VOLUME PERNAPASAN | SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the six key volumes involved in human respiration: tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, vital capacity, and total lung capacity. It highlights how lung capacity decreases with age, typically after 35, and factors influencing lung volume, such as genetics, physical training, and altitude. The video also emphasizes that male lung volume is generally larger than female lung volume. The content encourages viewers to understand respiratory volumes and how they relate to overall lung health, with practical examples and measurements used to gauge lung capacity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lung capacity in normal conditions is about 6 liters, but it decreases with age, especially after 35.
- 😀 Lung volume can be affected by diseases and physical conditions, with some people experiencing reduced capacity at a younger age.
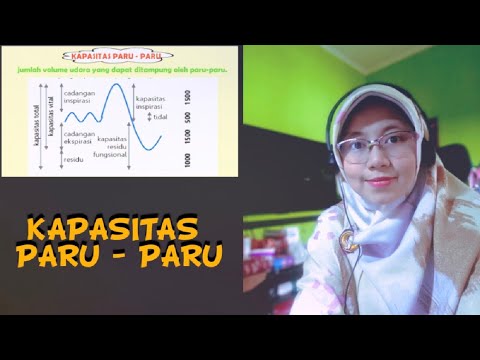
- 😀 The 6 key types of lung volumes include tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, vital capacity, and total lung capacity.
- 😀 Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, approximately 500 mL.
- 😀 Inspiratory reserve volume is the additional air that can be inhaled after normal breathing, around 1500 mL.
- 😀 Expiratory reserve volume is the additional air that can be exhaled after normal breathing, also about 1500 mL.
- 😀 Residual volume is the air left in the lungs after maximum exhalation, typically 1000 mL.
- 😀 Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a deep breath, about 3500 mL.
- 😀 Total lung capacity is the maximum amount of air the lungs can hold, around 4500 mL, including all lung volumes.
- 😀 Factors like age, physical fitness, environmental conditions (altitude), and gender influence lung capacity, with athletes and those living at high altitudes often having larger volumes.
Q & A
What is the normal lung capacity, and how does it change with age?
-The normal lung capacity for an adult is about 6 liters. As a person ages, lung capacity and function typically decrease, especially after the age of 35. However, lung capacity can also decline in younger individuals, particularly those with certain health conditions.
Can lung capacity decrease in individuals younger than 35 years?
-Yes, lung capacity can decrease in people younger than 35 years, especially in individuals who suffer from specific diseases, such as respiratory conditions or other health issues.
What is tidal volume, and how much air is typically involved in normal breathing?
-Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal, relaxed breathing. Typically, tidal volume is about 500 cc (or 500 mL) of air.
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), and how much air can be inhaled maximally?
-Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), also known as complementary air, is the amount of air that can be inhaled maximally after a normal inspiration. The typical volume of IRV is about 1500 cc (or 1500 mL).
What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV), and how much air can be exhaled maximally?
-Expiratory reserve volume (ERV), or supplemental air, is the volume of air that can be exhaled maximally after a normal exhalation. It is typically around 1500 cc (or 1500 mL).
What is residual volume in the lungs, and how much air does it represent?
-Residual volume is the amount of air that remains in the lungs after a maximal exhalation. This volume is typically around 1000 cc (or 1000 mL).
What is vital capacity, and how is it calculated?
-Vital capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after taking a maximal inhalation. It is calculated by adding tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume. The typical vital capacity is about 3500 cc (or 3500 mL).
How do you calculate the total lung capacity (TLC)?
-Total lung capacity (TLC) is the maximum volume of air the lungs can hold. It is calculated by adding residual volume to vital capacity. The total lung capacity is typically around 4500 cc (or 4500 mL).
How does lung volume vary among individuals?
-Lung volume varies from person to person. Factors like genetics, physical fitness, and environmental conditions can influence lung volume. Athletes, especially swimmers, and individuals who practice yoga tend to have larger lung volumes. People living at higher altitudes, where oxygen levels are lower, may also have larger lung volumes.
How does lung volume differ between males and females?
-On average, males tend to have larger lung volumes than females. This is due to physiological differences such as body size and lung structure.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)