Praktikum Fisiologi - Spirometri
Summary
TLDRIn this instructional video, viewers are introduced to the spirometer, a vital tool for measuring lung function and respiratory health. Demonstrated at Andalas University, the process includes setting up the device and conducting spirometry tests to record vital capacity, tidal volume, and forced expiratory volume. The speaker explains the significance of each measurement while providing a step-by-step guide on proper usage, including inhalation and exhalation techniques. With a focus on practical application, the video aims to enhance understanding of pulmonary function assessment, making it an informative resource for medical students and health professionals.
Takeaways
- 😀 Spirometry is a crucial test for assessing lung function by measuring the volume and speed of air inhaled and exhaled.
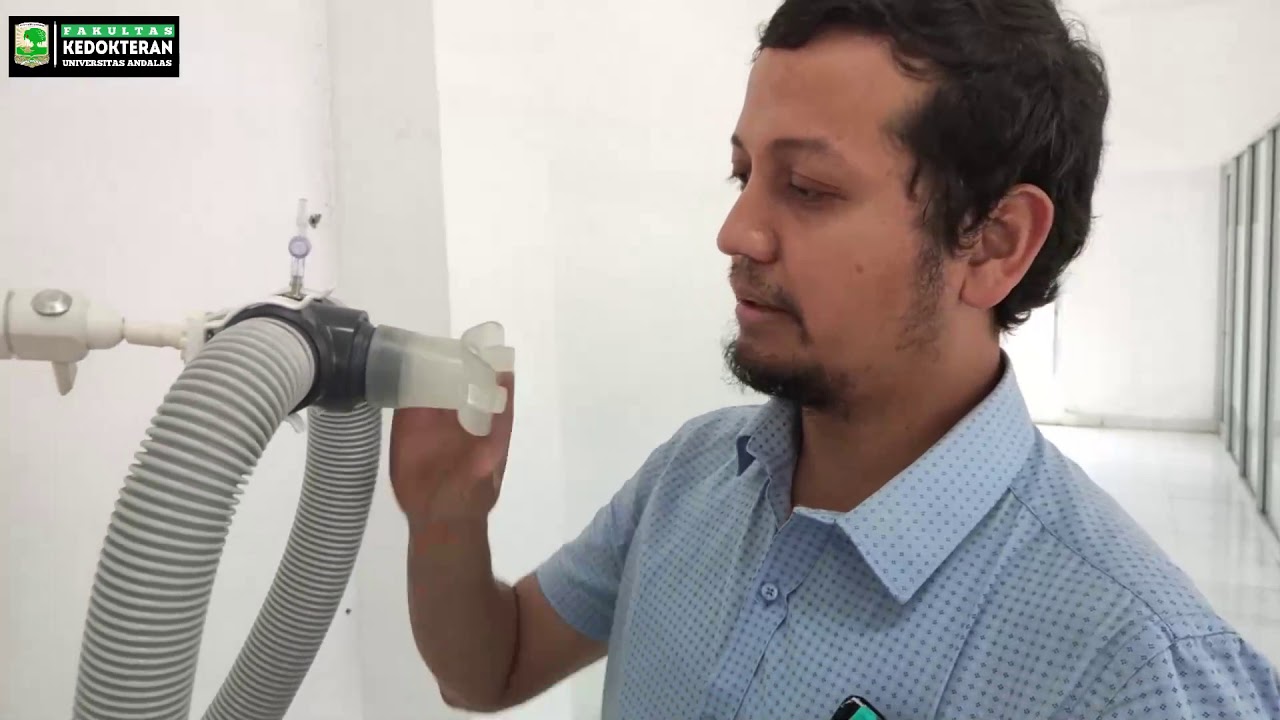
- 🛠️ The Benedict respirometer is a key tool used in spirometry, featuring an oxygen chamber and a floating drum for recording measurements.
- 🌊 Water is essential in the spirometer to allow the floating drum to move freely, enabling accurate recordings.
- 🌬️ The measurement process involves various breathing techniques, starting with normal breaths followed by deep inhalations and forceful exhalations.
- 📊 The resulting spirogram shows fluctuations in air volume, which are recorded to assess lung capacity and function.
- 🔍 Key lung volumes measured include Tidal Volume (TV), Vital Capacity (VC), and Residual Volume (RV).
- 📏 Tidal Volume represents the amount of air exchanged during normal breathing, while Vital Capacity measures the maximum air exhaled after full inhalation.
- 📉 Residual Volume is the air left in the lungs after exhalation, which cannot be measured directly by spirometry.
- 🚀 Accurate spirometry results are vital for diagnosing respiratory conditions and monitoring lung health over time.
- 🙏 The presentation emphasizes the significance of spirometry in healthcare and its role in evaluating respiratory function.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of using a spirometer?
-The main purpose of using a spirometer is to measure lung function and assess respiratory health by tracking the volume of air inhaled and exhaled.
How does the Benedict Respirometer work?
-The Benedict Respirometer works by using a floating drum connected to an oxygen chamber. As the person breathes in and out, the drum moves up and down, and this movement is recorded on paper by a pen, producing a spirogram.
What are the key components of the spirometer?
-The key components of the spirometer include the oxygen chamber, a floating drum, a pen for recording, and a system for adjusting the pen's speed.
What are the steps involved in the spirometry test?
-The steps involve preparing the spirometer, adjusting settings like pen speed, ensuring the drum is filled with water, performing normal breathing, followed by deep breaths, and forced inhalation and exhalation to record lung volume.
What does the spirometer measure during normal breathing?
-During normal breathing, the spirometer measures the tidal volume, which is the amount of air breathed in and out during regular respiration.
What is meant by Vital Capacity in spirometry?
-Vital Capacity is the maximum amount of air a person can exhale after taking the deepest possible breath. It is a key indicator of lung function.
What is the significance of Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1)?
-Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1) is the volume of air exhaled in the first second of a forced exhalation. It is an important measure for assessing lung health and function.
What are the components of lung volume that cannot be measured by spirometry?
-The residual volume, which is the air remaining in the lungs after a forceful exhalation, cannot be measured by spirometry.
How is the total lung capacity calculated?
-Total lung capacity is calculated by adding the Vital Capacity and the Residual Volume, although the Residual Volume cannot be directly measured with a spirometer.
What is the role of the water in the spirometer?
-The water in the spirometer is necessary to allow the floating drum to move smoothly with the inhalation and exhalation of air, ensuring accurate measurement.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)