Genetic Recombination, Linked Genes, and Crossing Over
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment and its deviations, focusing on the concept of genetic linkage and recombination. It uses fruit flies as an example to illustrate how genes for eye color, body color, and wing type can recombine during meiosis, explaining non-recombinant and recombinant types. The script further explores recombination frequency and genetic distance measured in centimorgans, highlighting how close genes are on a chromosome and their likelihood to recombine. It concludes with the significance of linkage in gene mapping, which helps in understanding gene locations and distances on chromosomes.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment states that genes are assorted independently during meiosis, but this can be deviated by the concept of linkage.
- 🔍 Linkage is a newer development that helps understand deviations from the Mendelian rule and is crucial for gene mapping.
- 📚 The example of fruit flies is used to illustrate the concepts of recombination and linkage, focusing on traits like eye color, body color, and wing type.
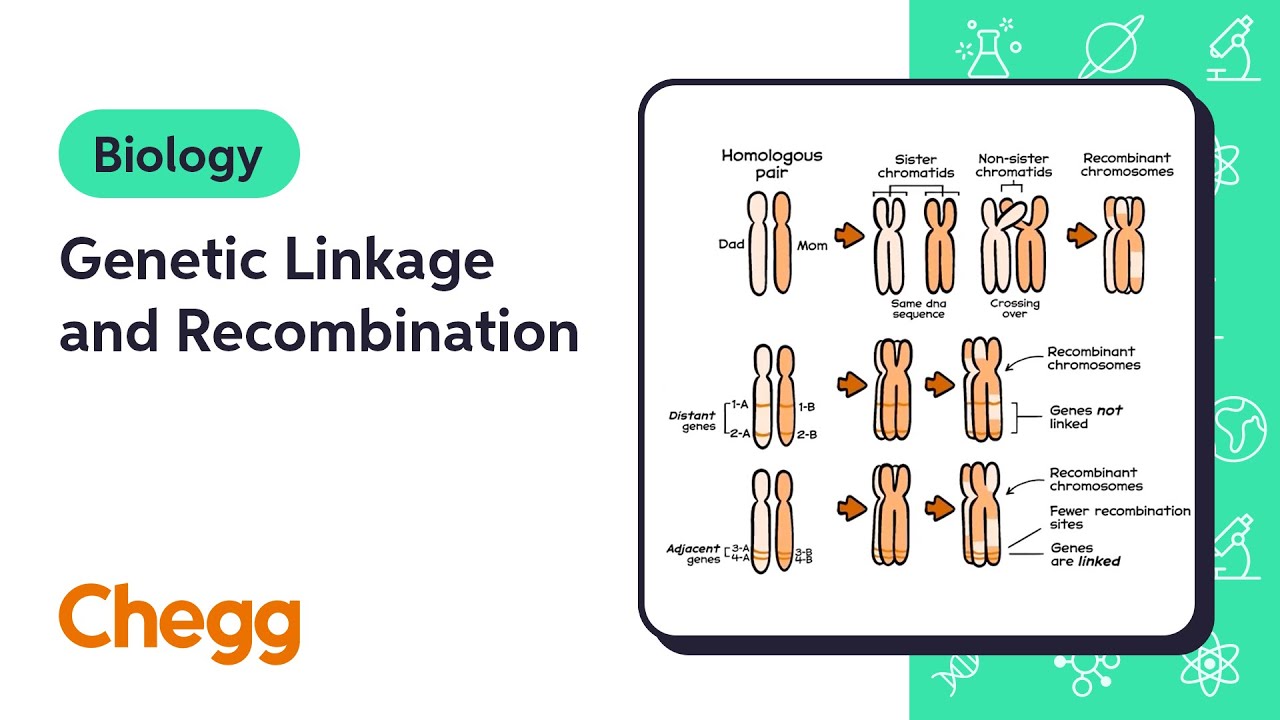
- 🌟 Recombination is the process where genes on homologous chromosomes switch places during meiosis, leading to new combinations of alleles.
- 🔄 Nonrecombinant types are combinations of alleles that are passed on unchanged through meiosis, while recombinant types result from crossing over.
- 📏 Recombination frequency is the percentage of meiotic events where alleles recombine, indicating the likelihood of genes switching places.
- 📊 Genetic distance, measured in centimorgans (cM), represents the likelihood of genes recombining, with lower values indicating closer proximity on a chromosome.
- 🔗 Linkage is the likelihood that two alleles will be inherited together and is directly related to their physical distance on a chromosome.
- 🧭 Gene mapping uses linkage and recombination frequencies to determine the relative positions of genes on chromosomes.
- 🧬 The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the more likely they are to be inherited together and the less likely they are to recombine.
- 🔬 Test crosses are used to experimentally determine whether recombination has occurred by observing the phenotypes of offspring from a cross with a homozygous recessive organism.
Q & A
What is Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment?
-Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment states that each pair of alleles segregates independently of any other pair of alleles during the process of meiosis, meaning that the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another.
What is the concept of linkage in genetics?
-Linkage refers to the tendency of certain genes to be inherited together because they are located close to each other on the same chromosome. It is a deviation from the Law of Independent Assortment when genes are not assorting independently.
What is recombination in the context of genetics?
-Recombination is the process during meiosis where genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes, resulting in new combinations of alleles in the offspring.
