Ball & Socket Joint (DCF)
Summary
TLDRThe ball and socket joint is a versatile and crucial structure in the human body, allowing for movement in multiple directions, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction. The two primary ball and socket joints are located at the hip and shoulder. While the hip joint offers stability with its deep socket, it sacrifices some range of motion. In contrast, the shoulder joint has a shallower socket, providing greater flexibility but less stability, making shoulder dislocations more common.
Takeaways
- 😀 The ball and socket joint is considered the 'champion' of all joints due to its versatility.
- 😀 Its structure consists of a ball fitting into a socket, which allows for a wide range of motion.
- 😀 This joint can move in all axes: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction.
- 😀 The two ball and socket joints in the human body are located at the hip and the shoulder.
- 😀 The hip joint features a deep socket, which provides stability but limits some range of motion.
- 😀 The shoulder joint has a shallower socket, offering greater range of motion at the cost of stability.
- 😀 The trade-off between stability and mobility explains why the shoulder is more prone to dislocations.
- 😀 Dislocating the shoulder is a common injury due to the shallowness of its socket.
- 😀 The ball and socket joint's design is simple but highly effective in allowing complex movements.
- 😀 The hip joint's deeper socket sacrifices some flexibility to provide better support and stability.
- 😀 Both joints are crucial for enabling many daily movements and activities, but they have distinct roles in the body.
Q & A
What is the structure of a ball and socket joint?
-A ball and socket joint consists of a ball-like structure that fits into a cup or socket. This design allows for movement in multiple directions, including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction.
What are the main functions of the ball and socket joint?
-The main function of a ball and socket joint is to provide a wide range of motion in multiple axes, allowing for complex and flexible movement of the body.
How many ball and socket joints are in the human body?
-There are two primary ball and socket joints in the human body: the hip joint and the shoulder joint.
How does the structure of the hip joint differ from the shoulder joint?
-The hip joint has a deep socket, which provides greater stability but limits its range of motion. In contrast, the shoulder joint has a shallower socket, offering a greater range of motion but sacrificing some stability.
Why does the shoulder joint have a greater range of motion than the hip joint?
-The shoulder joint has a shallower socket, which allows for a wider range of motion. This design enables the arm to move freely in many directions, including overhead motions, but it also makes the joint less stable.
What is the trade-off between stability and range of motion in ball and socket joints?
-There is a trade-off between stability and range of motion: a deeper socket (like in the hip) offers more stability but less range of motion, while a shallower socket (like in the shoulder) allows for more mobility but reduces joint stability.
Why are shoulder dislocations common?
-Shoulder dislocations are common because the shoulder joint has a shallower socket, which increases its range of motion but reduces stability, making the joint more prone to dislocation.
What types of movements are possible with a ball and socket joint?
-A ball and socket joint allows for flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, and circumduction, providing a wide range of motion in multiple axes.
How does the stability of the hip joint affect its movement?
-The deep socket of the hip joint provides stability, which is essential for weight-bearing activities like walking and running. However, this stability comes at the cost of a reduced range of motion compared to the shoulder joint.
How does the ball and socket joint design benefit the human body?
