La propagazione del calore: conduzione, convezione, irraggiamento
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the three main modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. It explains how heat moves through materials, using relatable examples like metal spoons and wooden handles to illustrate conduction. Convection is demonstrated through water heating and air currents, showing how warmer substances rise and cooler ones sink. Finally, radiation is explored through the transfer of heat from the sun and how thermos bottles minimize heat loss. The video effectively combines scientific principles with practical applications, making complex concepts accessible and engaging.
Takeaways
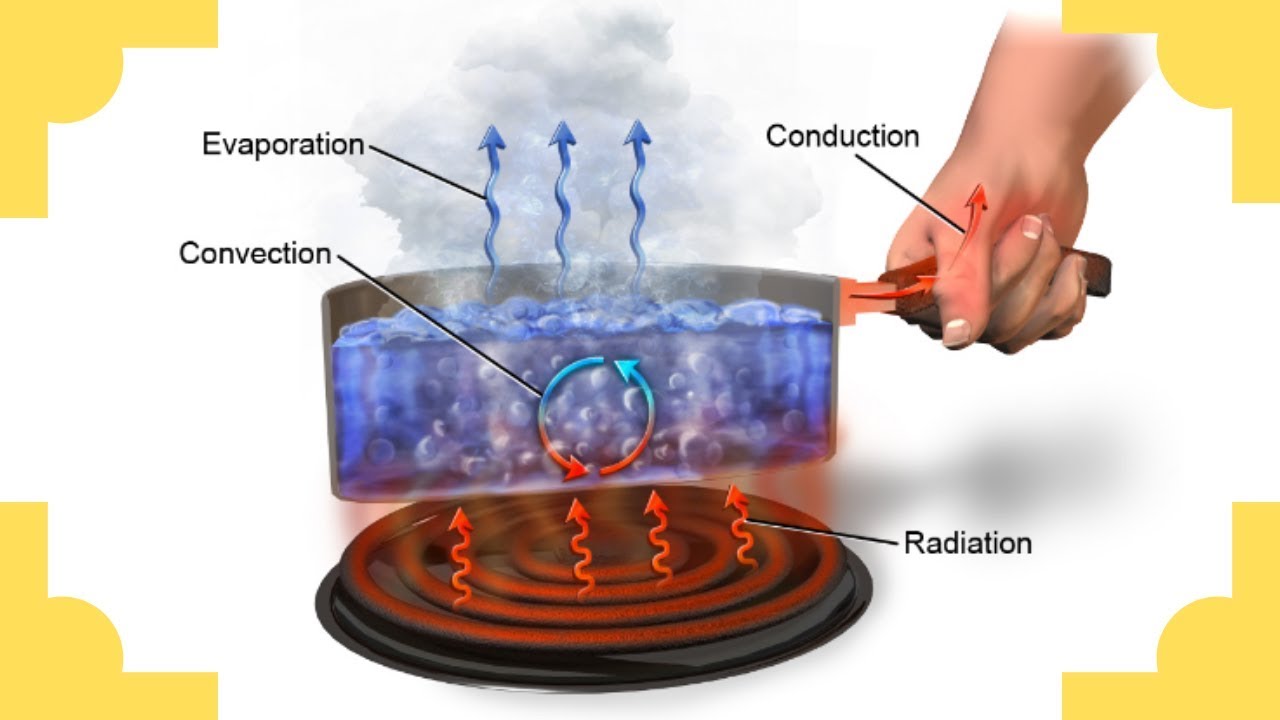
- 😀 Heat transfers spontaneously from a hotter body to a cooler one.
- 😀 There are three main methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- 😀 Conduction occurs when heat transfers between solid bodies through direct physical contact.
- 😀 In conduction, molecules in a hotter object transfer energy to cooler ones through collisions.
- 😀 Metals are good conductors of heat, which is why metal utensils heat up quickly, making them uncomfortable to hold.
- 😀 Materials like wood, plastic, and wool are poor conductors of heat and are used as insulators.
- 😀 In convection, heat transfer occurs through the movement of liquids or gases, as hot, less dense fluid rises and cooler, denser fluid sinks.
- 😀 The process of convection in water can be observed through 'convective cells,' which are circular patterns of fluid movement.
- 😀 Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves (mainly infrared) and can occur through a vacuum, such as the heat from the sun reaching Earth.
- 😀 Reflective materials, like those used in thermoses, help retain heat by reflecting infrared radiation, preventing heat loss.
- 😀 Even ice is a good thermal insulator, which is why igloos, made from ice, can keep warmth inside despite the cold external temperatures.
Q & A
What are the three main modes of heat transfer discussed in the script?
-The three main modes of heat transfer discussed are conduction, convection, and radiation.
How does heat transfer through conduction work?
-In conduction, heat is transferred through direct contact between particles. When a hot object touches a cooler one, the faster-moving molecules of the hot object collide with the slower-moving molecules of the cooler object, transferring energy.
Why do metal spoons heat up more quickly than wooden spoons when placed in a hot substance?
-Metals are good conductors of heat, meaning they transfer heat efficiently. This causes the metal spoon to heat up quickly, while wooden spoons are poor conductors and don’t heat up as much.
Why is wood considered a poor conductor of heat?
-Wood is made of materials that do not allow heat to pass through easily. Its molecular structure inhibits the transfer of energy, making it a good insulator.
What role does convection play in heat transfer in liquids and gases?
-In convection, heat causes molecules in a liquid or gas to move. When the molecules at the bottom are heated, they become less dense and rise, while cooler molecules sink, creating a cycle that distributes heat throughout the fluid.
How does convection help in heating a pot of water?
-As the water at the bottom of the pot heats up, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler water moves down to be heated. This movement of water creates a continuous cycle, transferring heat throughout the liquid.
Why does the ice on a lake surface not sink despite being solid?
-Ice is less dense than liquid water, so it floats. This property prevents it from sinking and forms a layer on the surface of lakes, which also acts as an insulator, keeping the water below warm enough to support life.
How does radiation transfer heat from the Sun to Earth?
-Radiation transfers heat via electromagnetic waves, specifically infrared radiation, which can travel through the vacuum of space. These waves reach Earth, warming it without the need for a medium.
What is the purpose of a thermos in terms of heat transfer?
-A thermos prevents heat transfer by using reflective surfaces and vacuum insulation. The reflective surface inside the thermos reflects infrared radiation, minimizing heat loss through radiation, while the vacuum reduces heat transfer through conduction and convection.
Why does a reflective surface inside a thermos help maintain the temperature of its contents?
-The reflective surface inside a thermos bounces infrared radiation back into the thermos, preventing heat from escaping. This reduces the heat transfer by radiation, keeping the contents at their initial temperature for longer periods.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Conduction -Convection- Radiation-Heat Transfer

The Physics of Heat: Crash Course Physics #22
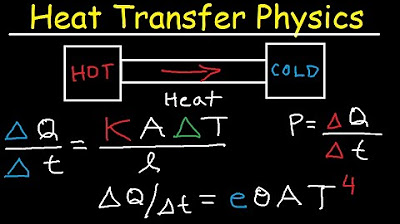
Thermal Conductivity, Stefan Boltzmann Law, Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convecton, Radiation, Physics

Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

Perpindahan Kalor

Heat Transfer - Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
