Plasma Arc Welding | Manufacturing Processes
Summary
TLDRPlasma Arc Welding (PAW) is a process similar to Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, using a tungsten electrode and argon as shielding gas. The key difference lies in the construction of the welding torch, where heat is generated through a constricted arc between the electrode and workpieces. This high heat melts the metal, forming a joint. PAW offers advantages like precise heat control, deep penetration, high metal deposit rates, and a small heat-affected zone. However, it comes with drawbacks such as expensive equipment and frequent nozzle replacements.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) is similar to Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, with the key difference being the construction of the welding torch.
- 😀 PAW uses a tungsten electrode and argon gas as an inert shielding gas, creating an arc between the electrode and the workpieces.
- 😀 The welding setup consists of a DC generator, a non-consumable tungsten electrode, constricting nozzles, and shielding gas nozzles.
- 😀 Plasma gas is formed when argon gas ionizes upon contact with the current-carrying electrode.
- 😀 The arc generated in PAW is called a 'transferred arc' as it travels from the electrode to the workpieces.
- 😀 The constricting nozzle in the welding torch helps focus the arc, increasing heat concentration and penetration.
- 😀 A keyhole is formed along the metal interface due to the high temperature of the plasma gas, allowing metal to melt and flow into it.
- 😀 The filler rod and welding torch move along the metal plates to join them, creating a molten joint.
- 😀 PAW offers advantages like controlled heat input, deep and uniform penetration, higher metal deposit rates, and a small heat-affected zone.
- 😀 The disadvantages of PAW include expensive equipment and frequent replacement of the nozzle surrounding the electrode.
Q & A
What is Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)?
-Plasma Arc Welding is a welding process that uses a constricted arc formed between a tungsten electrode and the workpieces, with the heat generated by plasma gas to join two metal workpieces.
How is Plasma Arc Welding similar to Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding?
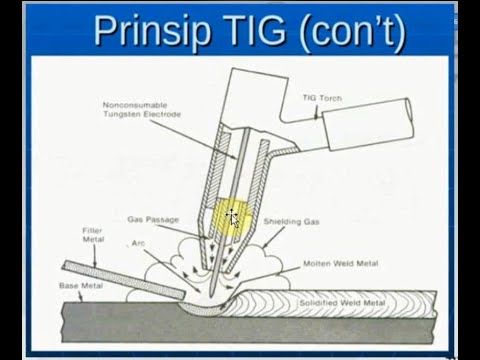
-Both Plasma Arc Welding and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding use a tungsten electrode and argon as an inert shielding gas. However, PAW differs in the design of the welding torch and the concentration of the arc.
What are the key components of the Plasma Arc Welding setup?
-The setup includes a DC generator, a clamp connected to the positive terminal, and a welding torch connected to the negative terminal. The torch consists of a tungsten electrode, a constricting nozzle, and a shielding gas nozzle.
What gases are typically used in Plasma Arc Welding?
-The most commonly used gases are argon for both plasma gas and shielding gas.
How is the plasma formed in Plasma Arc Welding?
-Plasma is formed when argon gas flows through the welding torch and ionizes upon contact with the current-carrying tungsten electrode.
What is the difference between transferred and non-transferred arcs in Plasma Arc Welding?
-In Plasma Arc Welding, a transferred arc is formed when the arc travels from the electrode to the workpiece. This contrasts with non-transferred arcs, where the arc remains stationary between the electrode and nozzle.
How does the constricting nozzle impact the welding process?
-The constricting nozzle focuses and concentrates the arc, producing a higher temperature at the interface between the workpieces. This allows for deep penetration and precise welding.
What is the role of the shielding gas in Plasma Arc Welding?
-The shielding gas protects the plasma arc and molten metal from contamination by the surrounding atmosphere, ensuring the integrity and quality of the weld.
What happens when the welding torch moves along the metal plates in Plasma Arc Welding?
-As the welding torch moves, the molten metal flows into the keyhole formed at the interface of the plates, creating a molten joint that joins the metal workpieces together.
What are some of the advantages of Plasma Arc Welding?
-Advantages of Plasma Arc Welding include precise heat control, uniform deep penetration, high metal deposition rates, and a small heat-affected zone, which improves the quality of the weld.
What are some of the disadvantages of Plasma Arc Welding?
-Disadvantages of Plasma Arc Welding include the high cost of the equipment and the need for frequent replacement of the nozzle surrounding the tungsten electrode.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)