-The ball and socket joint design benefits the body by offering versatile movement in multiple directions, which is crucial for various physical activities. It allows for a balance of mobility and stability, depending on the joint's specific location in the body.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
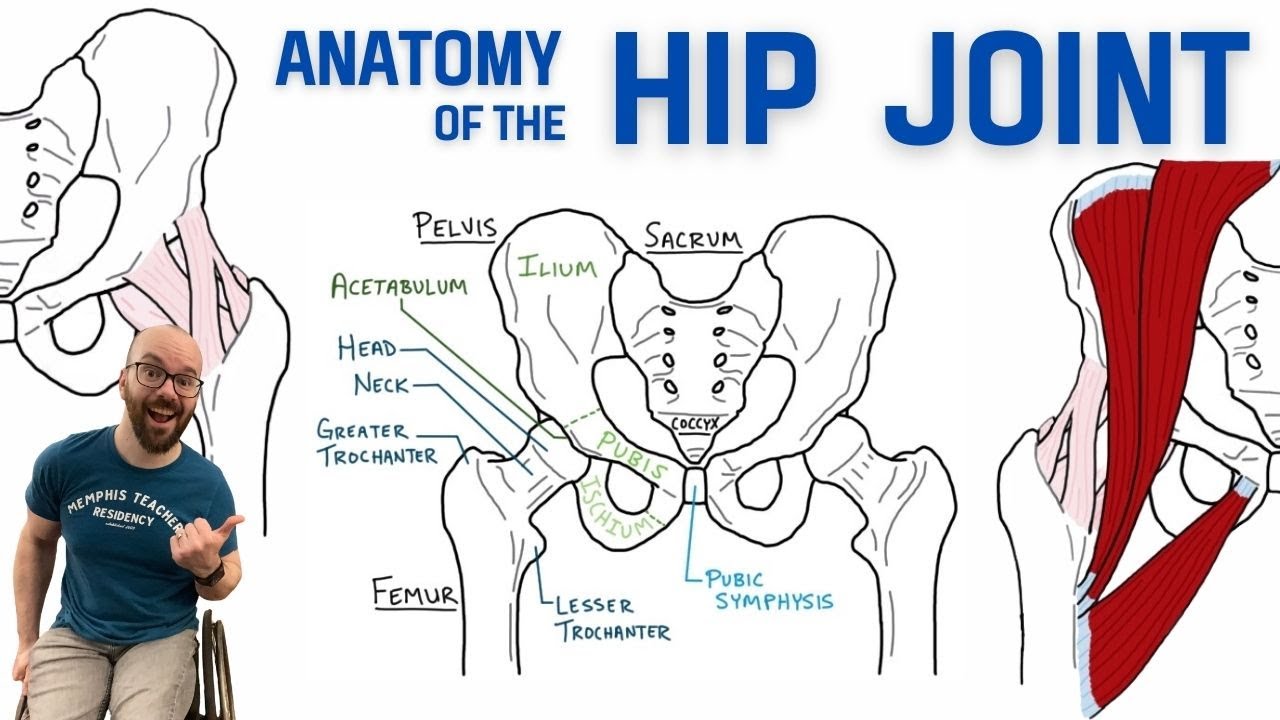
Anatomy of the Hip Joint | Bones, Ligaments, & Muscles
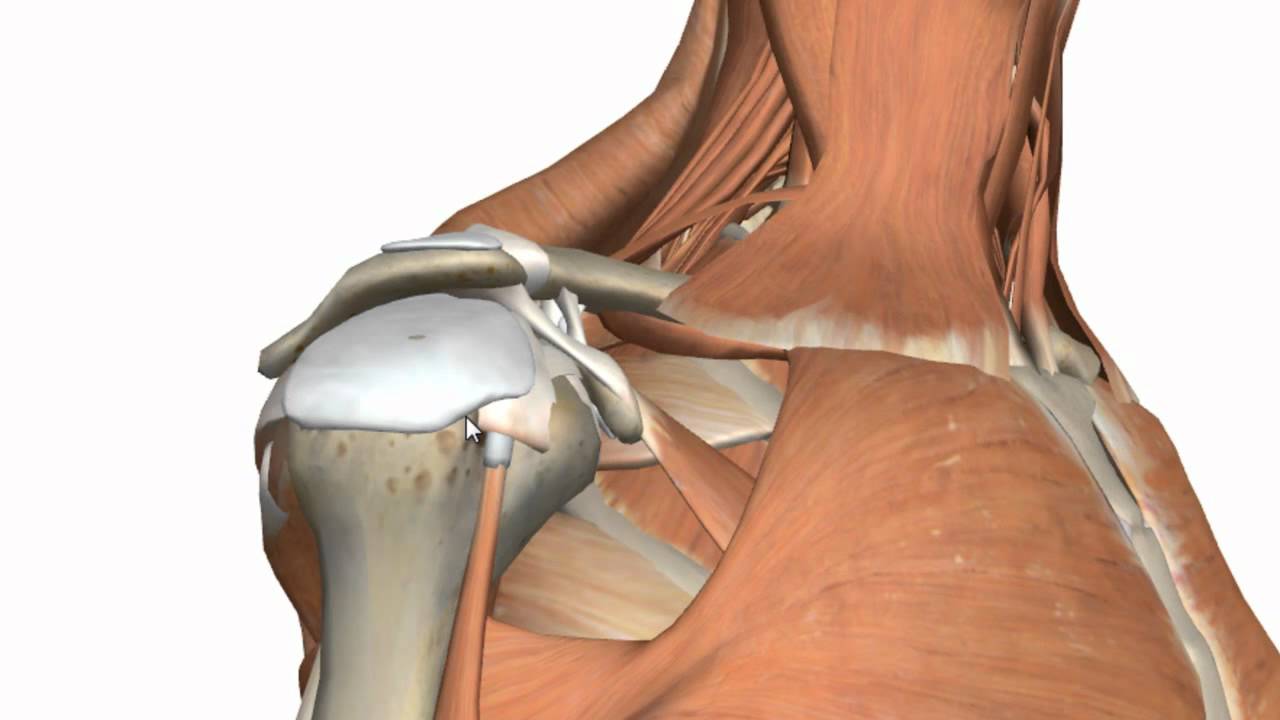
Shoulder Joint - Glenohumeral Joint - 3D Anatomy Tutorial

🥇 GENERALIDADES DE ANATOMÍA - Posición Anatómica, Terminología Anatómica. ¡Fácil y Sencillo!
