Immune tolerance - An introduction (FL-Immuno/76)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the immune system's defense mechanisms, focusing on the concept of immune tolerance. It distinguishes between foreign and self-antigens, outlining how the immune system responds to external threats while avoiding attacks on its own tissues. Central tolerance, occurring in the thymus and bone marrow, eliminates autoreactive lymphocytes during early development. Peripheral tolerance prevents any remaining autoreactive cells from causing harm in peripheral organs. The video also highlights how failures in self-tolerance can lead to autoimmune diseases, offering insight into the complex processes that protect the body from such attacks.
Takeaways
- 😀 Antigens are substances recognized by the immune system as either foreign or self, triggering immune responses against foreign antigens.
- 😀 Foreign antigens include bacteria, viruses, pollen, and parasites, whereas self-antigens are components of the body like cells and cell surface molecules.
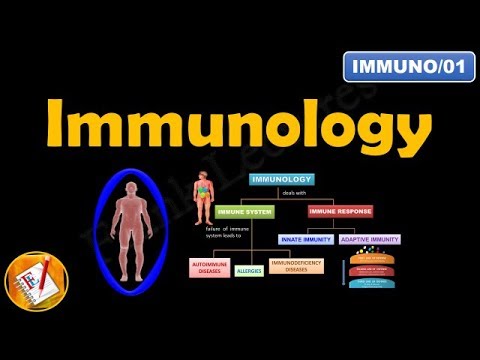
- 😀 The immune system's primary function is to protect against foreign antigens, achieved through a multi-tiered defense system: first, second, and third lines of defense.
- 😀 The third line of defense, consisting of B and T lymphocytes, is crucial for adaptive immunity, with receptors specific to antigens.
- 😀 B-cell and T-cell receptors are generated through random rearrangements of gene segments during lymphocyte development, allowing for diverse antigen recognition.
- 😀 Lymphocytes can produce receptors that target both foreign and self-antigens, leading to the creation of autoreactive lymphocytes, which can potentially attack the body’s own tissues.
- 😀 Immune tolerance prevents autoreactive lymphocytes from attacking self-antigens, maintaining the body's protection while avoiding autoimmunity.
- 😀 Immune tolerance is a state of unresponsiveness to self-antigens, and failure of this tolerance leads to autoimmunity, where the immune system attacks its own cells and tissues.
- 😀 The process of immune tolerance is divided into two steps: central tolerance and peripheral tolerance.
- 😀 Central tolerance occurs in primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow and thymus), where autoreactive lymphocytes are eliminated during early development.
- 😀 Peripheral tolerance happens in secondary lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen), where autoreactive lymphocytes that escape central tolerance are further regulated to prevent immune responses against self-antigens.
Q & A
What is an antigen?
-An antigen is a substance that is recognized by the immune system as foreign, prompting an immune response against it.
What is the difference between foreign antigens and self-antigens?
-Foreign antigens (heteroantigens) are not part of the body, such as bacteria, viruses, and pollen, while self-antigens are components of the body itself, like cells and cell surface molecules.
What are the three lines of defense in the immune system?
-The three lines of defense are the first line (physical barriers like skin), second line (innate immune responses), and third line (adaptive immunity involving B and T lymphocytes).
What role do B and T lymphocytes play in the immune system?
-B and T lymphocytes are responsible for the adaptive immunity and express antigen-specific receptors (B-cell receptor and T-cell receptor) to recognize and respond to specific antigens.
How are the antigen-specific receptors of B and T cells generated?
-These receptors are generated through random rearrangements of pre-existing gene segments during the early development of lymphocytes, before encountering specific antigens.
What are autoreactive or self-reactive lymphocytes?
-Autoreactive lymphocytes are those that have receptors against self-antigens, meaning they are capable of recognizing and potentially attacking the body's own cells.
How does the immune system avoid attacking self-antigens?
-The immune system avoids attacking self-antigens through immune tolerance mechanisms, such as central tolerance and peripheral tolerance, which prevent the activation of self-reactive lymphocytes.
What is immune tolerance?
-Immune tolerance is the state of unresponsiveness of the immune system to specific antigens, ensuring it does not mount an immune response against self-antigens or harmless foreign antigens.
What happens if immune tolerance fails?
-If immune tolerance fails, the immune system may start attacking self-antigens, leading to autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases, where the body's own cells, tissues, and organs are damaged.
What is central tolerance and where does it occur?
-Central tolerance is the process that eliminates most autoreactive B and T cells during their early development, occurring in the primary lymphoid organs, such as the bone marrow and thymus.
What is peripheral tolerance and why is it important?
-Peripheral tolerance occurs in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and spleen. It prevents autoreactive mature lymphocytes that escaped central tolerance from attacking self-antigens.
How do central and peripheral tolerance work together to prevent autoimmunity?
-Central tolerance eliminates most autoreactive lymphocytes early on, while peripheral tolerance ensures that any remaining autoreactive lymphocytes do not attack self-antigens in the body's peripheral organs.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)