What is a rectifier?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, we explore rectifiers and their operation, starting with the basics of diode biasing. A diode conducts when forward-biased and doesn't when reverse-biased. The video covers three types of rectifiers: the half-wave rectifier, where current flows in one direction; the full-wave bridge rectifier, which uses four diodes for current flow during both positive and negative cycles; and the center-tapped full-wave rectifier, which uses two diodes to provide continuous current. The script offers a simple explanation of each circuit's functioning and highlights how rectifiers convert AC to DC current.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
- 😀 A diode in forward bias allows current to flow, while reverse bias blocks current.
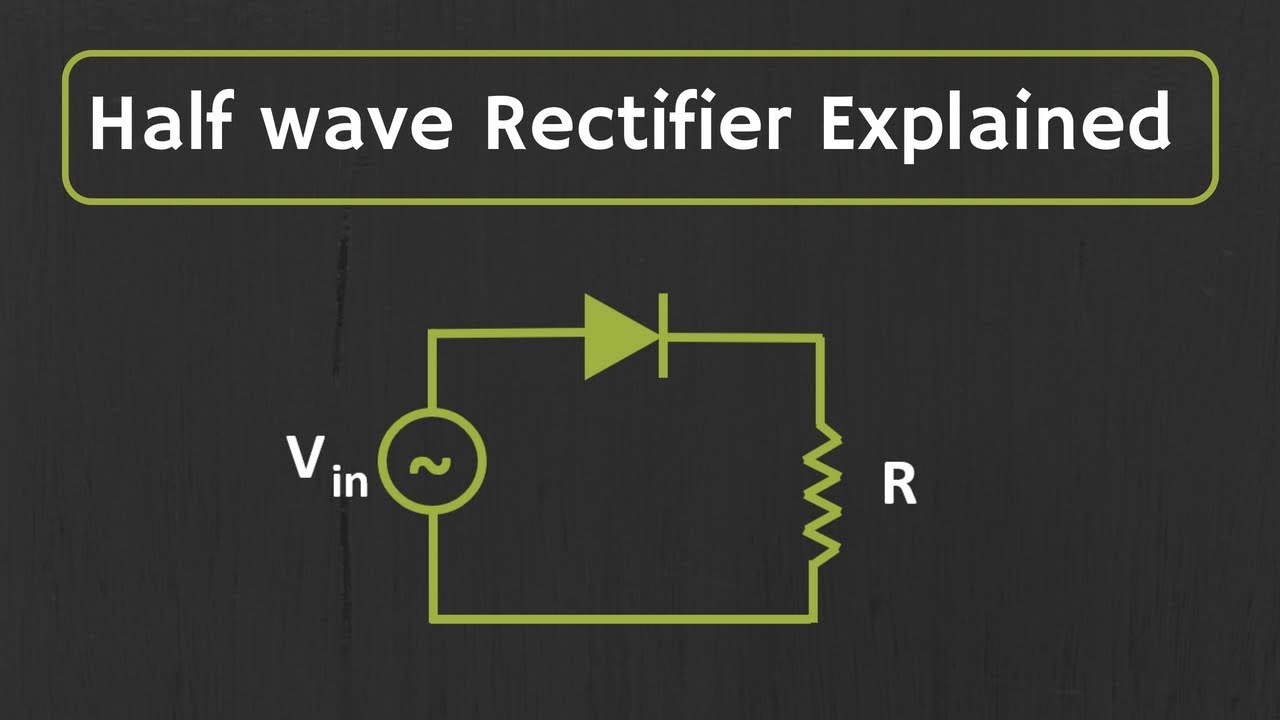
- 😀 A half-wave rectifier only conducts during the positive half cycle of the AC supply.
- 😀 In a half-wave rectifier, the output is a pulsating DC signal due to current flow only in one direction.
- 😀 A full-wave bridge rectifier uses four diodes to allow current to flow during both positive and negative half cycles of the AC supply.
- 😀 In a full-wave bridge rectifier, the current always flows in one direction through the load resistor, producing a smoother DC output.
- 😀 A center-tapped full-wave rectifier uses a center-tapped transformer and two diodes to produce a full-wave rectified output.
- 😀 During the positive half cycle in a center-tapped full-wave rectifier, current flows through one diode, and during the negative half cycle, it flows through the other.
- 😀 The center-tapped full-wave rectifier offers a more efficient conversion compared to a half-wave rectifier.
- 😀 Rectifiers are available in different sizes and shapes, depending on the application and power requirements.
Q & A
What is a rectifier?
-A rectifier is an electronic device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). It allows current to flow in only one direction.
What happens when a diode is connected in forward bias?
-When a diode is connected in forward bias, meaning its anode is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, the diode turns on, allowing current to flow through it.
What is the reverse bias condition of a diode?
-In reverse bias, when the anode of the diode is connected to the negative terminal of the supply, the diode does not turn on, and no current flows through it.
How does a half-wave rectifier work?
-In a half-wave rectifier, an AC supply is connected to a diode. During the positive half cycle of the AC, the diode becomes forward biased, allowing current to flow. During the negative half cycle, the diode is reverse biased, blocking current, resulting in current flow only in one direction.
What is the output of a half-wave rectifier?
-The output of a half-wave rectifier consists of only positive cycles of the AC supply, as the current flows in only one direction through the diode.
How does a full-wave bridge rectifier work?
-A full-wave bridge rectifier uses four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. During the positive half cycle, current flows through diodes D1 and D2, and during the negative half cycle, current flows through diodes D2 and D3, ensuring current flows in one direction through the load resistor.
What is the advantage of a full-wave bridge rectifier over a half-wave rectifier?
-The full-wave bridge rectifier provides smoother DC output with less ripple compared to a half-wave rectifier because it rectifies both the positive and negative halves of the AC signal, making the output more consistent.
What is a center-tapped full-wave rectifier?
-A center-tapped full-wave rectifier uses a transformer with a center tap. Two diodes are used to rectify the AC supply, with one diode conducting during the positive half cycle and the other during the negative half cycle. The current flows in one direction through the load resistor during both halves of the AC cycle.
How does the center-tapped full-wave rectifier differ from the bridge rectifier?
-In a center-tapped full-wave rectifier, only two diodes are used, and the transformer has a center tap. In contrast, a bridge rectifier uses four diodes and does not require a center-tapped transformer.
What is the significance of the diodes in a bridge rectifier circuit?
-The diodes in a bridge rectifier allow current to flow in one direction during both the positive and negative half cycles of the AC supply. They ensure that the output is always positive, converting AC to DC.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Half-Wave vs Full-Wave Rectifiers - Electronics Basics 19

How a DIODE Works?

Schottky Diode (Construction & Working) Special Purpose Diodes (Basics Electronics)

Half Wave Rectifier | IEE | GXEST104 | KTU 2024 |
Half wave Rectifier Explained

How does a Diode Work? A Simple Explanation | How Diodes Work | Electrical4U
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
