Overview of the Strategic Planning Process
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Erica Olsen outlines the strategic planning process through four key phases: Assess, Design, Build, and Manage. The process begins by assessing the current state through SWOT analysis. Next, it moves into designing the strategy by defining the mission, vision, competitive advantages, and strategic objectives. The plan is built with SMART goals and cascaded through all organizational levels. Finally, effective execution requires individual accountability, performance tracking systems, and regular reviews. The video emphasizes the importance of turning plans into actionable strategies for organizational success.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The strategic planning process consists of four phases: Assess, Design, Build, and Manage.
- 📝 Strategic plans are dynamic, involving periodic reviews and revisions if execution is not delivering desired results.
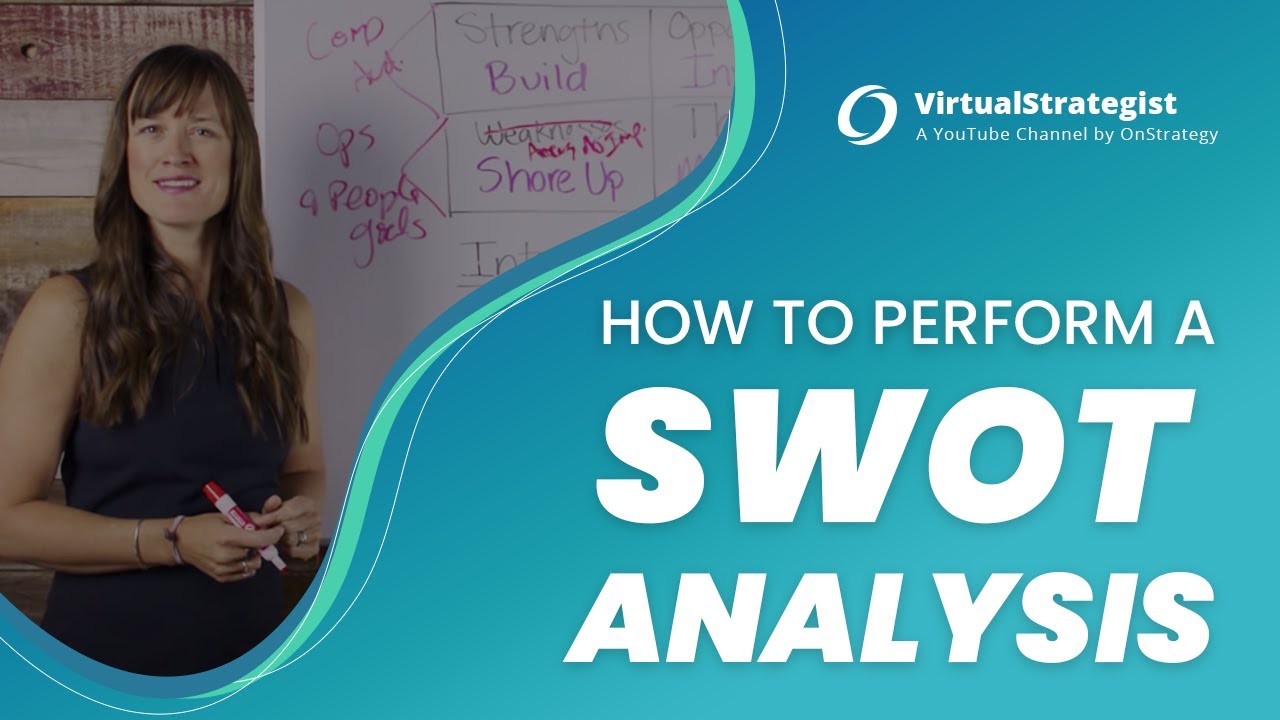
- 📊 Assessing the current state (Point A) involves gathering external (opportunities and threats) and internal (strengths and weaknesses) perspectives and summarizing them in a SWOT analysis.
- 🏢 The mission statement is crucial to defining the organization’s core purpose, specifying what's in and what's out.
- 🌟 The vision statement defines the future state and provides a roadmap for where the organization wants to go.
- 💼 Competitive advantages and long-term strategies guide the plan and ensure the organization remains competitive.
- 🔗 The strategic framework consists of long-term objectives in four areas: financial, customer, operational/internal, and people perspectives.
- 🎯 Corporate goals should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-bound) and cascaded from strategic objectives down to individual contributors.
- 👥 Effective execution requires three key elements: individual ownership/action plans, a system for tracking and managing performance, and regular performance reviews.
- 📆 Monthly or quarterly reviews are essential to ensure ongoing performance management and execution of the plan.
Q & A
What are the four phases of the strategic planning process mentioned in the video?
-The four phases are Assess, Design, Build, and Manage.
Why is it important to assess the current state before designing a strategy?
-Assessing the current state helps to understand where the organization stands today by gathering external and internal perspectives, which is essential for making informed strategic decisions.
What tool does the speaker suggest using to summarize external and internal perspectives?
-The speaker suggests using a SWOT analysis to summarize opportunities, threats, strengths, and weaknesses.
How does a mission statement help in the strategic planning process?
-A mission statement clarifies an organization's core purpose and defines what is in and out of scope for the organization, guiding its actions and priorities.
What role does the vision statement play in strategic planning?
-The vision statement defines the organization's future state, guiding it from where it is today (Point A) to where it wants to be in the future (Point B).
What are competitive advantages and why are they important in the strategy design phase?
-Competitive advantages are key factors that help an organization succeed and differentiate itself from competitors. They act as an umbrella over the strategic plan to ensure the organization remains competitive.
Why does the speaker suggest using fewer than six long-term strategic objectives in the framework?
-Fewer than six objectives help create a focused and holistic framework, ensuring the plan addresses key areas without overwhelming the organization.
What does SMART stand for, and why is it important when setting corporate goals?
-SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, and Time-Bound. It ensures that corporate goals are clear, quantifiable, and achievable within a specified timeframe.
How does cascading goals through different organizational levels improve plan execution?
-Cascading goals from corporate to department and then to individual levels ensures alignment across the organization, with each person understanding their role in achieving the broader strategic objectives.
What are the three key elements required for effective execution of a strategic plan?
-The three key elements are: 1) ensuring people have individual action plans, 2) using a system to track and manage performance, and 3) conducting regular performance reviews.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)