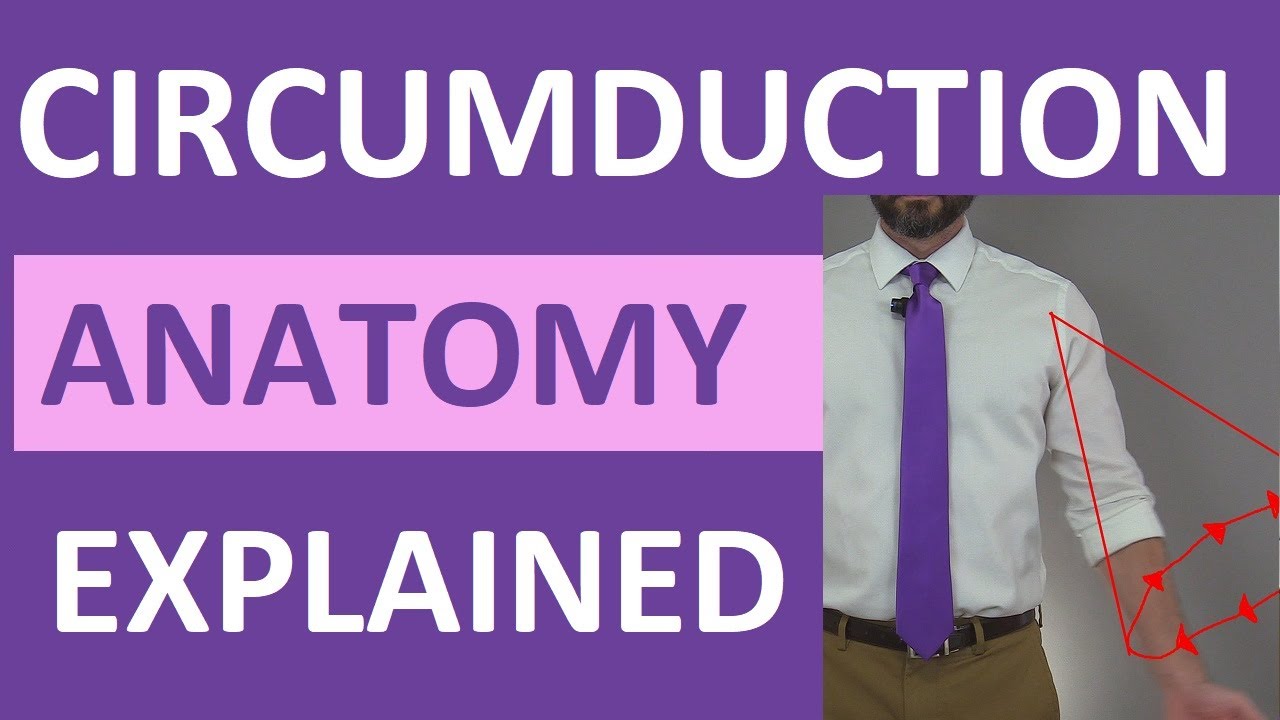
Circumduction Movement: Hip, Shoulder, Thumb, Fingers, Wrist, Ankle, Toes, Head

Kinesiologi Olahraga: Menganalisis Gerak Tubuh Dalam Kehidupan Sehari-hari

Bone Physiology and Anatomy of Animals (VETERINARY TECHNICIAN EDUCATION)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
