Sensorimotor Part 4
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the motor system, detailing the three types of muscles: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. It explains how muscle contractions occur through neuromuscular junctions, with acetylcholine playing a crucial role. The concept of antagonistic muscles is introduced, highlighting the coordination between flexors and extensors. Proprioceptors, such as muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs, monitor muscle tension and initiate reflexes like the knee-jerk response. Finally, the video discusses motor programs and central pattern generators that control sequences of movement, illustrating the complexity and efficiency of our motor functions.
Takeaways
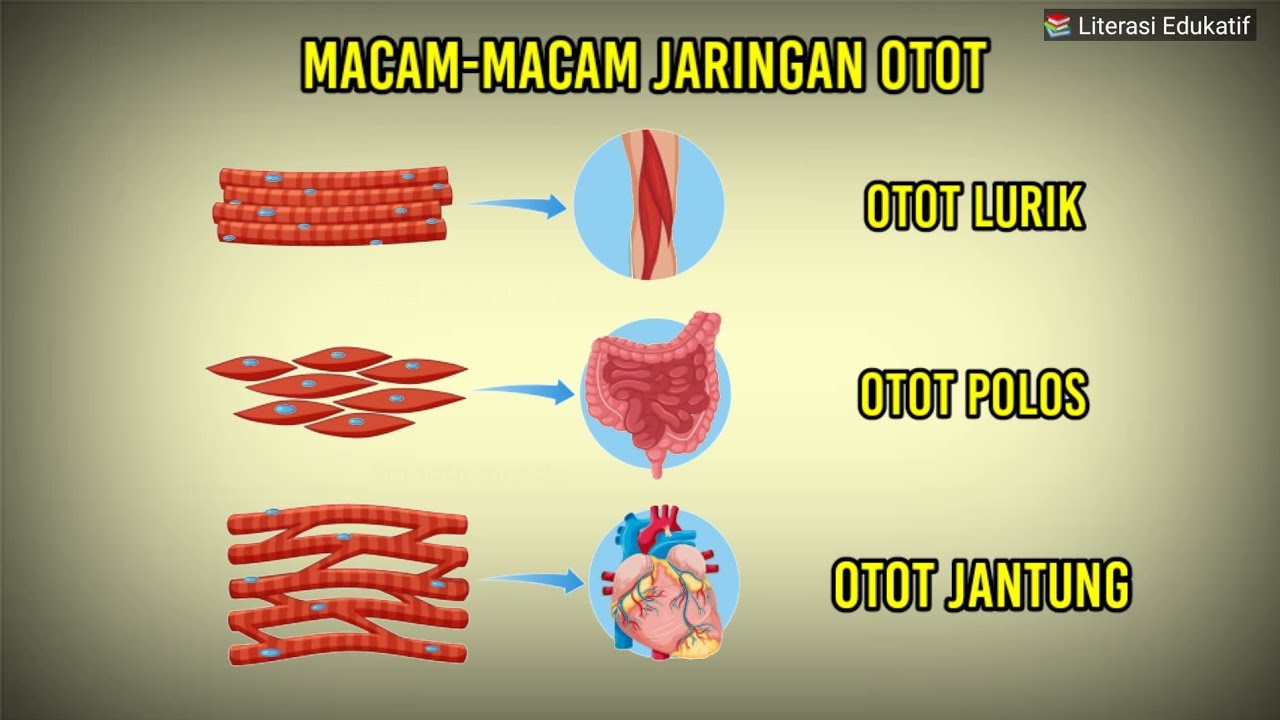
- 😀 Vertebrates have three types of muscles: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac.
- 😀 Smooth muscles control internal organs, while skeletal muscles facilitate body movement.
- 😀 Cardiac muscles are unique to the heart and contract in a synchronized manner.
- 😀 Each skeletal muscle fiber is connected to a single motor neuron, but one neuron can connect to multiple fibers.
- 😀 The neuromuscular junction is where motor neurons release acetylcholine to trigger muscle contraction.
- 😀 Antagonistic muscles work in pairs: when one set contracts, the other relaxes.
- 😀 Proprioceptors, like muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs, provide feedback on muscle tension and stretch.
- 😀 The stretch reflex is an automatic response that helps maintain posture and balance.
- 😀 Reflexes are fast and automatic, while voluntary movements are slower and can be adjusted.
- 😀 Central pattern generators in the spinal cord enable rhythmic movement sequences.
Q & A
What are the three types of muscles found in vertebrates?
-The three types of muscles in vertebrates are smooth muscles, skeletal (or striated) muscles, and cardiac muscles.
What is the function of smooth muscles?
-Smooth muscles control the digestive system and other internal organs.
How do skeletal muscles contribute to movement?
-Skeletal muscles control body movement when interacting with the surrounding environment.
What characterizes cardiac muscles?
-Cardiac muscles control the heart and have properties similar to both skeletal and smooth muscles.
What is a neuromuscular junction?
-A neuromuscular junction is the synapse between the axon of a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
What role does acetylcholine play in muscle contraction?
-Acetylcholine is released by motor neuron axons at neuromuscular junctions to trigger muscle contraction.
What are antagonistic muscles?
-Antagonistic muscles are pairs of muscles that work in opposition, such as flexor and extensor muscles.
What are proprioceptors, and what is their function?
-Proprioceptors are specialized receptors that detect the position and movement of body parts, including muscle stretch and tension.
What happens during a stretch reflex?
-In a stretch reflex, muscle spindles detect stretching and send signals to motor neurons, resulting in a reflexive muscle contraction.
What are central pattern generators?
-Central pattern generators are neural mechanisms in the spinal cord that execute rhythmic patterns of movement.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Muscle Tissue | Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth
APA BEDANYA OTOT LURIK OTOT POLOS DAN OTOT JANTUNG?

How your muscular system works - Emma Bryce

Types of Tissue Part 3: Muscle Tissue

Three Types of Muscle Tissue (Skeletal, Smooth, Cardiac) Anatomy Compilation Review

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Sistem Gerak Manusia (PART 2) | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
