vid 2
Summary
TLDRNiels Bohr, a Danish physicist and Nobel laureate, revolutionized atomic theory with his model of quantized electron orbits. He demonstrated that electrons occupy stable, discrete energy levels around the nucleus, allowing for energy absorption and emission during transitions between orbits. Bohr's experiments with gas discharge tubes revealed that atomic spectra are discontinuous, challenging classical theories. Although his model accurately explained hydrogen's spectrum, it struggled with more complex atoms and elliptical orbits. Bohr's work laid the foundation for modern quantum mechanics, significantly enhancing our understanding of atomic structure and the behavior of electrons.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Niels Bohr was a Danish physicist who made fundamental contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory.
- 🏆 He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922 for his work.
- ⚛️ Bohr's theory built upon Maxwell's physics, stating that negatively charged particles (electrons) orbit a positively charged nucleus.
- 📉 Electrons accelerate and spiral towards the nucleus, eventually leading to their collapse into the nucleus, which contradicts physical laws.
- 🌌 Bohr utilized a spectrometer to observe gas discharge, noting that electron collisions with gas emit light.
- 🌈 The emitted light can be broken down into discrete spectral lines, indicating that atomic spectra are quantized.
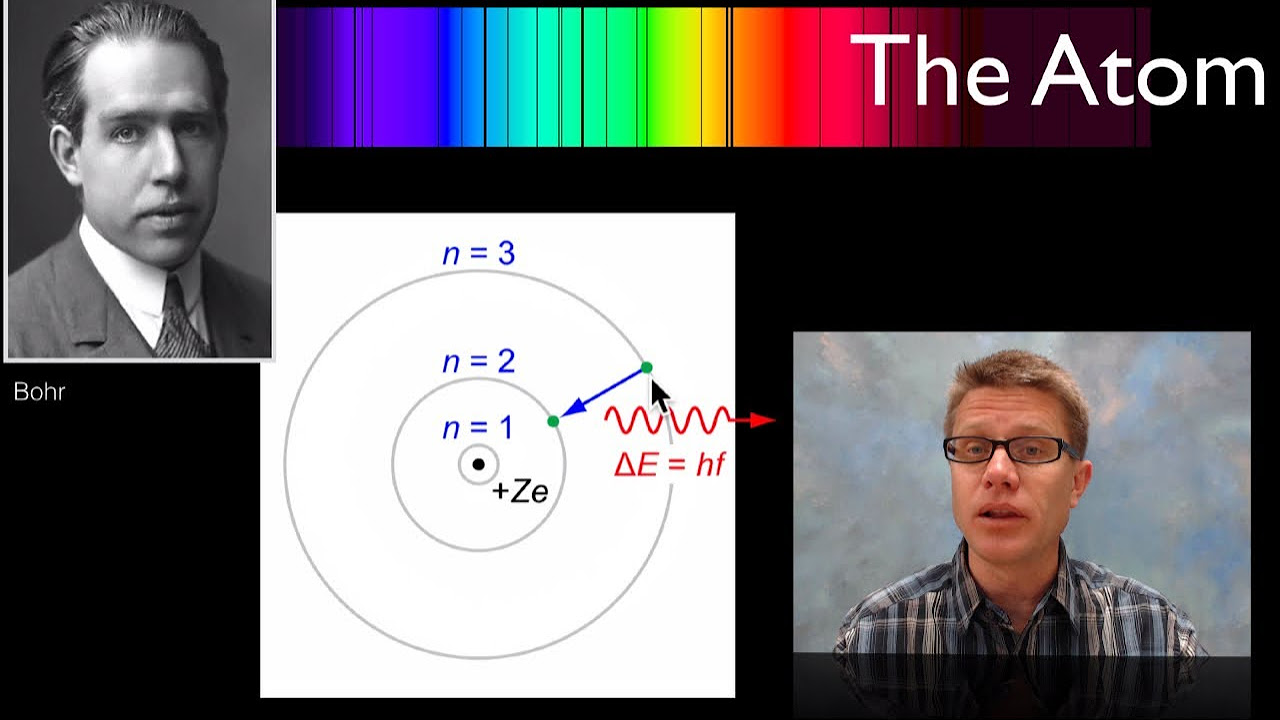
- 📏 Bohr proposed that electrons occupy specific stationary orbits or shells around the nucleus.
- 🔄 Electrons can move between orbits by absorbing or releasing energy, resulting in spectral lines.
- ⚠️ Bohr's model has limitations, as it accurately explains the hydrogen spectrum but fails for more complex atoms.
- 🌀 The assumption of circular orbits is not entirely accurate, as elliptical orbits are possible, and it doesn't explain fine spectral lines.
Q & A
Who is Niels Bohr and what is his contribution to physics?
-Niels Bohr was a physicist from Denmark who made fundamental contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and quantum theory. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
What does Maxwell's theory state regarding charged particles?
-Maxwell's theory states that if a negatively charged particle, such as an electron, orbits a positively charged nucleus, it will experience acceleration, causing the radius of its path to decrease and leading to a spiral trajectory.
Why do electrons not spiral into the nucleus despite Maxwell's theory?
-Electrons do not spiral into the nucleus because atoms are stable. This contradicts the predictions of classical physics, leading to the rejection of the spiral model.
What experimental setup did Bohr use to observe atomic behavior?
-Bohr used a spectrometer to observe a discharge tube filled with gas. When voltage was applied, electrons collided with the gas, causing the emission of light.
What are the spectral lines produced in Bohr's experiment?
-The light emitted by the atoms was analyzed using a prism, resulting in focused colors corresponding to specific wavelengths, creating discrete spectral lines.
What does the discrete spectrum of light emitted by atoms indicate?
-The discrete spectrum indicates that atoms emit light at specific wavelengths rather than a continuous spectrum, suggesting that electrons do not orbit the nucleus in spiral paths.
What are Bohr's first postulates regarding electron orbits?
-Bohr postulated that each electron in an atom orbits the nucleus in a defined stationary orbit or shell, and that electrons can transition between orbits by absorbing or emitting energy.
What limitations does Bohr's theory have?
-Bohr's theory can accurately explain the spectrum of hydrogen but fails for more complex atoms. It also inaccurately assumes that electron orbits are circular, neglecting elliptical orbits.
How does Bohr's theory relate to the dual nature of electrons?
-Bohr's theory considered electrons primarily as particles, but it later led to an understanding of their dual nature as both particles and waves, which is crucial for more advanced atomic theories.
What is the significance of Bohr's model in the context of atomic physics?
-Bohr's model was pivotal in the development of atomic physics, providing a foundation for quantum mechanics and influencing future theories on atomic structure and behavior.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
The Bohr Atom

Kuantum 2.5 Model Atom Bohr [Part 1]

What is the Bohr model of the atom?

SEJARAH PERKEMBANGAN TEORI ATOM

The Bohr Model of the atom and Atomic Emission Spectra: Atomic Structure tutorial | Crash Chemistry

Struktur Atom - Perkembangan Model Atom Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Mekanika Kuantum -Kimia X
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
