PEMANFAATAN SIG UNTUK KESEHATAN LINGKUNGAN
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the utilization of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in environmental health, particularly focusing on disease prevention and health management. It explains the definition of environmental health, its impact on human well-being, and the role of GIS in tracking disease distribution, risk factors, and spatial trends. GIS aids in managing public health data, predicting disease patterns, and planning interventions. The video also highlights GIS's benefits over conventional methods, such as improved data visualization, spatial analysis, and targeted health interventions, demonstrating its importance in effective health monitoring and decision-making.
Takeaways
- 😀 Environmental health is defined as a state of ecological balance between humans and their environment that supports healthy, happy lives.
- 😀 According to WHO, a balanced ecological relationship between humans and their environment is essential for human health.
- 😀 The Indonesian Health Law (1992) highlights key areas for environmental health implementation, including public spaces, residential areas, workplaces, public transportation, and special environments.
- 😀 Environmental factors can contribute to health issues through reservoirs, pathogens, transmission mediums, and vectors that spread diseases.
- 😀 SIG (Geographic Information Systems) has been a critical tool in environmental health management in Indonesia since 1990.
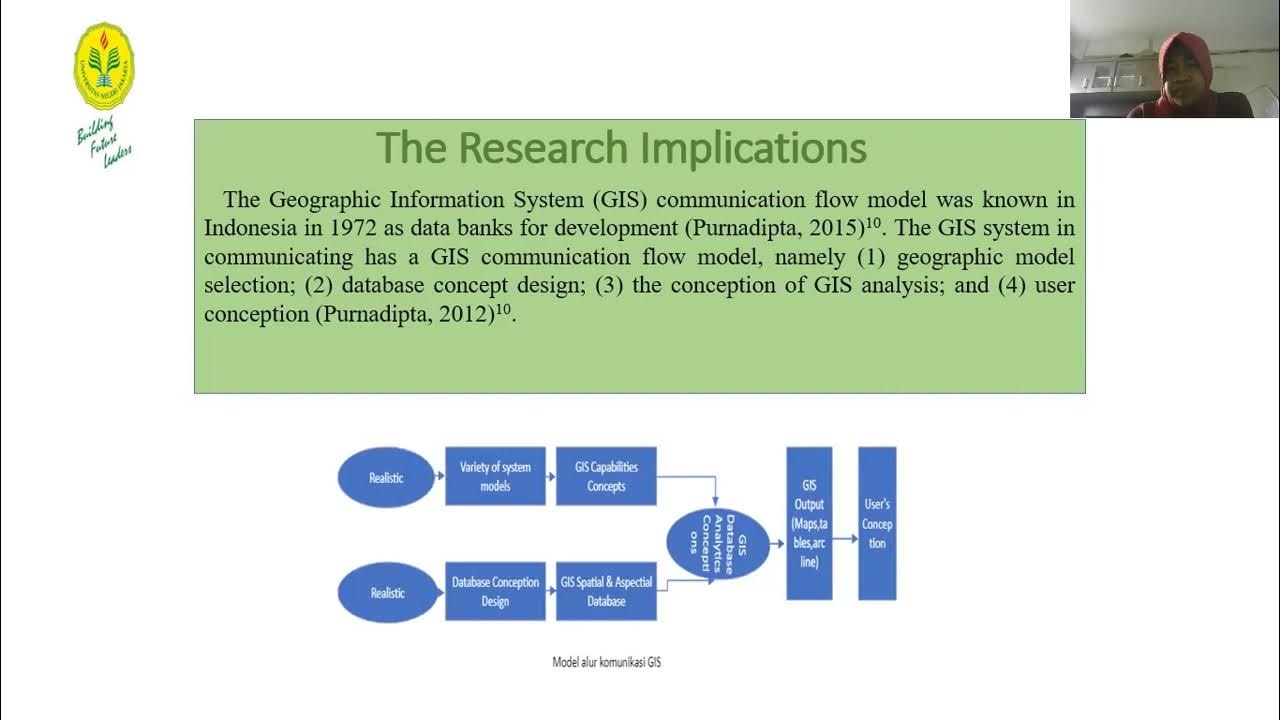
- 😀 SIG helps in mapping disease distribution, identifying disease spread patterns, and managing healthcare resources like hospitals and medical staff.
- 😀 SIG can assist in determining the geographical distribution of diseases and analyzing spatial and temporal trends.
- 😀 The system allows for visualizing risk areas and can model the spread of diseases like Ebola based on geographic data.
- 😀 SIG offers various advantages over conventional methods, such as efficient data management, spatial analysis, and the ability to visualize trends and make informed decisions.
- 😀 SIG allows for the creation of buffer zones to assess risks, like determining areas at risk of water contamination or disease spread.
- 😀 Querying capabilities within SIG allow for specific location-based insights, helping healthcare professionals, policymakers, and researchers make data-driven decisions.
Q & A
What is the definition of environmental health according to the transcript?
-Environmental health is the dynamic balance between humans and their environment that supports healthy and happy lives. According to WHO, it refers to the ecological balance necessary between humans and their environment to ensure human health.
What are the main targets of environmental health as mentioned in the transcript?
-The main targets of environmental health include public spaces (e.g., hotels, terminals, markets), residential areas (e.g., homes, dormitories), workplaces (e.g., offices, industrial zones), public transport (e.g., vehicles, ships, planes), and special environments (e.g., disaster zones, migration areas).
