Konsep Dasar Kategorisasi Skor
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses data categorization in statistics, emphasizing the distinction between discrete and continuous data. It highlights that continuous data offers a broader range of information, while discrete data is limited to countable values. The importance of detailed categorization for better insights is underscored, suggesting that using continuous data provides a more accurate representation of real-life complexities. Examples illustrate how simplification can lead to unfair evaluations, and the speaker advocates for capturing richer, more detailed data rather than relying on broad categories.
Takeaways
- 📊 Data is defined as facts and figures collected for specific purposes, primarily for analysis.
- 🔍 The quality of data significantly affects the success of problem-solving efforts.
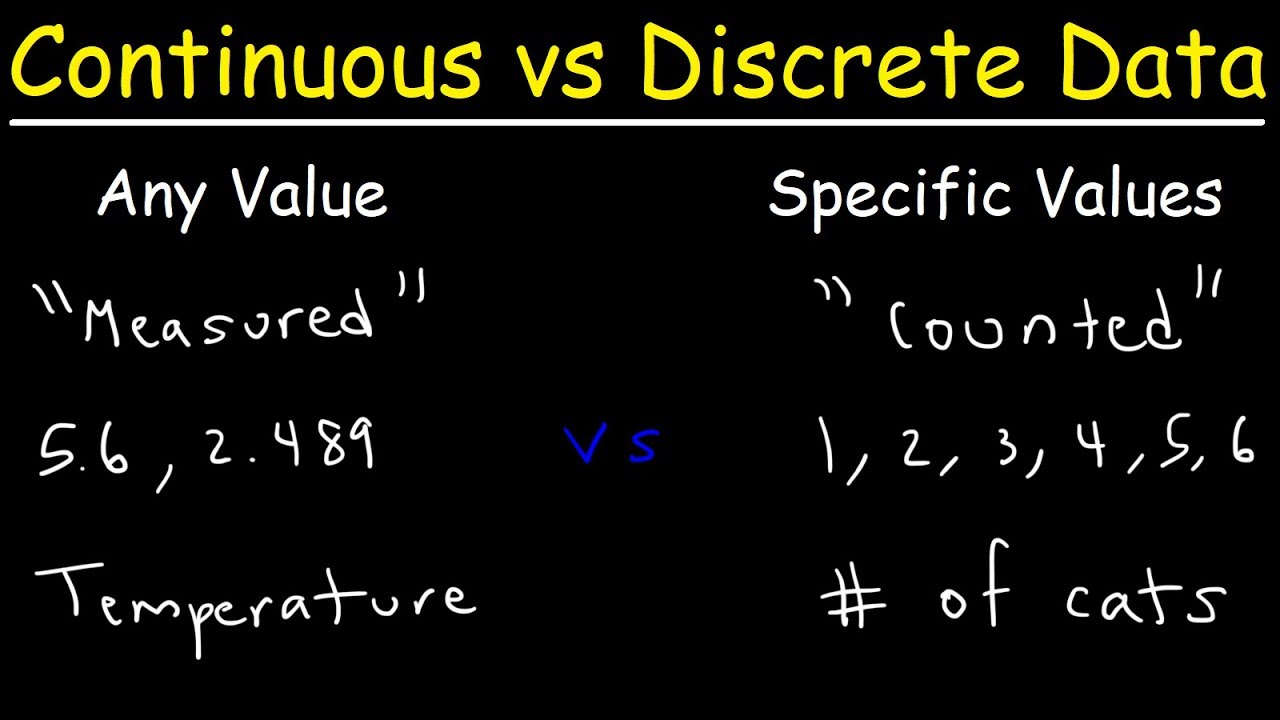
- 📈 Continuous data has an infinite range and can take any value, allowing for detailed measurement.
- 📉 Discrete data consists of distinct, separate values that can only be counted, limiting its detail.
- 🔗 Continuous data is often represented by smooth lines, while discrete data is shown as distinct points.
- ⚖️ Simplifying complex data into discrete categories can lead to unfair representations and loss of valuable insights.
- 📋 Collecting data in more detailed, continuous forms provides richer information for analysis.
- 🌈 Continuous data reflects the complexity and variety of real-life experiences, whereas discrete data oversimplifies them.
- 🔎 It is advisable to avoid unnecessary categorization, as it diminishes the richness of the data.
- 📅 Gathering specific details, such as exact age or education duration, yields better analytical outcomes than using broad categories.
Q & A
What is the definition of data in statistics according to the transcript?
-Data in statistics is defined as facts and figures that are collected together for a specific purpose, such as data analysis to solve problems.
How does the quality of data impact problem-solving?
-The success of problem-solving depends on the quality of the data, which can be assessed through various criteria including its continuity.
What are the two types of data mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of data mentioned are discrete data and continuous data.
How is continuous data characterized?
-Continuous data has a long range and unlimited values, consisting of a series of observations that can take any numeric value within a precise range.
What are some examples of continuous data provided in the transcript?
-Examples of continuous data include measurements such as weight and age.
What distinguishes discrete data from continuous data?
-Discrete data refers to quantitative data that relies on counts and consists of limited values that cannot be broken down into fractions or decimals.
What is the implication of categorizing data into discrete forms?
-Categorizing data into discrete forms simplifies complexity but may lead to unfair representations of data, as it can overlook the natural continuum of information.
How does the transcript suggest improving the quality of collected data?
-The transcript suggests obtaining data in a more natural form by seeking continuous values rather than discrete categories for a richer understanding.
What example is given for evaluating student performance?
-An example given is the use of IPK or GPA as a simplified measure of student performance, which could mask the finer nuances of their academic achievements.
Why should categorization of data be avoided unless necessary?
-Categorization should be avoided unless absolutely necessary because it can lead to loss of variation and richness in the data, reducing the depth of insights.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)