Current, Voltage and Resistance
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the basic properties of electrical circuits: current, voltage, and resistance. Current refers to the flow of electrons through a conductor, measured using an ammeter. Voltage, or potential difference, is the electrical pressure pushing electrons through the circuit, measured with a voltmeter. Resistance is the difficulty electrons face when passing through a component, influenced by material, size, and temperature. The video offers a qualitative exploration of how these properties interact, with a focus on understanding how changes in voltage and resistance affect the flow of current, without delving into quantitative formulas like Ohm's Law.
Takeaways
- 😀 Current is the rate of flow of electrons through a conductor and is measured using an ammeter.
- 😀 Voltage, also known as potential difference, is the electrical pressure that pushes electrons around the circuit, measured using a voltmeter.
- 😀 Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons in a circuit and depends on factors like the material, size, and temperature of the conductor.
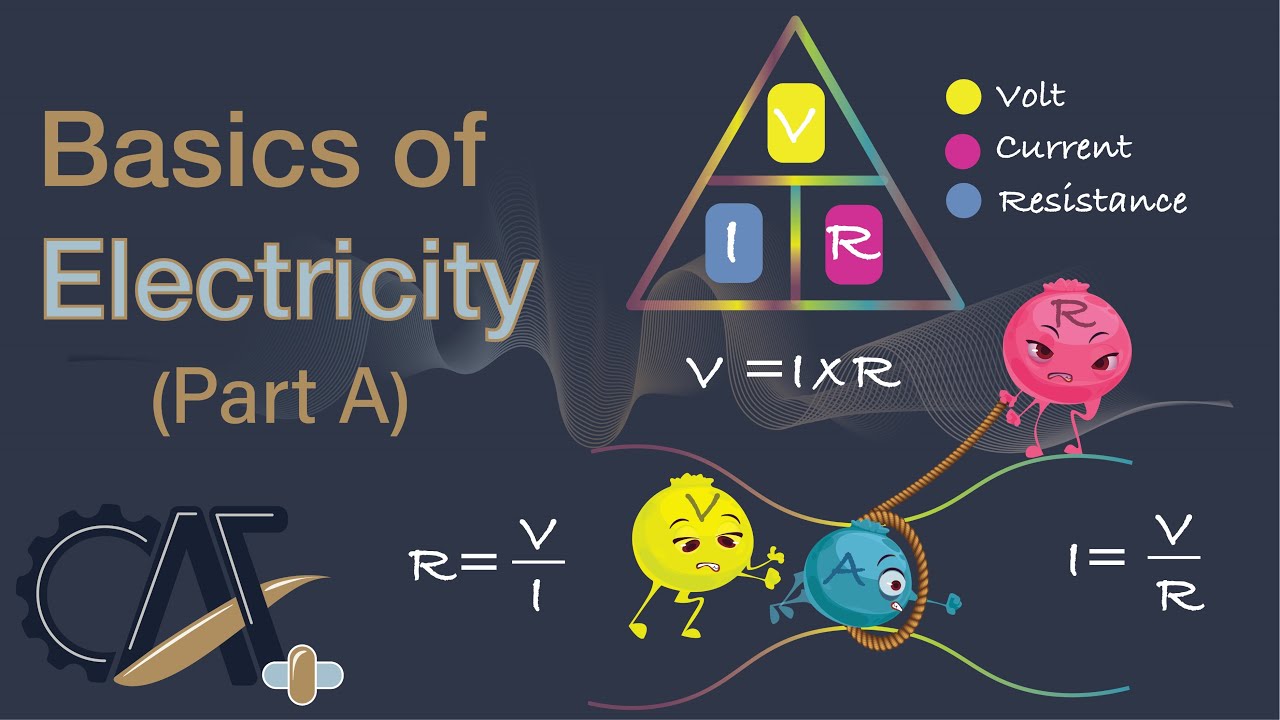
- 😀 Current is symbolized as 'I' in physics and represents the number of electrons passing through a point at a given time.
- 😀 Voltage is symbolized as 'V' and is the force pushing electrons through the circuit from high to low concentration.
- 😀 The unit of current is amperes (A), and the unit of voltage is volts (V).
- 😀 Resistance is symbolized by 'R' and is measured in ohms (Ω).
