FERTILISASI DAN KEHAMILAN
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fascinating process of fertilization and pregnancy, from the moment a sperm fertilizes an egg in the Fallopian tube to the development of a fetus in the womb. It covers the stages of embryonic development, including implantation, cell division, and the formation of vital organs. The video also describes the three trimesters of pregnancy, with key milestones in fetal growth and organ development, leading up to childbirth. By the end of the pregnancy, the fetus is fully developed, ready to be born after approximately nine months.
Takeaways
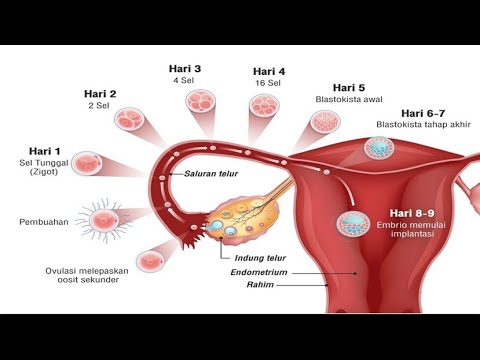
- 😀 Fertilization occurs when an egg from the fallopian tube is fertilized by sperm.
- 😀 The zygote, formed after fertilization, begins dividing and moves toward the uterus.
- 😀 Implantation happens when the zygote attaches to the uterine wall, beginning pregnancy.
- 😀 The embryo continues to divide, and the placenta nourishes it during development.
- 😀 The first trimester involves the development of vital organs such as the brain and heart.
- 😀 By the end of the first trimester, the fetus is about 2.5 cm long and weighs around 28 grams.
- 😀 During the second trimester, the fetus’s organs mature, and it begins to hear and absorb nutrients.
- 😀 At the end of the second trimester, the fetus weighs over 1 kg and measures around 10 cm.
- 😀 The third trimester sees further growth, with the fetus’s organs fully maturing.
- 😀 By the end of the third trimester, the fetus is ready for birth, weighing approximately 3 kg and measuring 50 cm.
- 😀 Throughout the pregnancy, the fetus changes position, with the head ideally pointing downward toward the birth canal.
Q & A
What is fertilization, and where does it occur?
-Fertilization occurs when a sperm meets an egg in the fallopian tube. The sperm enters the vagina, travels through the cervix and uterus, and reaches the fallopian tube, where it fertilizes the egg.
What happens after the sperm fertilizes the egg?
-Once the sperm fertilizes the egg, the sperm’s nucleus merges with the egg’s nucleus, forming a zygote. The zygote then begins to divide and travels to the uterus to implant in the uterine lining.
What is the zygote, and what does it do after fertilization?
-The zygote is a single-cell organism formed when the sperm and egg nuclei combine. It divides into multiple cells as it travels down the fallopian tube and then implants in the uterine wall.
What is implantation, and when does it occur?
-Implantation is the process by which the zygote, now called a blastocyst, attaches to the lining of the uterus. This typically happens between the 8th and 9th day after fertilization.
What is the role of the placenta in pregnancy?
-The placenta serves as the interface between the mother and fetus, allowing the transfer of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products. It also produces hormones to support pregnancy.
How is the development of the embryo divided in terms of trimesters?
-Embryonic development is divided into three trimesters. The first trimester involves organ development. The second trimester sees further growth and maturation of organs. The third trimester focuses on the final stages of development and preparation for birth.
What major developments occur in the first trimester?
-During the first trimester, the heart, brain, and other vital organs begin to form. The fetus develops basic features, including limbs and reproductive organs. By the 8th week, the heart starts beating.
How does the fetus grow in the second trimester?
-In the second trimester, the fetus’s organs continue to mature. The fetus can begin to hear sounds, and fine hair (lanugo) starts to grow. At the end of the trimester, the fetus is about 10 cm long and weighs over one kilogram.
What happens during the third trimester of pregnancy?
-During the third trimester, the fetus’s bones and organs mature. By the 32nd week, the fetus can open and close its eyes. The baby is preparing for birth, with its head typically moving into the downward position in the last weeks.
At what point is the fetus considered full-term?
-The fetus is considered full-term around 37 weeks, at which point all of its organs should be functioning independently and it is ready for birth.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)