Power world simulator for transient stability studies in power systems - part 1
Summary
TLDRThis video demonstrates how to use PowerWorld Simulator for transient stability analysis in a power system. The system involves a generator supplying power to an infinite bus through a double transmission line, with a fault occurring at bus 4. The analysis involves simulating the fault, clearing the fault by opening a transmission line, and evaluating the system's stability. Key parameters like rotor angle, acceleration power, and power variation between the generator and infinite bus are monitored. The system's stability is contingent on the fault clearing time, with higher power generation levels requiring quicker fault clearance to maintain stability.
Takeaways
- 😀 PowerWorld Simulator is used to perform transient stability analysis in power systems.
- 😀 The setup involves a generator supplying power to an infinite bus through a double transmission line.
- 😀 The fault scenario is a three-phase solid fault occurring at bus 4 at 5 seconds and cleared at 5.05 seconds by opening a transmission line.
- 😀 A simple synchronous machine model (Gen CC) is selected for transient analysis in PowerWorld Simulator.
- 😀 The simulation models the power system and analyzes transient stability after the fault occurs and the transmission line is opened.
- 😀 The generator's power output can be adjusted during the simulation to analyze different scenarios.
- 😀 After a fault occurs, transient stability is tested by measuring system parameters like rotor angle, power acceleration, and power flow between the generator and infinite bus.
- 😀 The fault is simulated as a balanced three-phase fault with the transmission line between bus 2 and bus 4 being opened after fault clearance.
- 😀 The system is analyzed for stability by plotting parameters like the rotor angle and power flow for different fault times and megawatt power values.
- 😀 The analysis concludes that the system remains stable for power levels up to 30 MW but becomes unstable if the fault is cleared too late, especially for higher power levels like 40 MW or 50 MW.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of this simulation in PowerWorld Simulator?
-The primary purpose of the simulation is to perform transient stability analysis in a power system where a generator supplies power to an infinite bus through double transmission lines, and to verify the system's stability after a fault occurs and is cleared.
What is the configuration of the power system in the simulation?
-In the simulation, a generator operates at 11 kV and supplies power to an infinite bus at 138 kV through a transformer. The fault occurs at Bus 4, and transmission lines are used to connect the various buses in the system.
What type of fault is simulated in the analysis?
-A three-phase solid fault is simulated at Bus 4 in the system.
How is the fault cleared in the simulation?
-The fault is cleared by opening the transmission line between Bus 2 and Bus 4 at the time of 5.05 seconds after the fault occurs.
Which machine model is selected for the generator in this simulation?
-The Gen CC model, a simple synchronous machine model, is selected for the generator in the simulation.
What key parameters are involved in the synchronous generator model for transient analysis?
-Key parameters in the synchronous generator model include inertia constant, damping constant, armature resistance, quadrature reactance, and other related constants.
What is the significance of choosing Bus 3 as the reference (slack) bus in the simulation?
-Bus 3 is selected as the reference bus because it is modeled as an infinite bus, which is necessary for setting the voltage reference and balancing the system's power flow during the simulation.
How is the generator's power supply to the infinite bus controlled during the simulation?
-The power supplied by the generator to the infinite bus is controlled by adjusting the power levels using the up/down arrows in the simulation, with the default setting being around 30 MW.
What are the key results that are analyzed in this transient stability simulation?
-The key results analyzed are the rotor angle (torque angle), the acceleration power (the difference between mechanical and electrical power), and the megawatt flow from the generator to the infinite bus.
How does the system behave when the fault clearing time is too long?
-If the fault clearing time is too long (i.e., more than a few seconds), the rotor angle increases significantly, and the system loses synchronism, leading to instability.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Praktikum Dasar Sistem Kendali - Unit 3