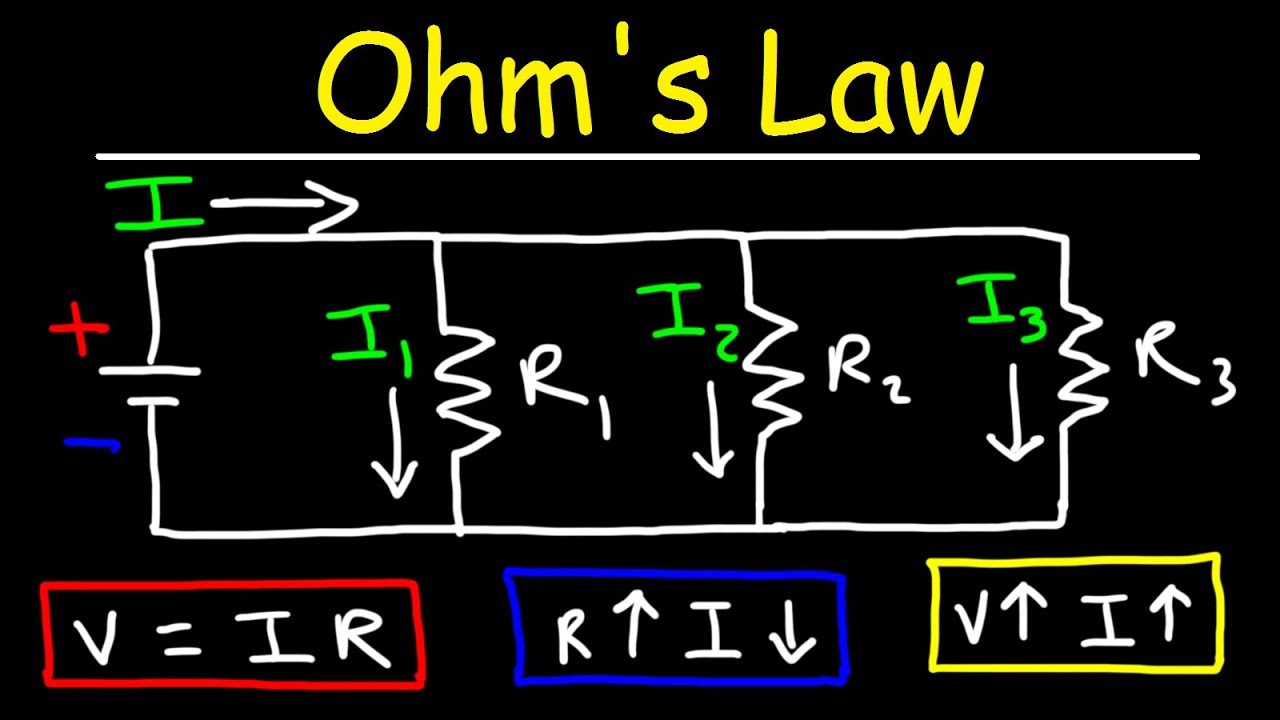
- 😀 An ammeter is connected in series to measure current, while a voltmeter is connected in parallel to measure voltage.
- 😀 The resistance of a material affects how easily electrons can flow through it, with different materials offering different levels of resistance.
- 😀 As temperature increases, resistance generally increases, making it harder for electrons to pass through.
- 😀 The relationship between current, voltage, and resistance can be described qualitatively, without going into quantitative details like Ohm’s Law.
Q & A
What is current in an electrical circuit?
-Current is the rate of flow of electrons through a conductor. It is measured in amperes (amps) and is denoted by the symbol 'I'.
How is current measured in a circuit?
-Current is measured using an ammeter. The ammeter is connected in series with the circuit so that all electrons pass through it, and it provides a reading in amperes (A).
What does voltage represent in an electrical circuit?
-Voltage, also known as potential difference, represents the electrical pressure that pushes electrons around the circuit. It is measured in volts (V).
How do we measure voltage in a circuit?
-Voltage is measured using a voltmeter. The voltmeter is connected in parallel across the two points where voltage is to be measured, and it reads out in volts (V).
What is resistance in an electrical circuit?
-Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons through a conductor. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and depends on the material, size, and temperature of the conductor.
What are the factors that influence resistance in a circuit?
-The resistance in a circuit is influenced by the material of the conductor, the size (or thickness) of the conductor, and the temperature. For example, thicker wires have lower resistance, and materials like copper have lower resistance compared to materials like iron.
How is resistance calculated if it cannot be directly measured?
-Resistance is calculated using the relationship between current and voltage. By measuring the voltage across a component and the current flowing through it, resistance can be calculated using the formula: R = V/I.
What happens to the current if voltage increases but resistance remains the same?
-If the voltage increases and resistance remains the same, the current will increase. This is because the increased voltage pushes more electrons through the conductor.
What happens to the current if resistance increases but voltage remains the same?
-If resistance increases and voltage remains the same, the current will decrease. Higher resistance makes it harder for electrons to flow, reducing the amount of current.
Why is it important to understand the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in electrical circuits?
-Understanding the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance is crucial for designing and analyzing electrical circuits. These three properties interact to determine the behavior of the circuit, and knowing how they affect each other helps in optimizing performance and ensuring safety.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)