Instantaneous speed and velocity | One-dimensional motion | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe script narrates a physics student's journey home to watch a 'Star Wars' marathon, using it as a metaphor to explain concepts of motion in physics. It distinguishes between instantaneous speed and velocity, highlighting the importance of direction. The student's varying speeds are used to illustrate these points. The script further clarifies the difference between average and instantaneous velocity, using examples and analogies. It also touches on the historical difficulty of defining motion at a point, leading to the development of calculus by Newton. Practical ways to calculate instantaneous velocity without calculus are suggested, such as constant velocity scenarios, analyzing graphs, and using kinematic formulas for constant acceleration.
Takeaways
- 🏃♂️ A physics student runs home from class to catch a Star Wars marathon, illustrating the concept of instantaneous speed.
- 📏 Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at a specific moment in time.
- 🧭 Instantaneous velocity includes both speed and direction, like running '8 meters per second to the right'.
- 🏠 The student's journey home involves varying speeds, demonstrating the difference between instantaneous and average velocity.
- 📊 Average velocity is calculated by dividing total displacement by total time, which is not necessarily equal to instantaneous velocities at specific points.
- 🔍 To find instantaneous velocity at a specific point, consider smaller displacements over shorter time intervals.
- 🤔 Ancient Greeks questioned the existence of motion due to the difficulty in defining instantaneous velocity.
- 📐 Sir Isaac Newton's invention of calculus provided a method to calculate instantaneous velocity.
- 📚 Calculus is used in physics to find instantaneous velocity, but the instructor offers alternative methods for those who haven't studied calculus yet.
- 📈 The slope of a position-versus-time graph at any point equals the instantaneous velocity at that time.
- 🔄 In cases of constant acceleration, the Kinematic Formulas can be used to calculate instantaneous velocity at any time.
Q & A
What is the difference between instantaneous speed and average speed?
-Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at a particular moment in time, whereas average speed is the total displacement divided by the total time taken over a period of time.
How is instantaneous velocity different from instantaneous speed?
-Instantaneous velocity includes both the speed and direction of an object at a specific moment in time, while instantaneous speed only refers to the magnitude of the velocity without considering direction.
Why is it challenging to find the instantaneous velocity at a particular point in time?
-Finding the instantaneous velocity at a particular point is challenging because it requires considering an infinitesimally-small displacement divided by an infinitesimally-small time interval, which mathematically results in zero divided by zero.
What did ancient Greeks question about motion due to the difficulty in defining it at a particular point in time?
-Ancient Greeks questioned whether motion had any meaning at all, and some even wondered if motion was just an illusion.
Who developed a new way to do math that helps in understanding motion at a particular point in time?
-Sir Isaac Newton developed a new way to do math called calculus that helps in understanding motion at a particular point in time.
What is the formula for instantaneous velocity according to a physicist?
-The formula for instantaneous velocity often involves calculus, which can be used to calculate the derivative of position with respect to time.
If the velocity of an object doesn't change, what can you use to find the instantaneous velocity?
-If the velocity is constant, the formula for average velocity can be used to find the instantaneous velocity at any point in time since they will be the same.
How can you find the instantaneous velocity by looking at an x-versus-t graph?
-On an x-versus-t graph, the slope at any particular point represents the instantaneous velocity at that point in time, as the slope gives the rate of change of position with respect to time.
What is a special case where the acceleration is constant, and how can it be used to find instantaneous velocity?
-When acceleration is constant, the Kinematic Formulas can be used to find the instantaneous velocity at any time, t.
How does the concept of instantaneous velocity relate to the story of the physics student running home to watch the Star Wars marathon?
-The physics student's varying speeds (6 m/s, 2 m/s, and 8 m/s) illustrate the concept of instantaneous velocity, showing how it changes at different moments during the student's journey home.
What is the average velocity of the physics student if it took 200 seconds to travel 1,000 meters?
-The average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time, which in this case is 1,000 meters / 200 seconds = 5 meters per second.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Gerak Lurus • Part 1: Gerak Lurus Beraturan (GLB) dan Gerak Lurus Berubah Beraturan (GLBB)

Cinemática no Cotidiano

PENDEKATAN PEMBELAJARAN MELALUI HUBUNGAN KETERKAITAN KONSEP FISIKA DALAM KEHIDUPAN NYATA
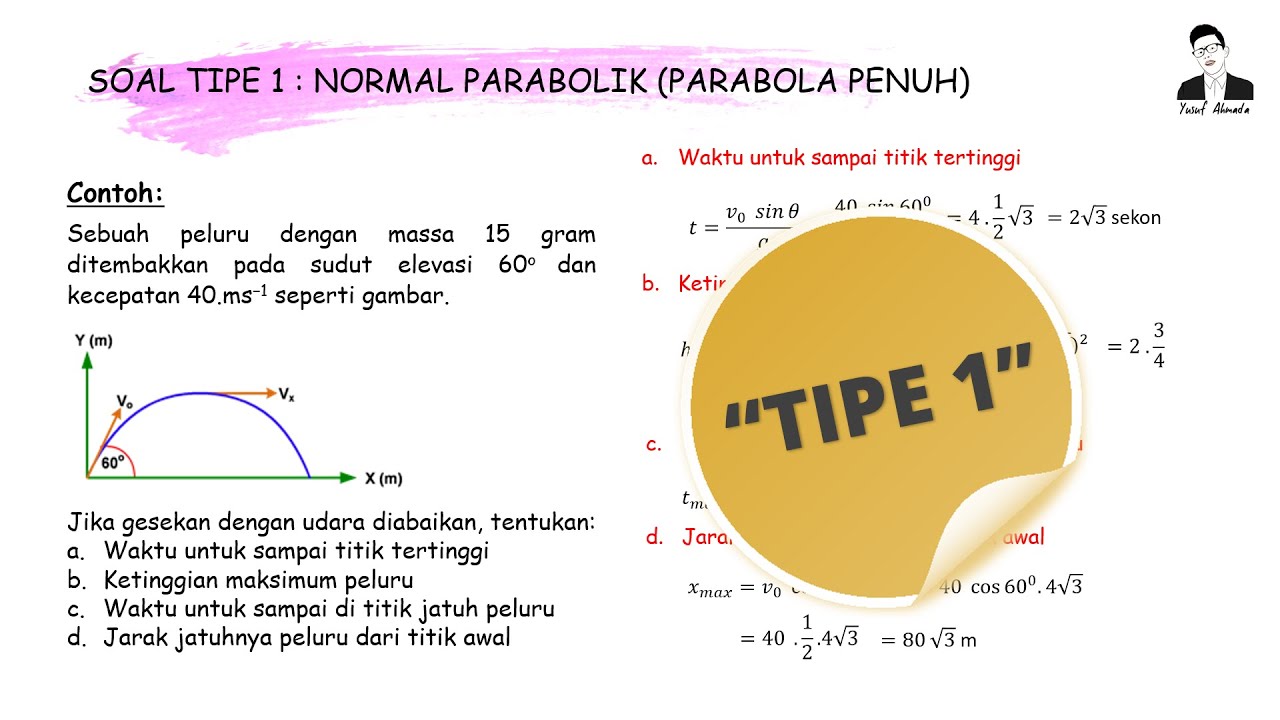
FISIKA KELAS X || CONTOH SOAL GERAK PARABOLA TIPE 1 (Parabola Penuh)

12th Physics | Chapter No 1 | Rotational Dynamics | Lecture 1 | JR Tutorials |

Two particles of masses m_1 and m_2 are tied to the ends of an elastic string of natural length a..
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
