Full Wave Bridge Rectifier + Capacitor filters + half wave rectifier
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the function and importance of a full wave bridge rectifier, which converts AC to DC for electronic devices. It details the arrangement of diodes, the nature of AC and DC voltages, and the rectification process, highlighting how to reduce ripple using capacitors. Viewers learn about voltage drops across diodes and how to achieve stable output with additional components like inductors and voltage regulators. The tutorial is ideal for understanding the essentials of power conversion in electrical engineering.
Takeaways
- 🔌 A full wave bridge rectifier is essential for converting AC electricity from power outlets into usable DC electricity for electronic devices.
- ⚡ Full wave rectifiers consist of four diodes arranged to allow current to flow in one direction during both halves of the AC cycle.
- 📊 AC electricity is characterized by alternating voltage and current, while DC electricity has a constant voltage that flows in one direction.
- 📈 The RMS (Root Mean Square) voltage is used for practical measurements of AC, as it reflects the effective value of fluctuating voltage.
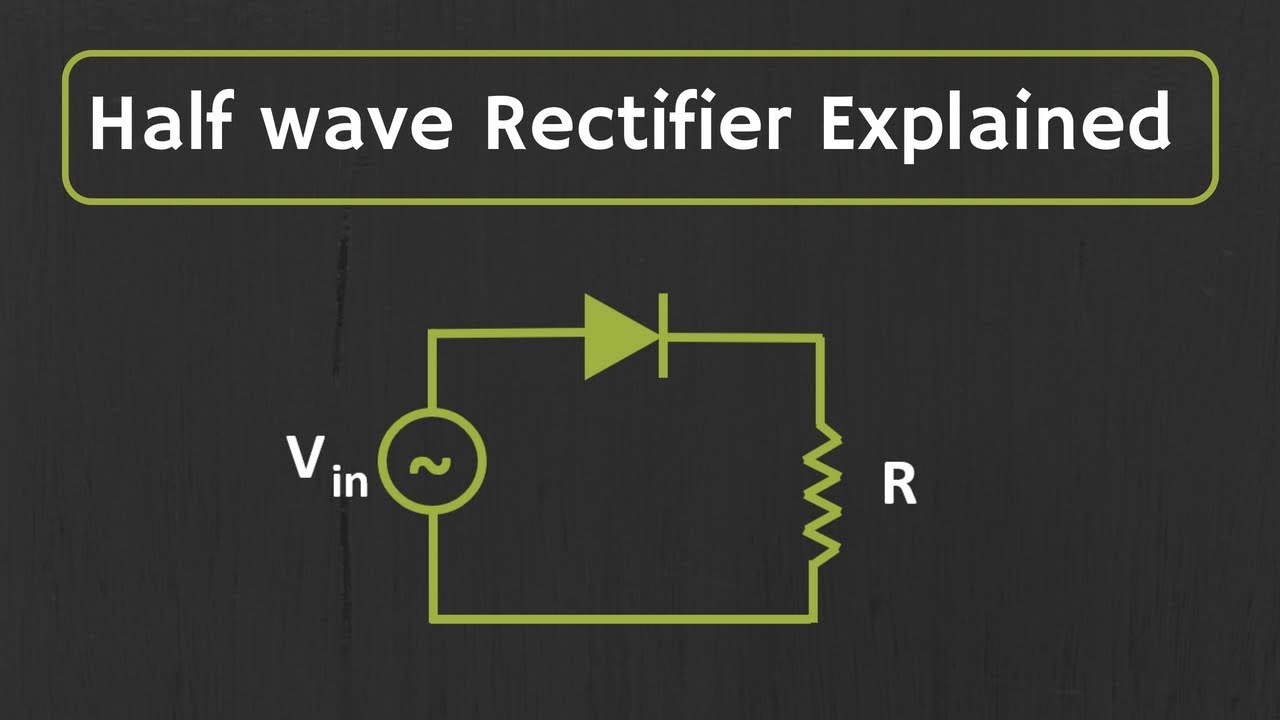
- 🔄 Half-wave rectification uses one diode to block half of the AC waveform, resulting in a pulsating DC output that is not very smooth.
- 💡 Full wave rectification provides a smoother output by utilizing both halves of the AC cycle, yielding a rippled DC waveform.
- 🔋 Capacitors are crucial for smoothing out the ripple in the DC output by storing and releasing energy during voltage fluctuations.
- ⚠️ Diodes introduce a voltage drop (approximately 0.7 volts each), which reduces the overall output voltage of the rectifier.
- 🧮 The output DC voltage can exceed the input AC RMS voltage due to capacitors charging to the peak voltage levels.
- 🛡️ Safety features like bleeder resistors help discharge capacitors when circuits are off, preventing hazardous voltage levels.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a full wave bridge rectifier?
-The primary function of a full wave bridge rectifier is to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), making it suitable for powering electronic devices.
How does a full wave bridge rectifier differ from a half wave rectifier?
-A full wave bridge rectifier uses four diodes to convert both halves of the AC sine wave into DC, while a half wave rectifier uses only one diode, allowing current to flow in only one direction and blocking the other half of the wave.
What role do diodes play in a bridge rectifier?
-Diodes in a bridge rectifier allow current to flow in only one direction, effectively converting the AC waveform into a pulsating DC output by conducting during different halves of the AC cycle.
Why is filtering necessary in a rectified output?
-Filtering is necessary to smooth the pulsating DC output from the rectifier, as the raw output contains ripples that can be undesirable for electronic components requiring a stable voltage.
What type of component is commonly used for filtering in a rectifier circuit?
-Capacitors are commonly used for filtering in a rectifier circuit, as they charge during voltage peaks and discharge during troughs, reducing the ripple in the output voltage.
How does the voltage drop across diodes affect the output voltage of a bridge rectifier?
-The output voltage of a bridge rectifier is lower than the input AC voltage due to the voltage drop across the diodes, typically around 0.7 volts per diode, resulting in a total drop of about 1.4 volts.
What is the root mean squared (RMS) voltage, and why is it important in AC circuits?
-Root mean squared (RMS) voltage is a way of expressing the effective value of AC voltage, which is crucial for calculations and comparisons with DC voltage, as it accounts for the varying nature of AC.
What are the benefits of using a voltage regulator after rectification?
-A voltage regulator provides a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage, ensuring that electronic devices receive a consistent and reliable power supply.
What happens to the output voltage when a capacitor is added to a rectifier circuit?
-When a capacitor is added to a rectifier circuit, it helps to smooth the output voltage by reducing the ripple, resulting in a more stable and constant DC voltage.
Can a rectifier convert DC into AC, and what device is needed for that purpose?
-A rectifier cannot convert DC into AC. To achieve that, an inverter is required, which uses different components to change the direction of current flow back into an alternating form.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)