Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (4 of 31) What is Conductance?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of conductance, which is the ability of an element to conduct electrical current. Conductance is the inverse of resistance, meaning lower resistance results in higher conductance, and vice versa. The unit of conductance is the siemens (S), and it is defined as 1 ampere per volt. The video further discusses how conductance relates to Ohm's Law, where G = 1/R, and how it can be used in calculating power dissipation in a circuit. Different equations involving conductance, resistance, and power are explored to deepen understanding.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Conductance is the ability of an element to conduct electrical current.
- 🔄 Conductance is the inverse of resistance. Higher resistance means lower conductance and vice versa.
- 📏 Conductance is measured in units of Siemens (S), which is equivalent to 1 ampere per volt.
- 🔄 The symbol for conductance is derived from the Ohm symbol, reversed, and it can also be called a mho.
- 📐 Ohm's Law is key to understanding conductance, as it relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R).
- 💡 Conductance (G) is defined as 1/R, meaning it represents how much current can flow per unit voltage.
- ⚡ Power dissipation can be expressed in multiple ways using conductance, such as P = I²/G.
- 🧩 When voltage and current are known, conductance can be calculated as G = I/V.
- 🔋 The power dissipation equations can be rewritten in terms of conductance for different circuit analysis approaches.
- 📊 Overall, understanding conductance helps analyze circuit behavior, especially how easily current flows.
Q & A
What is conductance?
-Conductance is the ability of an element to conduct electrical current. The more current it allows to flow through, the higher the conductance.
How is conductance defined in relation to resistance?
-Conductance is defined as the inverse of resistance. The lower the resistance, the higher the conductance.
What is the unit of conductance?
-The unit of conductance is the Siemens (symbolized as S), and 1 Siemens is equal to 1 ampere per volt.
What is the symbol for the unit of conductance in the script?
-The symbol for the unit of conductance in the script is 'mho', which is the ohm symbol upside down.
How is the relationship between current (I), voltage (V), and resistance (R) expressed in Ohm's law?
-Ohm's law is expressed as I = V/R, which means the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them.
How can conductance (G) be expressed using Ohm's law?
-Using Ohm's law, conductance (G) can be expressed as G = 1/R. Since G is the inverse of resistance, it can also be written as G = I/V.
What is the power dissipation equation in terms of conductance?
-The power dissipation equation in terms of conductance is P = I^2 * R. However, since G = I/V, power can also be expressed as P = G * V^2.
How can power dissipation be related to conductance and voltage?
-Power dissipation can be related to conductance and voltage by the equation P = G * V^2, showing that power is directly proportional to the square of the voltage and the conductance.
What does it mean when it's said that 'conductance is the inverse of resistance'?
-It means that as resistance decreases, conductance increases, and vice versa. They are inversely proportional to each other.
How does the script describe the relationship between power, current, and conductance?
-The script describes that power (P) is equal to the product of current (I) and voltage (V), and since G = I/V, power can also be expressed as P = G * V^2, showing that power is directly proportional to the square of the voltage and the conductance.
What is the significance of the mho as a unit of conductance?
-The mho, being the inverse of the ohm, signifies the reciprocal relationship between resistance and conductance, making it a convenient unit for expressing conductance.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Electrical Conductivity of Different Materials | Electrical4U

Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (15 of 31) Conductance in a Parallel Circuit

Listrik Dinamis "Arus Listrik & Hantaran Listrik"
What is CURRENT– electric current explained, electricity basics

Circuit Lab 1: Circuit Basics
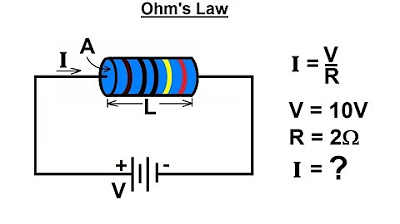
Electrical Engineering: Basic Laws (2 of 31) Ohm's Law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
