GCSE Science: Physics: Fleming's left hand rule and the motor effect
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the motor effect, demonstrating how a current-carrying wire experiences force when placed in a magnetic field. By using Fleming's Left-Hand Rule, viewers learn how to predict the direction of this force. The rule involves aligning your left hand to the magnetic field and current, with your thumb pointing in the direction of the force. Additionally, the video covers common missteps and the use of symbols in diagrams to represent the direction of current. This concept is vital for understanding many devices that rely on the motor effect, especially in GCSE physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 The motor effect describes how a current-carrying wire experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field.
- 😀 Magnetic fields surround all magnets and are represented by flux lines going from the North to the South pole.
- 😀 The motor effect is important in many devices and is used to predict the direction of force on the wire.
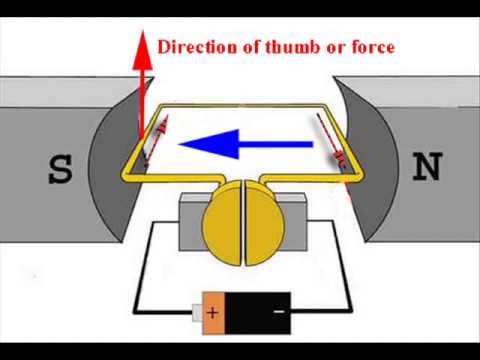
- 😀 To predict the direction of force, Fleming's left-hand rule is used, with each finger representing a different component (magnetic field, current, and force).
- 😀 Fleming's left-hand rule: Point your index finger in the direction of the magnetic field, your second finger in the direction of current, and your thumb will point in the direction of the force.
- 😀 In typical scenarios, the magnetic field and current are provided, and you must use Fleming's left-hand rule to determine the force's direction.
- 😀 An example: If the magnetic field is from left to right and the current is coming out of the page, the wire moves upwards.
- 😀 To solve problems, you can rotate the paper or your hand if needed to match the directions of the magnetic field and current without hurting yourself.
- 😀 Diagrams often use symbols, like a dot (•) to indicate current coming out of the page and a cross (×) for current going into the page.
- 😀 When using the left-hand rule with these symbols, the direction of the force can be determined based on the alignment of the current and magnetic field in the diagram.
- 😀 In conclusion, the motor effect is vital in understanding how forces are generated in wires carrying currents within magnetic fields, and Fleming's left-hand rule is the tool for predicting the direction of that force.
Q & A
What is the motor effect?
-The motor effect refers to the phenomenon where a current-carrying wire experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. This is the fundamental principle behind many electrical devices like motors.
What do the magnetic flux lines represent?
-Magnetic flux lines represent the magnetic field around a magnet. They show the direction of the field, moving from the North Pole to the South Pole.
How does the direction of the current affect the force on the wire?
-The direction of the current determines the direction of the force on the wire, which is perpendicular to both the magnetic field and the direction of current. The force can be predicted using Fleming's Left Hand Rule.
What is Fleming's Left Hand Rule?
-Fleming's Left Hand Rule is a way to determine the direction of force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field. You align your left hand such that the index finger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the second finger in the direction of the current, and the thumb will point in the direction of the force or movement.
How do you use Fleming's Left Hand Rule in practice?
-To use Fleming's Left Hand Rule, position your left hand with the index finger pointing along the magnetic field, the second finger in the direction of current, and your thumb will point in the direction of the wire's motion (the force).
Why do you need to use your left hand for Fleming's Left Hand Rule?
-You need to use your left hand because the left hand is specifically designed for the motor effect, ensuring the directions of the magnetic field, current, and force are correctly aligned.
What common mistakes should be avoided when using Fleming's Left Hand Rule?
-Common mistakes include using the right hand instead of the left hand and failing to adjust the paper when performing the rule, which can lead to awkward hand positions or incorrect results.
How do you represent the direction of current in a diagram?
-In diagrams, the direction of the current can be represented by arrows. A dot represents current coming out of the page towards you, while a cross represents current going into the page away from you.
What is the significance of the angle between the wire and the magnetic field?
-The wire and the magnetic field are always at right angles (90°) to each other in the motor effect, which is crucial for the wire to experience the maximum force.
How does the direction of the current influence the force in different scenarios?
-Depending on the direction of the current relative to the magnetic field, the force on the wire will move in different directions. This can be predicted by adjusting the position of your fingers according to Fleming's Left Hand Rule.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)