How are fruit flies used to explain the concept of recombination and linkage?
-Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) are used as a model organism in genetics because they have a short generation time and easily observable traits like eye color, body color, and wing type, which are genetically determined and can be used to demonstrate recombination and linkage.
What are the dominant and recessive phenotypes for eye color, body color, and wing type in fruit flies as mentioned in the script?
-In the script, red eye is the dominant phenotype while brown eye is recessive. For body color, yellow-brown or tan is dominant and black is recessive. Regarding wing type, functional wings are dominant while vestigial wings are recessive.
What does it mean for an individual to be heterozygous for a trait?
-An individual is heterozygous for a trait if it has two different alleles for that trait, one from each parent, which may result in a blend of the two phenotypes or the expression of one over the other.
What are nonrecombinant and recombinant types in the context of genetic recombination?
-Nonrecombinant types are the combinations of alleles that are passed on without any recombination, maintaining the original configuration from the parent chromosomes. Recombinant types are the new combinations of alleles that result from recombination events during meiosis.
How is recombination frequency calculated and what does it indicate?
-Recombination frequency is calculated as the percentage of meiotic events that result in recombination, rather than the nonrecombinant configuration. It indicates the likelihood of alleles being inherited together versus being separated during meiosis.
What is the significance of centimorgans in genetics?
-Centimorgans (cM) is a unit of genetic distance that represents the likelihood of alleles being inherited together. It is used to measure the distance between genes on a chromosome and is inversely proportional to the recombination frequency.
How is the concept of linkage related to gene mapping?
-Linkage is related to gene mapping as it helps determine the relative positions of genes on chromosomes. By studying the frequency of recombination between genes, researchers can create a genetic map that shows the arrangement of genes and their distances from one another.
What is a test cross and how is it used to determine recombination?
-A test cross is a breeding experiment where an individual with an unknown genotype is crossed with a homozygous recessive individual. The phenotypes of the offspring can reveal whether recombination has occurred by showing new allele combinations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Genetic Linkage and Recombination | Biology

Segunda Lei de Mendel [Muito fácil!] - Aula 10 - Mód. 2 - Genética | Prof. Guilherme

110 Mendel 2 Testcross, Dihybrid Cross

Mendelian Inheritance & Punnett Square | Review | Science 8/9 - Quarter 1 (Review for MELC 3)

BIOLOGIA - Lezione 11 - Genetica: Le Leggi di Mendel

Dihybrid
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)