How does the environment influence human health according to the transcript?
-The environment can influence human health in various ways, such as being a reservoir for disease-causing agents, acting as an agent that causes illness, serving as a transmission medium (e.g., air, water, food), or being a vector for disease (e.g., mosquitoes, flies, cockroaches).
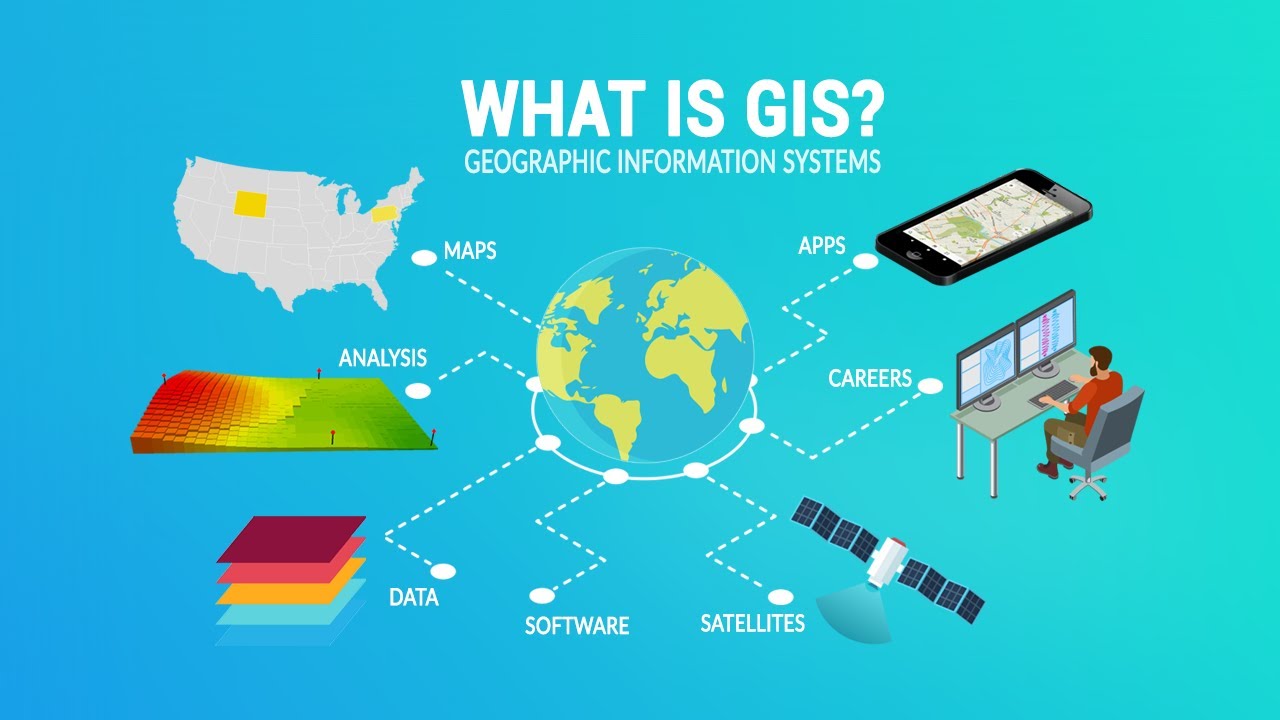
What is the role of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in environmental health?
-GIS plays a crucial role in environmental health by mapping disease distribution, identifying at-risk populations, and helping make data-driven health decisions. It enables the analysis of disease trends, and supports health interventions through spatial data analysis.
How has GIS technology been used in Indonesia for public health since 1990?
-Since 1990, GIS technology has been used in Indonesia to improve public health by analyzing disease distribution, identifying patterns of spread, and determining the locations of healthcare facilities and medical personnel. It has been used both by government and private health institutions.
What are some of the specific advantages of using GIS for public health as stated in the transcript?
-Some advantages of using GIS include: managing and integrating data from multiple sources, providing spatial visualization for disease trends, conducting overlay analysis to understand disease patterns, creating buffer zones around areas of interest to assess exposure or risk, and enabling detailed queries for health data analysis.
How does GIS help in creating buffer zones, and what is the significance of these zones?
-GIS can create buffer zones around areas of interest, such as healthcare facilities or high-risk areas. These zones help assess the reach of health services, the spread of disease, or the risk of contamination, for example, by measuring the distance between homes and hospitals or the proximity to polluted areas.
What kind of analysis can GIS perform to support public health decisions?
-GIS can perform overlay analysis, where different layers of information (e.g., disease prevalence, environmental factors) are combined to help decision-makers understand the relationships between various factors and their impact on public health. It also allows for spatial and temporal trend analysis to identify emerging health risks.
How can GIS be used to estimate the number of disease cases in a specific area?
-GIS can be used to estimate disease cases by analyzing data from geographic locations, creating buffer zones, and combining information on disease incidence to predict the number of cases in a specific area or zone.
Why is it important for GIS to be adopted by health administrators, epidemiologists, and policymakers?
-It is important for GIS to be adopted by these professionals because it enables better decision-making based on spatial data analysis. GIS helps them manage health information, plan interventions, track disease outbreaks, and allocate resources effectively, ultimately improving public health outcomes.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)