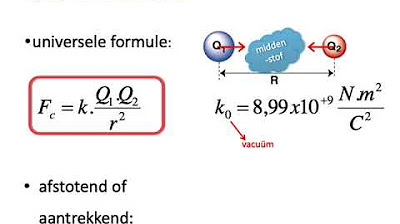
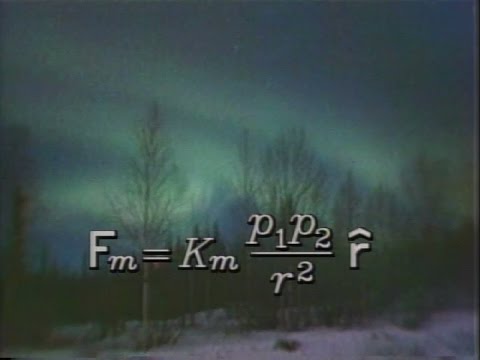KEMAGNETAN dan PEMANFAATANNYA IPA KELAS 9
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the concept of magnetism, its properties, and practical applications in daily life. It covers the role of magnetic fields in animal migration, types of magnetic materials (ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, diamagnetic), and how magnets are made and demagnetized. The video also explores the Earth’s magnetic field, including magnetic declination and inclination, and introduces the Lorentz force. It highlights the use of electromagnets in devices like electric bells, motors, and steel lifters, offering a thorough understanding of magnetism’s real-world relevance and applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Magnetism plays a crucial role in animal migration, with animals like sea turtles, salmon, birds, lobsters, and magnetotactic bacteria using magnetic fields to navigate.
- 😀 A magnet is defined as an object capable of attracting certain materials, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
- 😀 There are different shapes of magnets, including bar magnets, cylindrical magnets, needle magnets (used in compasses), horseshoe magnets, U-shaped magnets, and circular magnets.
- 😀 Materials can be classified based on their magnetic properties: ferromagnetic (strongly attracted to magnets), paramagnetic (weakly attracted), and diamagnetic (not attracted).
- 😀 Magnets have two poles: North and South, and opposite poles attract while like poles repel each other.
- 😀 There are three methods for creating magnets: rubbing a piece of iron or steel with a magnet, using electricity to create an electromagnet, and induction by bringing a magnet close to a material.
- 😀 Magnetic properties can be lost by heating, hammering, or applying alternating electric current.
- 😀 Iron and steel are commonly used in magnets, with iron being easy to magnetize but losing its magnetic properties quickly, while steel is harder to magnetize but retains its magnetism longer.
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field is essential for navigation, with the magnetic declination (angle between the compass needle and Earth's magnetic poles) and inclination (angle between the compass needle and Earth's surface) being key components.
- 😀 The Lorentz force describes the force acting on a current-carrying conductor within a magnetic field, which can be demonstrated using the right-hand rule.
- 😀 The practical applications of electromagnetism include devices like bells, telephones, electromagnetic switches, and electric cranes.
Q & A
What is the role of the Earth's magnetic field in animal migration?
-Many animals, such as sea turtles, salmon, and birds, use the Earth's magnetic field to navigate during migration. The magnetic field helps them orient themselves and find their way over long distances.
What are the three types of magnetic materials based on their magnetic properties?
-The three types of magnetic materials are: 1) **Ferromagnetic** materials, which are strongly attracted to magnets (e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt), 2) **Paramagnetic** materials, which are weakly attracted to magnets (e.g., aluminum, magnesium), and 3) **Diamagnetic** materials, which are not attracted to magnets (e.g., copper, gold, bismuth).
How can a magnet be created?
-Magnets can be created in three ways: 1) **By stroking**: Rubbing a magnetic material with a magnet in one direction, 2) **Electromagnetic method**: Passing an electric current through a wire coil around a metal core, 3) **Induction**: Placing a metal object near a magnet to transfer magnetic properties.
What is the difference between ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials?
-The main difference is the strength of attraction to a magnet. **Ferromagnetic** materials are strongly attracted to magnets (e.g., iron, steel), while **paramagnetic** materials are weakly attracted (e.g., aluminum, magnesium).
What happens to a magnet's magnetic properties if it is heated or struck?
-If a magnet is heated or struck, its magnetic properties can be weakened or completely lost. High temperatures or physical impacts can disrupt the alignment of the magnetic domains, causing the material to lose its magnetism.
What is the magnetic field, and how is it represented?
-The magnetic field is the area around a magnet where its magnetic force is felt. It is represented by magnetic field lines, which show the direction of the magnetic force. These lines extend from the north pole of a magnet to the south pole.
What is the significance of the magnetic poles in a magnet?
-A magnet has two poles, **north** and **south**. The magnetic force is strongest at the poles, and the poles of the same type will repel each other, while opposite poles will attract. This is a fundamental property of magnets.
How does Earth's magnetic field affect navigation?
-Earth's magnetic field is used by navigational tools such as compasses. The **magnetic declination** refers to the angle between the compass needle and the Earth's geographic poles, while **magnetic inclination** refers to the angle between the compass needle and the Earth's surface.
What is the Lorentz force, and how is it applied in real life?
-The Lorentz force is the force experienced by a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. It is used in various devices, such as electric motors and electromagnetic pumps. The force depends on the current, magnetic field, and the length of the conductor in the field.
What are some real-world applications of electromagnetism?
-Electromagnetism is used in many everyday devices, including electric bells, telephones, electromagnetic switches, motors, fans, and other electrical equipment. These devices rely on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric currents to function.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)