LED light Emitting Diode (Unit 3 Special purpose diode and Transistors) in हिन्दी
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), focusing on their construction, operation, and practical applications. It explains how LEDs convert electrical energy into light energy through a PN junction, emphasizing the importance of forward bias for functionality. The video details the processes involved in creating N-type and P-type semiconductors, as well as the mechanisms of electron excitation and light emission. Additionally, it warns against reverse bias, which can damage LEDs. Overall, the video offers a comprehensive overview of LED technology, making it accessible for beginners in basic electronics.
Takeaways
- 😀 LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) convert electrical energy into light energy, commonly used in decorations and displays.
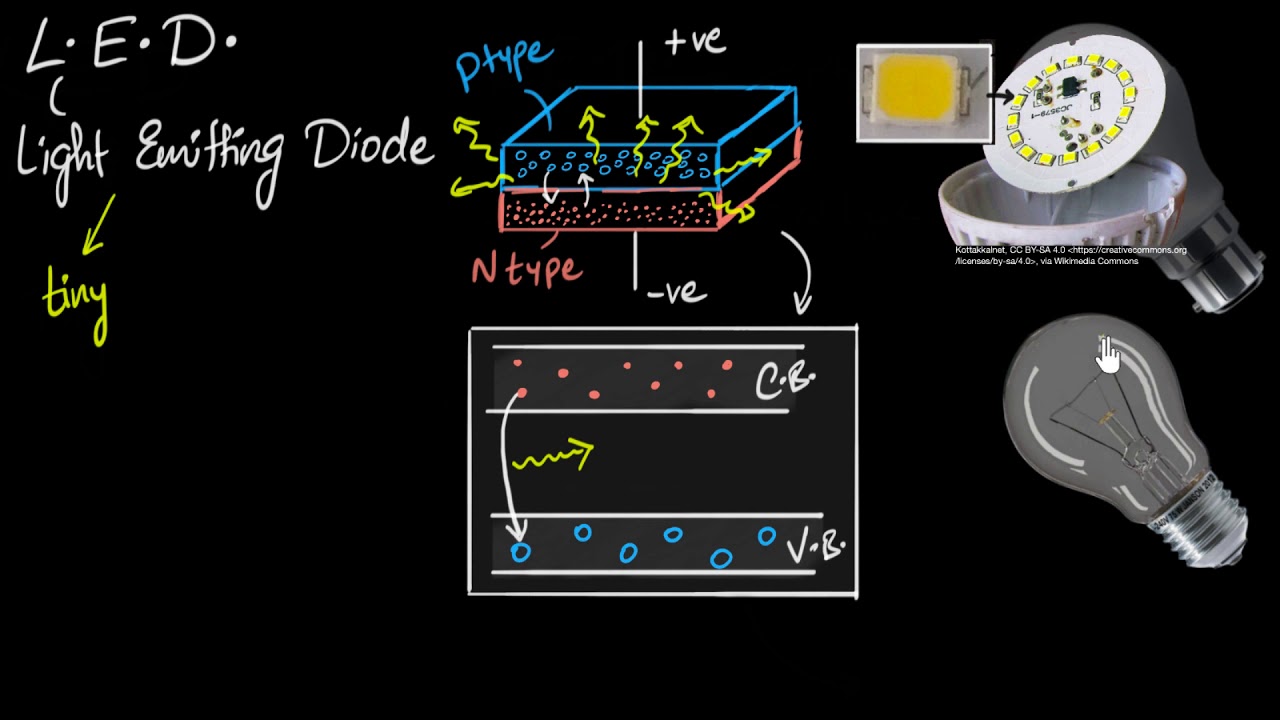
- 📚 An LED operates on the principle of a PN junction diode and requires forward biasing to function properly.
- ⚡ The positive terminal of a battery connects to the P-type semiconductor, while the negative terminal connects to the N-type semiconductor for correct operation.
- 🔋 When forward-biased, electrons and holes combine, creating a depletion layer that allows current to flow.
- 🔍 N-type semiconductors are created by mixing pentavalent impurities like phosphorus with silicon, while P-type semiconductors use trivalent impurities like aluminum.
- 💡 When electrons gain energy, they can jump to a higher energy level and, upon returning to a lower level, emit light (photons).
- 🌌 The recombination process between electrons and holes releases energy in the form of light, making LEDs efficient light sources.
- 🚫 Reversing the bias on an LED can damage it due to increased potential barriers and excessive current flow.
- 📊 The safe operation of LEDs requires understanding their forward biasing and the consequences of reverse biasing.
- 🛠️ In summary, LEDs are efficient light sources that operate effectively when correctly biased and can be damaged if reverse-biased.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the transcript?
-The main topic is about Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), focusing on their construction, working principle, and applications.
How do LEDs convert electrical energy into light energy?
-LEDs convert electrical energy into light energy by using a process where electrons recombine with holes in a semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons, which produce light.
What is a PN junction diode, and why is it important for LEDs?
-A PN junction diode consists of p-type and n-type semiconductors. It is crucial for LEDs because it creates the necessary conditions for the recombination of electrons and holes, enabling light emission.
What is the role of forward bias in the operation of LEDs?
-Forward bias allows current to flow through the LED, enabling the recombination of electrons and holes, which leads to light emission. LEDs operate effectively only under forward bias.
What happens if an LED is connected in reverse bias?
-When an LED is connected in reverse bias, it can cause damage because the potential barrier increases, which can lead to excessive current flow and potentially destroy the LED.
What is the depletion layer in a PN junction, and how does it affect LED operation?
-The depletion layer is an area within the PN junction where mobile charge carriers (electrons and holes) are depleted. It creates a potential barrier that influences the flow of current and is essential for the LED's operation under forward bias.
Can you explain the significance of doping in semiconductors for LEDs?
-Doping introduces impurities into semiconductor materials, allowing the formation of p-type and n-type semiconductors. This is essential for creating the junctions needed for LED operation.
What is the energy level transition in an LED, and why is it important?
-The energy level transition occurs when electrons absorb energy and jump to a higher energy level, then release energy as they return to a lower level, emitting light. This transition is fundamental for the light-emitting process in LEDs.
What types of impurities are used to create p-type and n-type semiconductors?
-P-type semiconductors are created using trivalent impurities like aluminum, while n-type semiconductors use pentavalent impurities like phosphorus. These impurities control the conductivity of the semiconductor.
Why is it important to operate LEDs under specified conditions to prevent damage?
-Operating LEDs under specified conditions, particularly avoiding reverse bias and excessive current, is essential to prevent overheating and potential destruction of the diode, ensuring longevity and proper functionality.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

What is LED Light Emitting Diode | How Does LED Works | Electronic Devices & Circuits | Engineering

How LED Works - Unravel the Mysteries of How LEDs Work!

Prinsip Kerja dan Fungsi LED
LED working & advantages | Semiconductors | Physics | Khan Academy

Light Emitting Diode (LED) Explained (Working, Advantages and Types of LED Explained)

Diodos: o guia básico para entender de forma fácil
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
