Dasar Elektronika : Rectifier
Summary
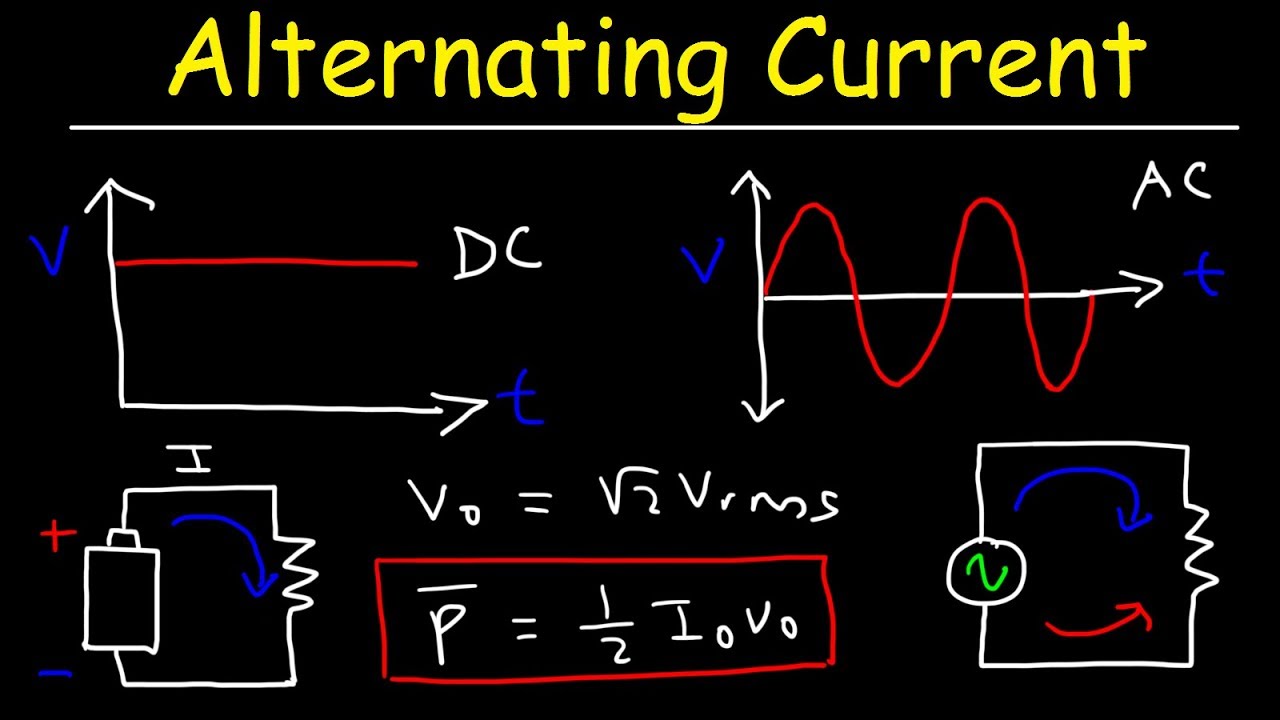
TLDRThis video script discusses the concept of rectifiers, electronic circuits that convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), essential in various electronic devices. It explores different types of rectifiers, including half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, comparing their efficiency and applications. The half-wave rectifier uses a single diode, allowing current flow only during the positive half-cycle of an AC signal, resulting in a lower efficiency and high ripple. In contrast, the full-wave rectifier employs two diodes, providing smoother DC output with higher efficiency. The script also introduces bridge rectifiers, which use four diodes for even more efficient and refined DC output. Additionally, it mentions the use of capacitors as filters to reduce ripple and stabilize the DC output.
Takeaways
- 😀 Rectifiers are electronic circuits that convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
- 🔌 There are two main types of rectifiers: half-wave and full-wave rectifiers.
- 🔄 Half-wave rectifiers allow current to flow through the load during only the positive half-cycle of the AC input signal.
- 🔋 Full-wave rectifiers use two diodes and allow current to flow during both the positive and negative half-cycles of the AC input.
- 📉 Half-wave rectifiers have lower efficiency and produce a higher ripple in the output DC signal compared to full-wave rectifiers.
- 💡 Full-wave rectifiers produce a smoother DC output with lower ripple and are more efficient than half-wave rectifiers.
- 🏭 Bridge rectifiers, a type of full-wave rectifier, use four diodes to provide an even more efficient and smoother DC output.
- 🔌 The choice between half-wave and full-wave rectifiers depends on the power requirements of the application, with half-wave used for low power and full-wave for medium to high power.
- ⚡ Ripple is the fluctuation in the DC output voltage that occurs due to the rectification process and can be reduced using filters.
- 🔌 Capacitors are often used as filters in rectifiers to reduce ripple and provide a more stable DC output.
- 🛠️ Practical applications of rectifiers include charging batteries and powering various electronic devices found in homes and other settings.
Q & A
What is a rectifier in electronics?
-A rectifier is an electronic circuit that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), which is essential in various electronic devices.
What are the two main types of rectifiers mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of rectifiers mentioned are half-wave rectifiers and full-wave rectifiers.
How does a half-wave rectifier work?
-A half-wave rectifier allows current to flow only during half of the sinusoidal cycle, specifically during the positive half. During the negative half, the diode is off, and no current flows.
What is the efficiency of a half-wave rectifier?
-The efficiency of a half-wave rectifier is quite low because it only uses half of the sinusoidal wave cycle to produce current.
Why does the half-wave rectifier produce a high ripple?
-The half-wave rectifier produces a high ripple because it only passes the positive half of the sinusoidal cycle, resulting in a DC output with significant fluctuations.
What is the primary application of half-wave rectifiers?
-Half-wave rectifiers are typically used in low-power applications such as battery charging and small power supplies.
How does a full-wave rectifier differ from a half-wave rectifier?
-A full-wave rectifier uses two diodes to allow current to flow during both the positive and negative halves of the sinusoidal cycle, resulting in a smoother and more efficient DC output.
What is the advantage of a full-wave rectifier over a half-wave rectifier?
-A full-wave rectifier is more efficient than a half-wave rectifier because it uses both halves of the sinusoidal wave to produce a DC output with lower ripple and smoother characteristics.
What is a bridge rectifier?
-A bridge rectifier is an improved version of the full-wave rectifier that uses four diodes to deliver current during both halves of the sinusoidal wave, making it more efficient and producing an even smoother DC output.
What is the purpose of a capacitor in a rectifier circuit?
-A capacitor in a rectifier circuit is used as a filter to reduce ripple in the DC output by storing energy during the positive half-cycle and releasing it during the negative half-cycle, resulting in a smoother DC current.
How does the capacitance of a capacitor affect the rectifier's output?
-The capacitance of a capacitor determines how much energy can be stored and released, which in turn affects the smoothness and stability of the DC output voltage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)