GAYA LORENTZ KELAS 9 (MEMBUKTIKAN ADANYA GAYA LORENTZ)
Summary
TLDRThis practical lesson introduces the Lorentz force and its applications in everyday life. It explains the concept of magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor within a magnetic field, commonly referred to as the Lorentz force. Through hands-on experimentation, students observe how altering the direction of the magnetic field or current affects the force’s direction. The tutorial also highlights the use of the Lorentz force in devices like electric motors and ammeters, emphasizing how this fundamental principle converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. The lesson concludes with real-life applications of Lorentz force, demonstrating its significance in technology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains the concept of Lorentz force and its application in daily life.
- 😀 The basic competency being studied is the application of magnetism, electromagnetic induction, and the use of magnetic fields.
- 😀 One key indicator is investigating the Lorentz force in a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
- 😀 Lorentz force is the force exerted on a conductor carrying an electric current in a magnetic field, and it's a principle used in devices that convert electrical energy into motion.
- 😀 An example of this principle in action is an electric motor, which transforms electrical energy into kinetic energy.
- 😀 The materials required for the experiment include a power supply, connecting cables, a permanent magnet, aluminum foil, scissors, and static tools.
- 😀 The first step in the experiment is to attach the aluminum foil to a static surface and connect it to the power supply.
- 😀 After powering up the system, the effect of Lorentz force can be observed when a permanent magnet creates a magnetic field around the aluminum foil.
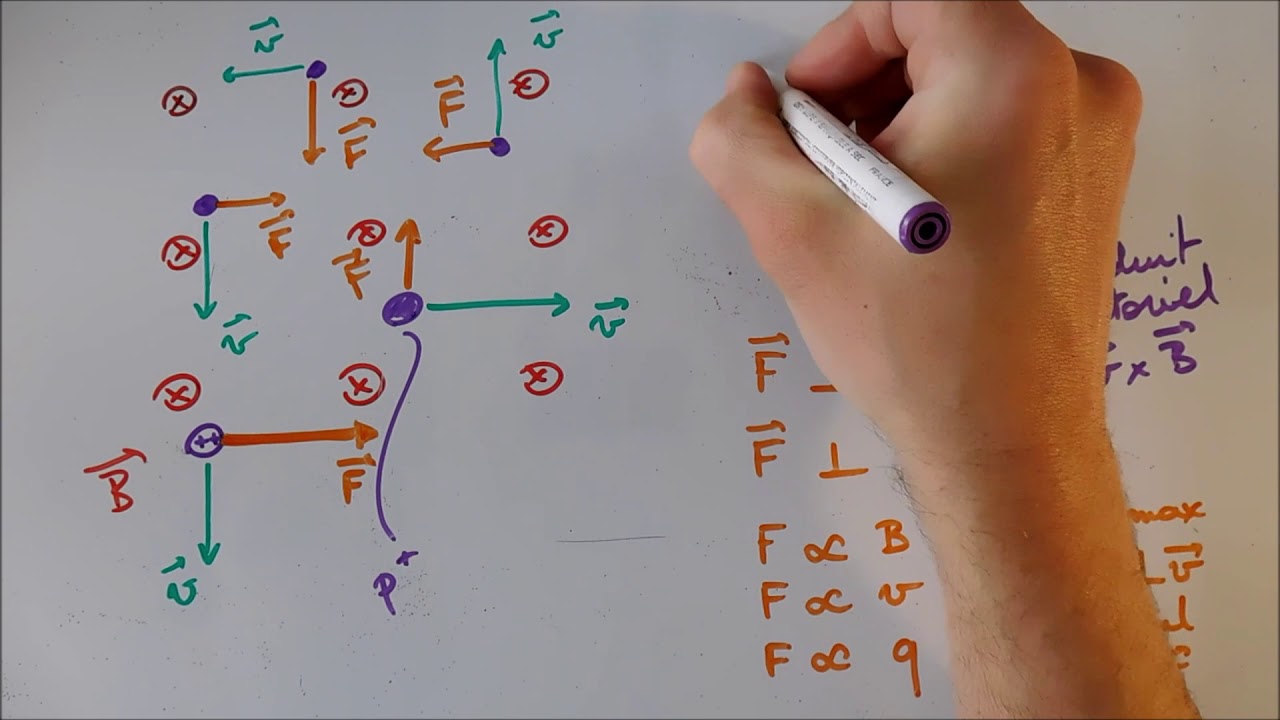
- 😀 The direction of the Lorentz force can be determined using the right-hand rule, where the thumb indicates the current direction, the index finger shows the magnetic field direction, and the middle finger points to the force direction.
- 😀 Changes in the direction of the magnetic field result in a change in the direction of the Lorentz force, demonstrating its dependency on both the current direction and magnetic field.
- 😀 Practical applications of Lorentz force are seen in devices such as ammeters (which measure small currents) and electric motors, both of which rely on the interaction between current and magnetic fields.
Q & A
What is the main concept being explored in this practical experiment?
-The main concept is the Lorentz force, which is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
What are the learning objectives of this practical activity?
-The learning objectives are to investigate the Lorentz force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field and to explain the direction of the Lorentz force using the right-hand rule.
What equipment is needed for the Lorentz force practical experiment?
-The required equipment includes a voltage supply (or DC battery), two connecting wires, a permanent magnet, scissors, aluminum foil, and tape.
How do you set up the experiment to observe the Lorentz force?
-The aluminum foil is fixed in place with tape, then connected to the power supply. The magnet is placed around the foil to create a magnetic field, and the power supply is turned on.
What happens when the power supply is turned on in the experiment?
-When the power supply is turned on, current flows through the aluminum foil, and the magnetic field from the magnet exerts a force on the foil, causing it to move. This is the Lorentz force.
What is the right-hand rule and how is it applied to determine the direction of the Lorentz force?
-The right-hand rule helps determine the direction of the Lorentz force. The thumb points in the direction of current, the index finger in the direction of the magnetic field, and the middle finger indicates the direction of the force (Lorentz force).
What is the relationship between the direction of the magnetic field and the Lorentz force?
-The direction of the magnetic field influences the direction of the Lorentz force. When the direction of the magnetic field is changed, the Lorentz force also changes direction accordingly.
What happens when the direction of current flow in the experiment is reversed?
-When the current flow is reversed, the direction of the Lorentz force also reverses, demonstrating that the force depends on both the current and the magnetic field.
How does the Lorentz force principle apply to everyday devices?
-The Lorentz force is used in devices such as electric motors and galvanometers, where the force results in motion, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion.
What is the principle behind the operation of an electric motor as described in the script?
-The electric motor operates on the principle of the Lorentz force, where a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field experiences a force that causes the coil to rotate, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)