LTspice simulation | Examples in LTspice | RC Circuits | SPICE simulation
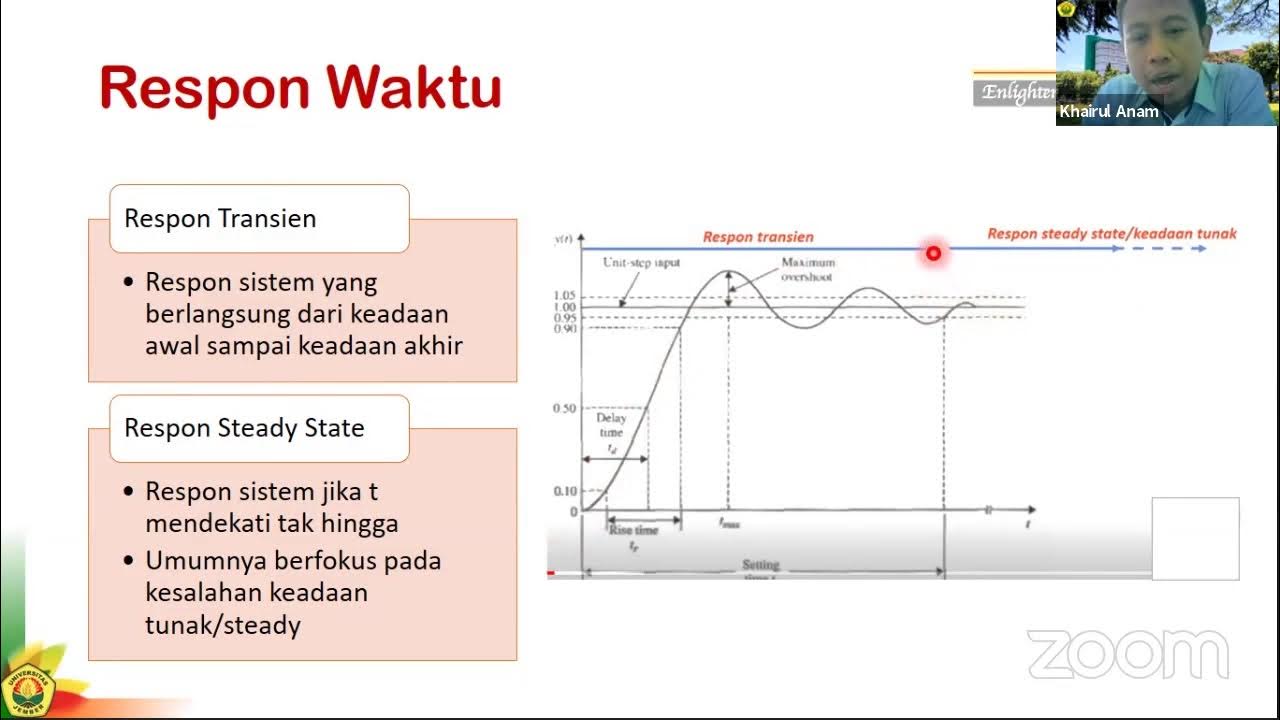
Sistem Kontrol #3a: Analisis Repon Sistem - Pendahuluan

Grin's Ebike Motor Simulator Tutoral: --PART 1-- Basic Overview
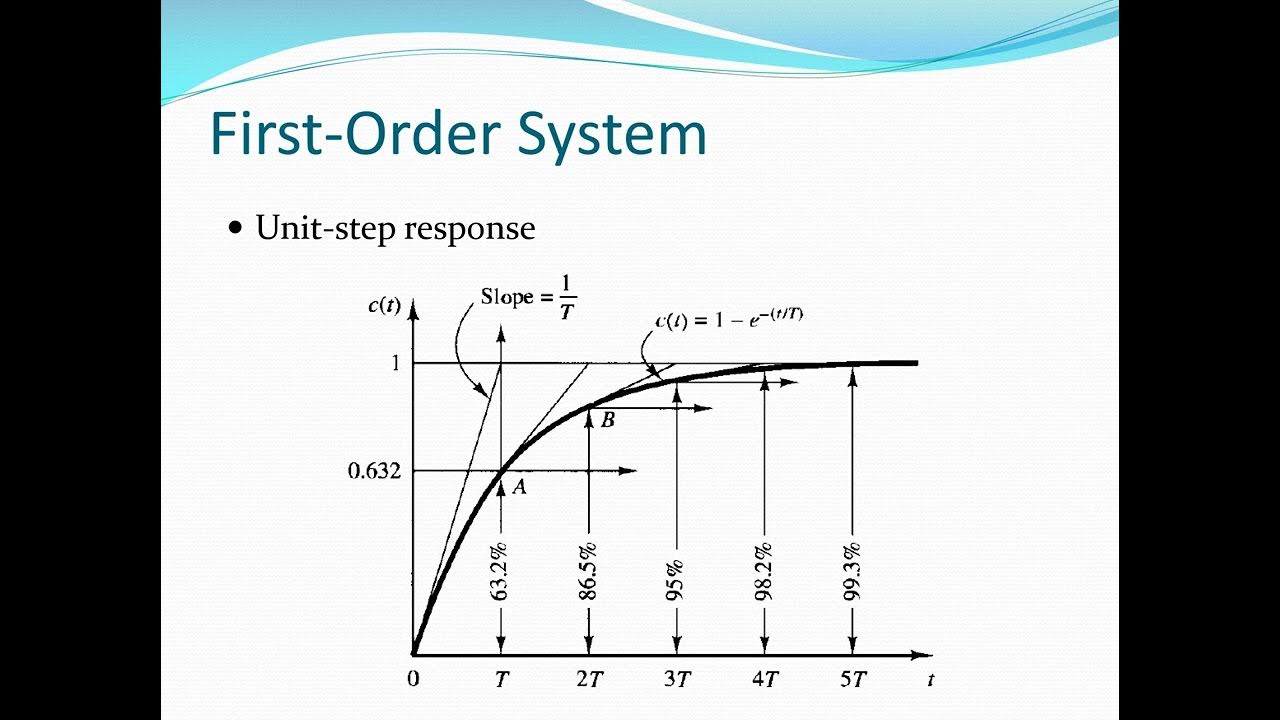
Week 08 Transient Analysis

Sistemas de Controle (aula 06) Estabilidade, e Pólos dominantes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
