RANGKAIAN LISTRIK : 1.1 Konsep Arus (Additional)
Summary
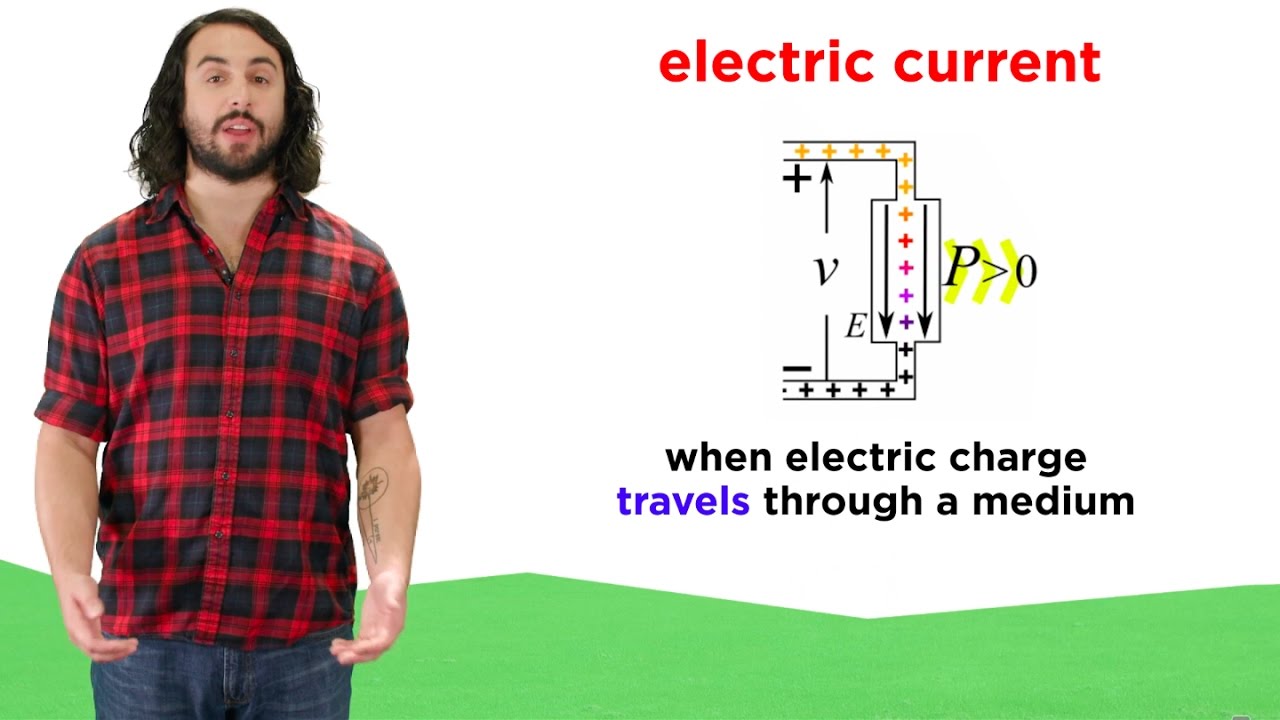
TLDRThe video lecture introduces the basics of electric current, explaining its definition as the flow of electric charge, denoted by the symbol 'i' and measured in amperes. It highlights the importance of understanding charge movement and the distinction between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). AC changes direction and is commonly used in homes, while DC flows in one direction and powers electronic devices. The lecture also touches on voltage, charge types, and the conventional direction of current flow, emphasizing that a solid grasp of these concepts is essential for further studies in electrical circuits.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electric current is defined as the flow of electric charge over time, represented by the symbol 'I'.
- 🔌 The mathematical formula for current is I = ΔQ/Δt, where ΔQ is the change in charge and Δt is the change in time.
- ⚡ The unit of electric current is the Ampere (A), which measures how much charge passes through a conductor in one second.
- 🚦 Current only exists when charges are in motion; if charges are static, there is no current.
- 🔄 Electric current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal in conventional current flow.
- 🔋 There are two types of electric current: Alternating Current (AC), which changes direction, and Direct Current (DC), which flows in one direction.
- 🏡 AC is commonly used in household electricity, while DC is typically found in battery-powered devices.
- 📈 AC can be graphically represented as a waveform, showing its alternating nature, while DC maintains a constant polarity.
- 🔧 Voltage, the potential difference, is crucial for driving current flow in a circuit.
- 🔍 Understanding the basic structure of atoms and how charges interact is essential for grasping concepts of electric current.
Q & A
What is electric current symbolized by?
-Electric current is symbolized by the letter 'i'.
How is electric current mathematically defined?
-Electric current is defined as the change in charge (Q) per unit time (t), expressed as i = dQ/dt.
What is the unit of measurement for electric current?
-The unit of measurement for electric current is the ampere (A).
What happens to electric current when charge is stationary?
-When charge is stationary, the electric current ceases to exist.
Can you explain the flow of electric current in a circuit?
-Electric current flows from the positive terminal through the load and returns to the negative terminal, creating a continuous circuit.
What are the two types of electric charge mentioned?
-The two types of electric charge mentioned are positive charge and negative charge.
What is the difference between the flow of conventional current and electron flow?
-Conventional current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, while electron flow is in the opposite direction, from negative to positive.
What are the two types of electric current discussed?
-The two types of electric current discussed are alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC).
What characterizes alternating current (AC)?
-Alternating current (AC) is characterized by its ability to change direction, having both positive and negative polarities.
In what devices is direct current (DC) commonly found?
-Direct current (DC) is commonly found in electronic devices, where a power supply is used to convert AC to DC for consistent polarity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Arus Listrik (Rumus Kuat Arus Listrik - Contoh Soal Kuat Arus Listrik)

Current | Electricity | Physics | FuseSchool

Introduction to circuits and Ohm's law | Circuits | Physics | Khan Academy
Electric Potential, Current, and Resistance

O que é corrente elétrica?

repost pembelajaran listrik Dinamis @ABSains
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
