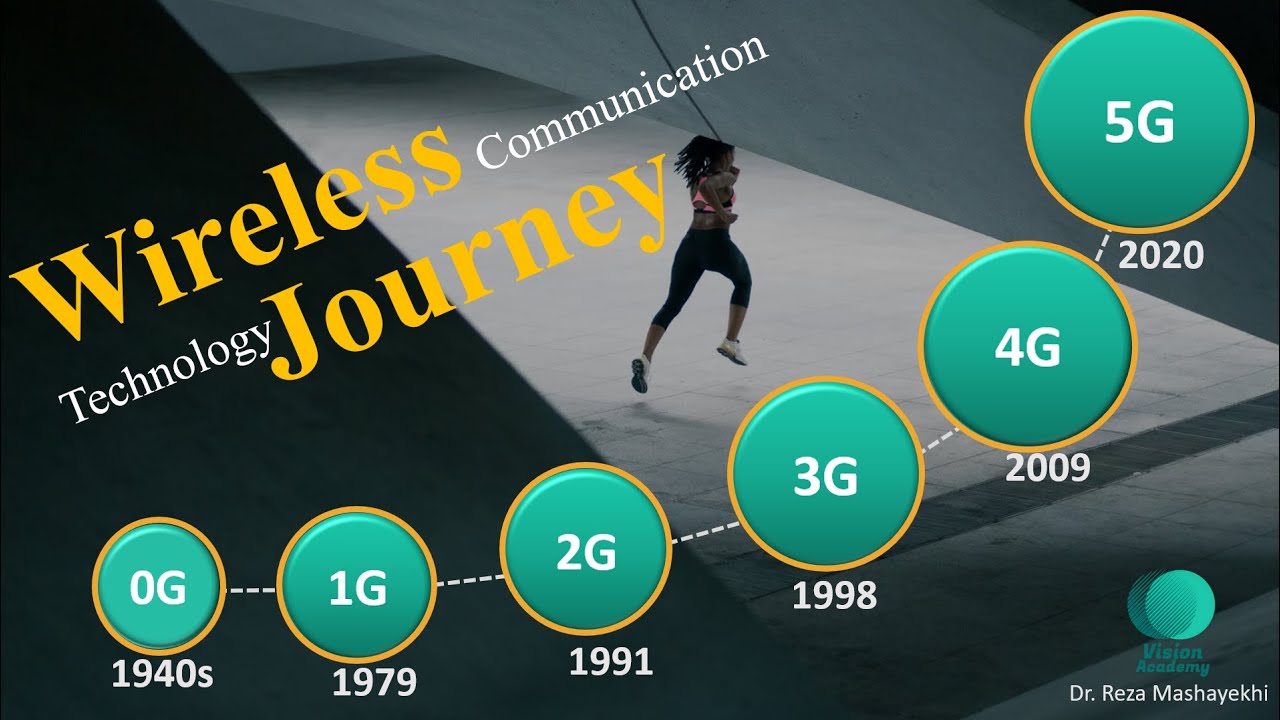
TLDRThis video explores the evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G, highlighting key milestones in mobile technology. Starting with 1G in 1979, which was limited to voice calls, the script progresses through 2G's introduction of encrypted calls and SMS, 3G's internet browsing capabilities, and 4G's high-speed mobile internet. The arrival of 5G in 2019 revolutionizes industries, enabling faster speeds, lower latency, and supporting technologies like AI and IoT. The video showcases how each generation transformed communication and technology, with 5G paving the way for the future of automation and digital innovation.
Takeaways
- 😀 1G was launched in 1979 and initially covered only boys' calls in Japan, with very poor call quality and slow speeds.
- 😀 The first SMS was sent in 1992 with the text 'Merry Christmas' from a computer to a phone using 1G technology.
- 😀 2G, introduced in 1991, brought encrypted calls, improved call quality, SMS, MMS, and faster data transfer up to 64 kbps.
- 😀 3G, introduced in 2001, enabled internet browsing, international roaming, and video streaming with speeds up to 2 Mbps.
- 😀 Switching from 2G to 3G required changing SIM cards for enhanced services like video calls and emails.
- 😀 4G, launched in 2009, revolutionized mobile internet with fast data speeds (up to 1 Gbps), improved video streaming, and online gaming.
- 😀 4G's data speeds are 100 Mbps, with low latency between 10-30 milliseconds, offering enhanced mobile internet performance.
- 😀 5G was first implemented in South Korea in 2019 and offers download speeds ranging from 60 Mbps to 1 Gbps, depending on location.
- 😀 5G significantly improves mobile internet with faster speeds, low latency, and supports up to 10 times more devices than 4G.
- 😀 5G is not only about faster internet but also enables innovations in AI, IoT, cloud computing, automation, and blockchain technologies.
- 😀 South Korea leads the world in 5G speeds with an average of 360 Mbps, followed by Taiwan and the UAE with 309.9 Mbps and 269 Mbps, respectively.
Q & A
When was 1G launched, and where was it first introduced?
-1G was launched in 1979 and was first introduced in Tokyo.
What was a major limitation of the 1G network?
-The 1G network only supported voice calls, and the call quality was poor with static and background noises. Additionally, there was no security, meaning calls could be intercepted.
What significant event occurred in 1992 in the history of mobile communication?
-In 1992, the world's first SMS was sent, with the text 'Merry Christmas' from a computer to a phone.
What technological improvements did 2G introduce compared to 1G?
-2G introduced encrypted calls, improved quality, SMS and MMS messaging, and data transfer at speeds up to 64 kbps.
When was 3G first implemented, and what new features did it bring?
-3G was first implemented in Japan in 2001. It introduced internet browsing, international roaming, and data transfer speeds of up to 2 Mbps, facilitating video streaming, video calls, and email use.
What was required to switch from 2G to 3G?
-Switching from 2G to 3G required changing SIM cards.
What were the key benefits of 4G compared to earlier generations?
-4G offered high-quality video streaming, fast mobile internet access with speeds up to 1 Gbps for fixed users, and improved latency of 10 to 30 milliseconds, enhancing online gaming and HD video experiences.
When and where was 4G first implemented?
-4G was first implemented in Sweden and Norway in 2009, using the LTE (Long-Term Evolution) standard.
What speeds can 5G achieve, and how does it compare to 4G?
-5G speeds can range from 60 Mbps to 1000 Mbps, depending on the location. Compared to 4G, 5G offers much faster download speeds, higher connection density, and lower latency (less than 2 milliseconds compared to 50 milliseconds on 4G).
How does 5G contribute to the digital revolution in various industries?
-5G enables the development of technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing. It revolutionizes industries by supporting automation, controlling machines and robots, enhancing medical equipment, and enabling blockchain technologies.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

[MOOC] - Apps para dispositivos móviles (ed. 2016) - Generaciones de telefonía móvil
What are 0G, 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G Cellular Mobile Networks - History of Wireless Telecommunications

4G LTE: One Standard To Rule Them All

Everything You Need to Know About 5G

Where Do Your Texts Go?

New Trends and Future Directions of Information Technology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
