CILINDRO (AULA 11/16)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the instructor provides a comprehensive explanation of cylinders, covering their basic elements such as bases, axis, generatrices, height, and radius. The lesson distinguishes between right and oblique cylinders, with a focus on right cylinders. The instructor also introduces the concept of a cylinder as a solid of revolution and explains the meridian section and the concept of an equilateral cylinder. The video also walks through the formulas for volume, lateral surface area, and total surface area, concluding with practical examples to reinforce understanding.
Takeaways
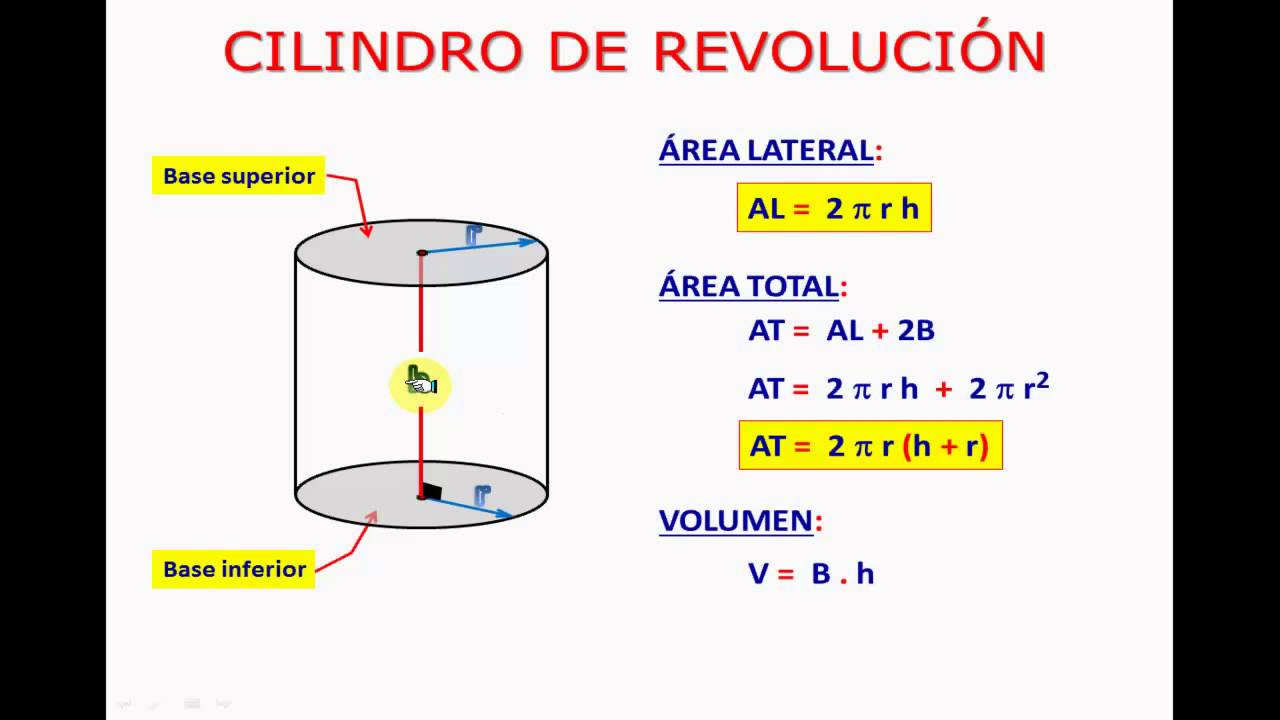
- 😀 A cylinder is a solid shape with two congruent circular bases and a lateral surface connecting them.
- 😀 The key elements of a cylinder include the bases (two congruent circles), axis (line through the centers of the bases), generatrix (lateral lines parallel to the axis), and height (distance between the bases).
- 😀 An oblique cylinder has an axis that is not perpendicular to the bases, while a right cylinder has an axis that is perpendicular to the bases.
- 😀 In a right cylinder, the height is equal to the generatrix, which is the slant height that connects the two bases.
- 😀 A cylinder is considered a solid of revolution, generated by rotating a rectangle around an axis.
- 😀 The meridian section of a cylinder is a rectangle that results from a plane intersecting the cylinder along its axis.
- 😀 An equilateral cylinder is a cylinder where the meridian section is a square, meaning the generatrix is twice the radius of the base.
- 😀 The volume of a cylinder is calculated using the formula: Volume = π * radius^2 * height.
- 😀 The lateral area of a cylinder is calculated as: Lateral Area = 2 * π * radius * height.
- 😀 The total surface area of a cylinder is the sum of the areas of two bases and the lateral surface: Total Area = 2 * π * radius^2 + 2 * π * radius * height.
- 😀 The script provides detailed examples, such as calculating the lateral area, volume, and total area of cylinders with specific measurements like radius 4 cm and height 10 cm.
Q & A
What is a cylinder and what are its main characteristics?
-A cylinder is a solid formed by two congruent circular faces, parallel to each other, and a lateral surface that connects these faces. Its main characteristics include the radius of the base (r), the height (h), the axis that connects the centers of the two bases, and the generatrix (or slant height) that is parallel to the axis.
What is the difference between a right cylinder and an oblique cylinder?
-A right cylinder has its generatrix perpendicular to its bases, meaning the axis is at a 90-degree angle to the bases. In contrast, an oblique cylinder has an axis that is not perpendicular to its bases, meaning the angle between the axis and the generatrix is not 90 degrees.
What is the significance of the generatrix in a cylinder?
-The generatrix is a line that connects the points on the circumference of one base to the corresponding points on the other base. In a right cylinder, the generatrix is equal in length to the height (h). In an oblique cylinder, the generatrix and height are not the same.
What is the concept of 'sólido de revolução' (solid of revolution) in the context of a cylinder?
-A cylinder is considered a 'solid of revolution' because it is generated by rotating a rectangle around an axis. The base of the cylinder is formed by rotating a line segment (the rectangle's side) around the axis, creating a circular shape.
What is a meridian section of a cylinder?
-A meridian section is created by intersecting a cylinder with a plane that passes through its axis. This creates a rectangle, where the length of the rectangle's sides corresponds to the diameter of the base (2r) and the height (h) of the cylinder.
What defines a cylindrical shape as 'equilateral'?
-A cylinder is called 'equilateral' when its meridian section is a square. This happens when the generatrix is twice the radius of the base (i.e., generatrix = 2r) and the height of the cylinder is equal to the generatrix.
What is the formula for the volume of a cylinder?
-The volume of a cylinder is calculated by multiplying the area of its base (πr²) by its height (h). Therefore, the formula for volume is V = πr²h.
How is the lateral surface area of a cylinder calculated?
-The lateral surface area of a cylinder is calculated using the formula A_lateral = 2πrh, where r is the radius of the base and h is the height of the cylinder.
What is the total surface area of a cylinder?
-The total surface area of a cylinder is the sum of the areas of both circular bases and the lateral surface. The formula is A_total = 2πr² + 2πrh.
In the example with a cylinder of radius 4 cm and height 10 cm, how is the lateral area calculated?
-The lateral surface area is calculated using the formula A_lateral = 2πrh. With r = 4 cm and h = 10 cm, the lateral surface area is 2π × 4 × 10 = 80π cm².
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)