PAUTAN GEN - POLA-POLA HEREDITAS
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of gene linkage, focusing on how certain genes on chromosomes are inherited together. It covers autosomal and gonosomal gene linkages, with examples using Drosophila melanogaster. The script discusses the work of Thomas Hunt Morgan, who identified gene linkage through experiments with fruit flies. Additionally, it explores Mendelian inheritance patterns and how gene linkages alter expected ratios in offspring. The video also touches on sex-linked traits, such as eye color in Drosophila and coat color in cats, providing a detailed explanation of how these traits are passed down through generations.
Takeaways
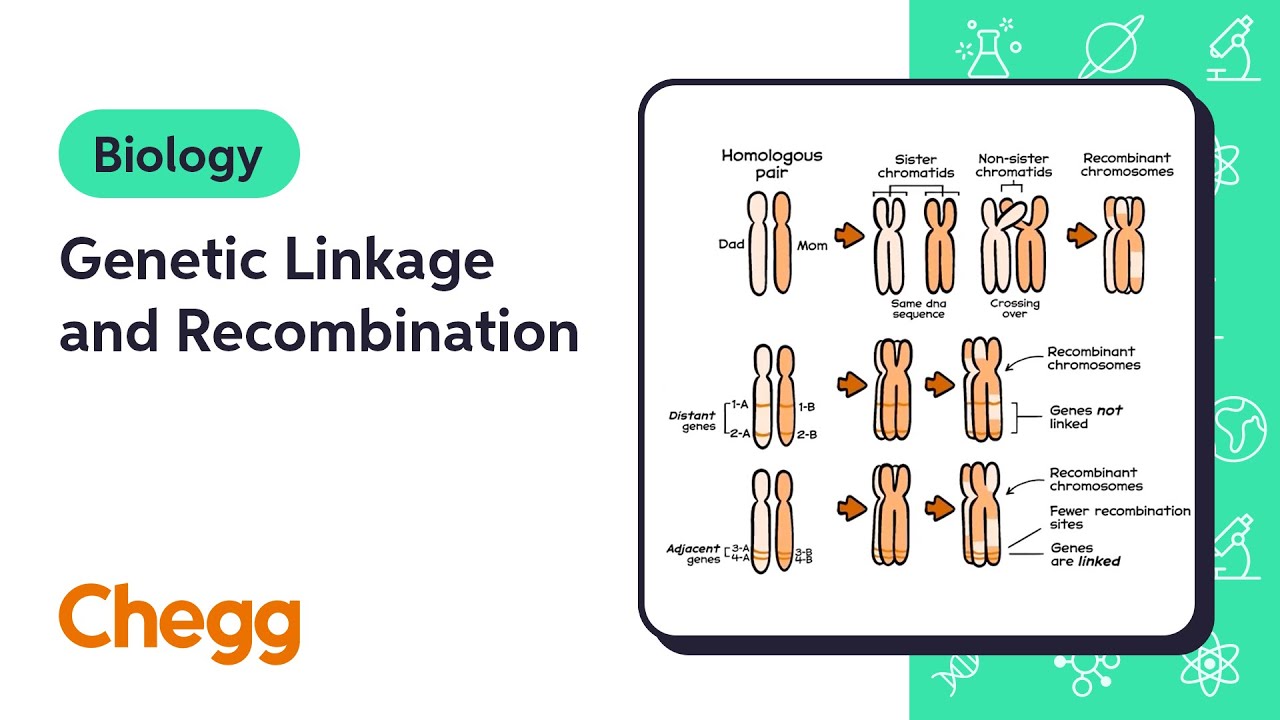
- 😀 Genetic linkage refers to genes located close together on the same chromosome, making them likely to be inherited together.
- 😀 There are two types of genetic linkage: autosomal linkage (on body chromosomes) and gonosomal linkage (on sex chromosomes).
- 😀 Autosomal linkage can cause genes to not segregate independently, leading to a deviation from Mendelian inheritance ratios, like a 3:1 instead of a 9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio.
- 😀 In Drosophila melanogaster (fruit flies), genetic linkage is demonstrated by the inheritance of genes for wing shape and body color that are located on the same chromosome.
- 😀 The gene for eye color in Drosophila melanogaster is linked to the X chromosome, with red eyes being dominant and white eyes being recessive.
- 😀 In crosses involving Drosophila, female offspring can inherit eye color genes from both parents, while male offspring inherit eye color only from their mother.
- 😀 When a red-eyed female Drosophila is crossed with a white-eyed male, the offspring show a 3:1 ratio of red to white eyes, with white eyes being exclusive to males.
- 😀 This inheritance pattern supports that the red-eye color gene is located on the X chromosome, not the Y chromosome.
- 😀 Human traits like color blindness and hemophilia are also X-linked, meaning they follow similar inheritance patterns as seen in Drosophila eye color.
- 😀 Some traits, like hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth), are Y-linked, meaning they are passed down only through the paternal line.
Q & A
What is the concept of 'linked genes' or 'gene linkage'?
-Gene linkage refers to genes located on the same chromosome that are inherited together. These genes do not assort independently during meiosis because they are close to each other on the chromosome, leading to the formation of gametes with certain combinations of alleles.
How does gene linkage differ between autosomal and gonosomal chromosomes?
-Autosomal gene linkage occurs on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes), whereas gonosomal linkage occurs on sex chromosomes (X or Y). The genes on autosomes typically determine traits unrelated to sex, while those on sex chromosomes often govern sexual characteristics or conditions related to sex-linked inheritance.
What is the significance of Thomas Hunt Morgan's discovery regarding gene linkage?
-Thomas Hunt Morgan discovered that genes could be linked on chromosomes through his experiments with the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. His work provided evidence for the concept of gene linkage and demonstrated that genes located on the same chromosome are more likely to be inherited together.
How do linked genes affect the formation of gametes?
-Linked genes reduce the independent assortment of alleles during meiosis. Instead of forming a variety of gametes with different combinations of alleles, gametes formed from linked genes will tend to carry alleles from both genes together or remain unchanged.
What are the expected phenotypic ratios in dihybrid crosses involving linked genes?
-In a typical dihybrid cross involving linked genes, the expected phenotypic ratio will differ from the standard 9:3:3:1. Instead, a 3:1 ratio is observed for traits governed by linked genes because the gametes formed by the parents have limited combinations of the alleles.
What is an example of gene linkage in Drosophila melanogaster?
-An example of gene linkage in Drosophila melanogaster is the linkage between genes determining wing shape and body color. These genes are located on the same chromosome, leading to gametes that inherit these traits together rather than independently.
Why are gametes with mixed alleles not formed in gene linkage?
-Gametes with mixed alleles are not formed because the linked genes are physically close on the same chromosome. As a result, during meiosis, the genes do not separate independently, which prevents the formation of gametes with recombined alleles.
How does gene linkage contribute to the inheritance of sex-linked traits in Drosophila?
-In Drosophila, sex-linked traits like eye color are determined by genes located on the X chromosome. These traits exhibit gene linkage because the genes on the X chromosome are inherited together, affecting both male and female offspring in different ways.
What are some human traits that exhibit X-linked inheritance?
-Some human traits that exhibit X-linked inheritance include color blindness and hemophilia. These conditions are controlled by genes on the X chromosome, which results in different inheritance patterns between males (XY) and females (XX).
What genetic conditions are linked to the Y chromosome?
-Genetic conditions linked to the Y chromosome include traits like hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth on the ears) and certain forms of male-pattern baldness. These traits are inherited by males, as they possess a Y chromosome.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)