Listrik Dinamis-Beda Potensial dan Penghantar Listrik (Part 2)
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the concepts of electrical potential difference (voltage) and electrical conductors are explored. The presenter explains how a battery’s positive and negative terminals create a potential difference, enabling the flow of electric current. The video also delves into how the properties of electrical conductors, such as material type, length, and diameter, affect resistance. Through practical examples and calculations, viewers learn how to determine potential difference and resistance in circuits, providing a comprehensive foundation in electrical principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses dynamic electricity, focusing on potential difference and electrical conductors.
- 😀 A battery has two poles: a positive pole with higher potential and a negative pole with lower potential, creating a potential difference (voltage).
- 😀 When a battery is used up, the potential difference is equalized, meaning no current can flow through it anymore.
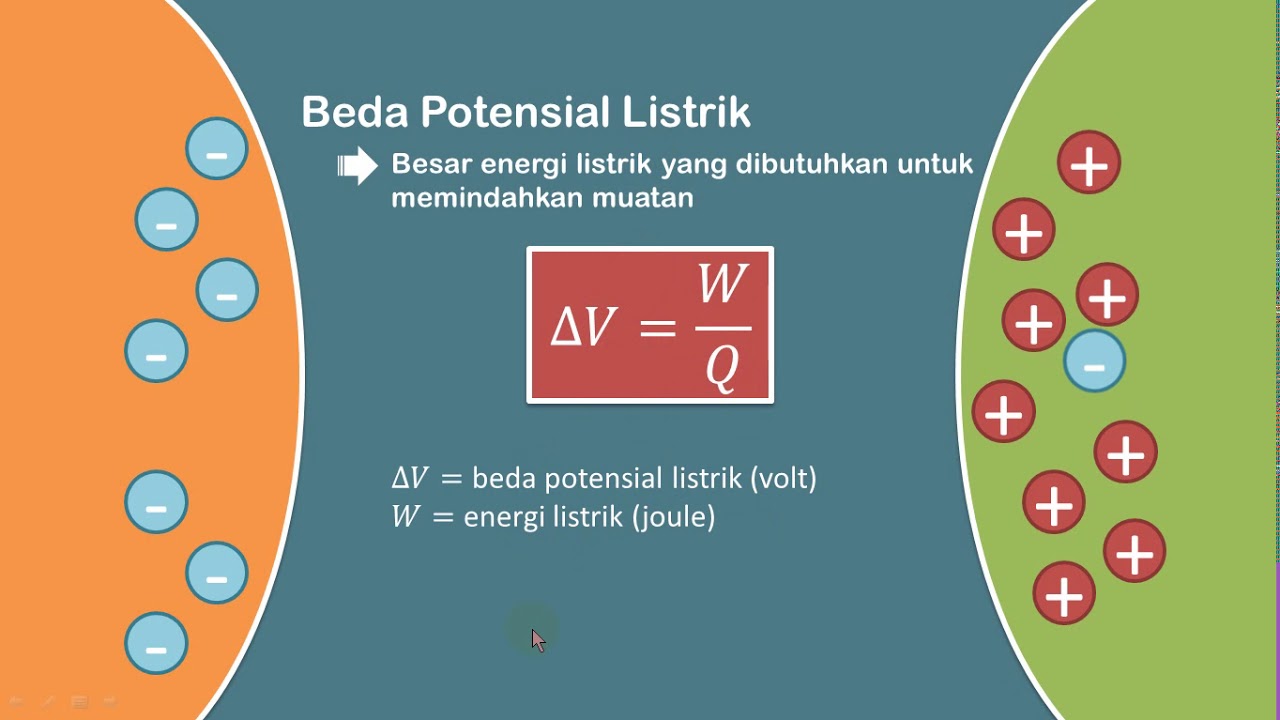
- 😀 Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move electrical charges from one point to another, and can be calculated using the formula: V = W/Q.
- 😀 In an example, 5600 Joules of energy is used to move 80 Coulombs of charge, giving a potential difference of 70 volts.
- 😀 Electrical conductors, such as wires, are materials that allow current to flow. Copper is a common conductor, often coated with an insulating layer to prevent heat loss.
- 😀 The efficiency of electrical conductors depends on factors like length, diameter, and material type.
- 😀 Longer conductors have higher resistance, while larger diameters have lower resistance, making current flow more efficiently.
- 😀 The resistance of a conductor depends on the material’s resistivity, and various materials (e.g., copper, aluminum) have different resistivity values.
- 😀 The resistance of a conductor can be calculated with the formula: R = ρ * L / A, where ρ is the resistivity, L is the length, and A is the cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Q & A
What does 'beda potensial' mean in the context of electricity?
-'Beda potensial' translates to 'potential difference' in English. It refers to the difference in electric potential between two points in a circuit, which drives the flow of electric current.
Why do battery terminals have different shapes, with one part protruding and the other being flat?
-The protruding part of the battery terminal indicates the higher electric potential (positive pole), while the flat part indicates the lower electric potential (negative pole). This difference in potential is essential for the flow of current.
What happens when a battery is used continuously?
-When a battery is used continuously, the potential difference between the positive and negative terminals decreases, eventually leading to the battery running out of charge, as the potentials become equal.
What is the formula for calculating the electrical potential difference (voltage)?
-The formula for calculating electrical potential difference (voltage) is: v = w / Q, where 'v' is the potential difference in volts, 'w' is the energy in joules, and 'Q' is the charge in coulombs.
In the example problem, if 5600 Joules of energy are used to move 80 coulombs of charge, what is the potential difference?
-By applying the formula v = w / Q, we get v = 5600 Joules / 80 Coulombs, which equals 70 volts.
What factors affect the resistance of a conductor?
-The resistance of a conductor is influenced by the length of the conductor, its diameter, and the type of material it is made from. A longer conductor and smaller diameter increase resistance, while the material's resistivity also plays a significant role.
How does the length of a conductor affect its resistance?
-The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length. The longer the conductor, the greater its resistance.
Why does increasing the diameter of a conductor decrease its resistance?
-Increasing the diameter of a conductor increases its cross-sectional area, which allows more space for electrons to flow. As a result, the resistance decreases.
What is the formula for calculating the resistance of a conductor?
-The formula for calculating the resistance of a conductor is: R = ρ * l / A, where 'R' is the resistance in ohms, 'ρ' is the resistivity of the material in ohm-meters, 'l' is the length of the conductor in meters, and 'A' is the cross-sectional area in square meters.
In the example problem with a copper wire, if the wire's length is 200 meters, cross-sectional area is 2 mm², and resistivity is 0.02 Ohm-meters, what is the resistance?
-To calculate the resistance, we first convert the cross-sectional area from mm² to m², which becomes 2 / 1,000,000. Using the formula R = ρ * l / A, the resistance is calculated to be 2 million ohms, or 2 * 10^6 ohms.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Seri Belajar Elekronika Dasar : Pengertian Tegangan Listrik

Qual a diferença entre volt, watt e ampere? #ManualMaker Aula 2, Vídeo 1

Mau tahu kenapa arus listrik bisa terjadi ?,,
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Statis IV (Potensial Listrik dan Energi Listrik)

W2_L1_Introduction to "Voltage"

Shocking Footage of Electrocution.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)