4 Biological Molecules: Structure and Their Function || A quick guide to Understanding biomolecules
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a concise yet informative overview of the four major biomolecules that sustain life: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. It explains their basic structures, monomeric units, and bond types, highlighting their crucial roles in energy storage, genetic information transfer, and cellular functions. From glucose and amino acids to DNA and lipids, each biomolecule is presented with clear examples and practical applications in living organisms. This video is an engaging introduction to the building blocks of life, ideal for those looking to understand biology at a fundamental level.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbohydrates are made up of monosaccharides (e.g., glucose) joined by glycosidic bonds, and they serve as a primary energy source and structural components in plants and animals.
- 😀 Proteins are composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They perform diverse functions including enzyme catalysis, structural support (e.g., collagen), and immune defense (e.g., antibodies).
- 😀 Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides, joined by phosphodiester bonds, and store genetic information (DNA) or mediate information flow (RNA) in the cell.
- 😀 Lipids are made from fatty acids and glycerol connected by ester bonds. They are hydrophobic and play critical roles in long-term energy storage and membrane structure.
- 😀 The four major biomolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids—are essential for the structure and function of all living organisms.
- 😀 Carbohydrates can be simple sugars (monosaccharides) or complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides), such as starch and cellulose, which are involved in energy storage and cell structure.
- 😀 Proteins are highly diverse in function and structure, including roles as enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and carriers of oxygen in the blood (e.g., hemoglobin).
- 😀 Nucleotides, the building blocks of nucleic acids, consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is single-stranded.
- 😀 Lipids, unlike other biomolecules, lack a common monomer unit and are primarily composed of fatty acids and glycerol. They also contribute to hormone production (e.g., steroids).
- 😀 Lipids form the structural basis of biological membranes (e.g., the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane) and are involved in protecting organs and insulating the body.
Q & A
What are the four major biomolecules discussed in the video?
-The four major biomolecules discussed in the video are carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids.
What is the monomeric unit of carbohydrates?
-The monomeric unit of carbohydrates is called a monosaccharide, such as glucose.
How are monosaccharides in carbohydrates linked together?
-Monosaccharides are linked together by glycosidic bonds to form disaccharides and polysaccharides.
What are the primary functions of carbohydrates in living organisms?
-Carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source, provide short-term energy, and form structural components like cellulose in plants and chitin in fungi.
What is the bond that joins amino acids in proteins?
-Amino acids in proteins are joined by peptide bonds.
What is the function of proteins in living organisms?
-Proteins have diverse functions, including acting as enzymes, structural components (e.g., collagen and keratin), defense molecules (e.g., antibodies), and transporters (e.g., hemoglobin).
What are the monomeric units of nucleic acids?
-The monomeric units of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
How are nucleotides linked together in nucleic acids?
-Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester bonds.
What is the function of nucleic acids in organisms?
-Nucleic acids store genetic information (e.g., DNA), transmit biological information (e.g., RNA), and are involved in protein synthesis.
What are the components of lipids, and how are they bonded together?
-Lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol, which are joined together by ester bonds.
What is the function of lipids in organisms?
-Lipids serve as long-term energy storage, protect organs, insulate the body, and form biological membranes like the phospholipid bilayer.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)

Biomolecules (Older Video 2016)

These are the 4 main types of carbon-based molecules necessary for life
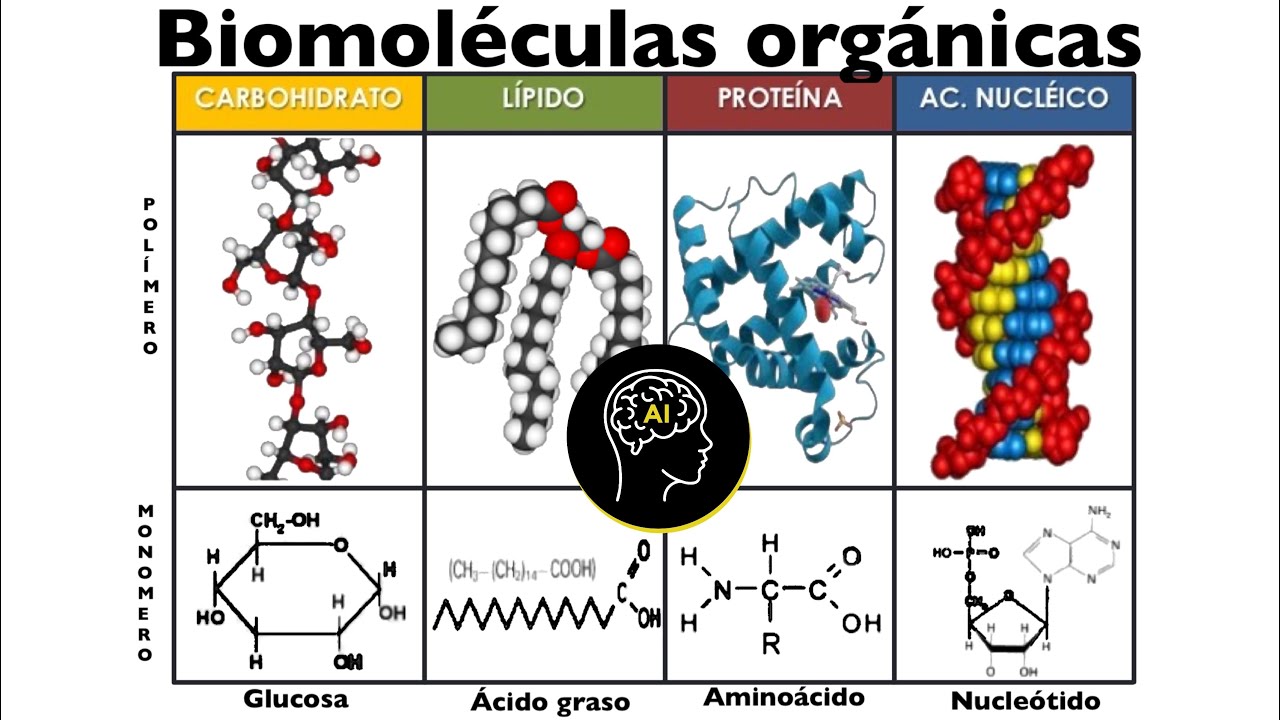
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
