Grade 8 Science Q1 Ep 10
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script, hosted by Teacher MJ, delves into the fundamentals of electricity, focusing on the concepts of electric current, voltage, and resistance. It explains how electricity powers everyday devices and uses Ohm's Law to demonstrate the relationship between these electrical components. The script is interactive, featuring quizzes to test viewers' understanding and practical examples to illustrate the principles discussed.
Takeaways
- 🔌 **Electric Current**: The rate of flow of electric charges in a circuit, measured in amperes.
- 💡 **Voltage**: The driving force that pushes electrons, measured in volts, and is the difference in electrical potential energy per unit of charge.
- 🛠️ **Electrical Resistance**: The opposition to the flow of electric charges through a conductor, measured in ohms.
- 🔗 **Ohm's Law**: States that the electric current is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
- 🔋 **Sources of Voltage**: Batteries and generators are primary sources of electric current in a circuit.
- 🔄 **Charge Flow**: Free electrons flow in conducting wires when connected to a voltage source.
- 🌡️ **Conductivity and Temperature**: Higher temperatures increase resistance due to more collisions against the flow of current.
- 🏗️ **Factors Affecting Resistance**: Wire thickness, length, material conductivity, and temperature affect electrical resistance.
- 📉 **Impact of Resistance on Current**: Increasing resistance at constant voltage decreases the current flow.
- 📈 **Impact of Voltage on Current**: Increasing voltage at constant resistance increases the current flow.
- 🔍 **Understanding Ohm's Law**: Ohm's Law is fundamental for calculating current, voltage, and resistance in electrical circuits.
Q & A
What causes an electric current to flow in a conductor?
-An electric current flows in a conductor due to the movement of free electrons when there is a difference in electric potential (voltage) across the conductor.
What is the relationship between electric current, voltage, and resistance?
-According to Ohm's Law, the electric current (I) in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the resistance (R), represented by the formula: V = I * R.
How is electric current measured, and what is its SI unit?
-Electric current is measured as the rate of flow of electric charges, and its SI unit is the ampere (A), which represents one coulomb of charge passing through a wire per second.
What factors affect the electrical resistance of a conducting wire?
-The electrical resistance of a conducting wire depends on its thickness, length, material (conductivity), and temperature. Thicker, shorter wires with high conductivity materials like copper offer less resistance.
What happens to the current if the voltage is increased while resistance remains constant?
-If the voltage is increased while the resistance remains constant, the current will increase proportionally according to Ohm's Law.
What is voltage, and how does it affect electric current?
-Voltage is the potential difference that drives the movement of electric charges, creating an electric current. Higher voltage means a stronger force pushing the electrons, which increases the current.
What is the SI unit of voltage, and how is voltage mathematically expressed?
-The SI unit of voltage is the volt (V). Mathematically, voltage is expressed as V = W/Q, where V is voltage, W is the work done in joules, and Q is the charge in coulombs.
How does the temperature affect the electrical resistance of a conductor?
-As temperature increases, the atoms in the conductor vibrate more vigorously, causing more collisions with the free electrons, which increases the resistance.
What is the formula used to calculate electrical resistance?
-The formula to calculate electrical resistance is R = V / I, where R represents resistance (in ohms), V represents voltage (in volts), and I represents current (in amperes).
What happens to the current if the resistance is tripled, assuming the voltage remains constant?
-If the resistance is tripled while the voltage remains constant, the current will be reduced to one-third of its original value.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 3 (Rangkaian Hambatan Seri dan Paralel)

KELISTRIKAN PART 2 : LISTRIK DINAMIS (IPA KELAS 9 SMP)

Qual a diferença entre volt, watt e ampere? #ManualMaker Aula 2, Vídeo 1

Hukum Ohm (Ohm's Law) - Konsep Tegangan (V), Kuat Arus (I), Hambatan (R)
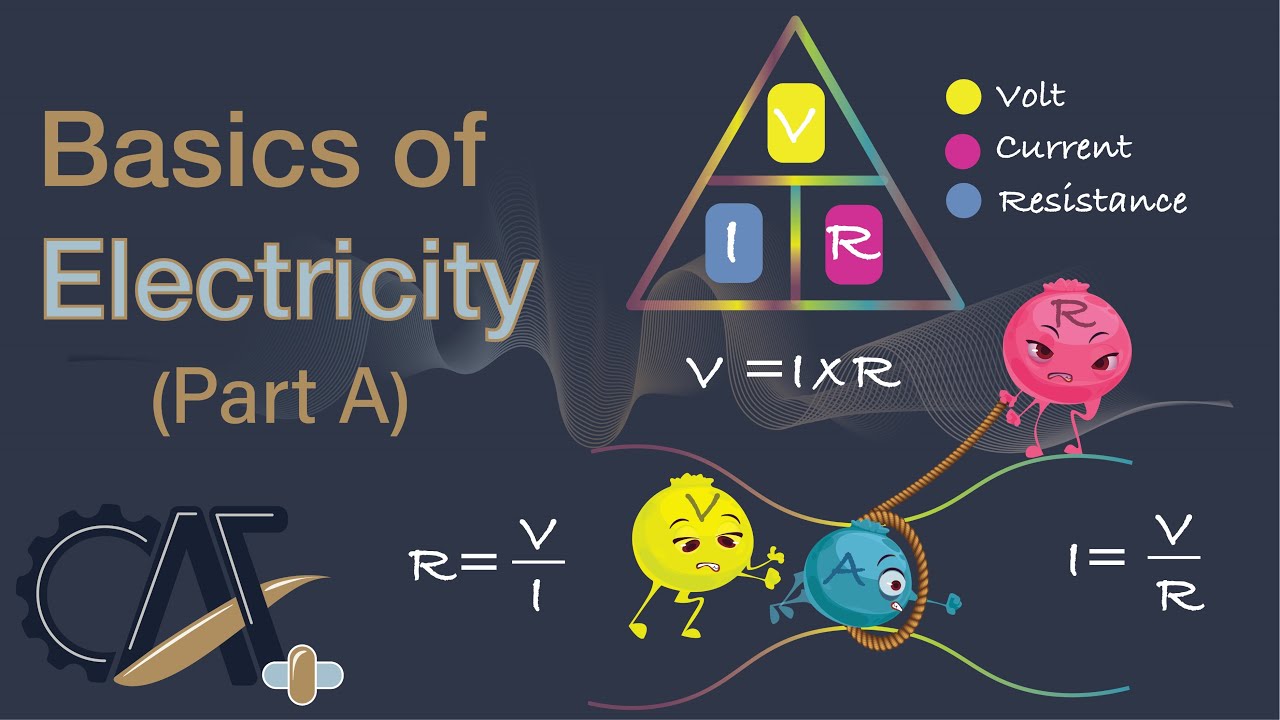
Basics of Electricity-Part A [Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law]

Electricity | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 5 Part 1 Voltage, Current, Resistance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
