Which DNA test is best? Whole Genome Sequencing, Whole Exome Sequencing, and Genotyping - EXPLAINED
Summary
TLDRThis video compares three DNA testing methods: whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, and genotyping. It discusses their coverage of the 3.2 billion base pair human genome, their processes, costs, and what they reveal. Whole genome sequencing covers everything, exome focuses on the 1.2% coding DNA, and genotyping checks a few hundred thousand spots. The video explains how these methods vary in effectiveness for ancestry tracing and specific mutation detection, concluding that whole genome sequencing offers the most comprehensive and future-proof data.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The human genome is 3.2 billion base pairs long, with 1.2% being coding DNA that codes for proteins.
- 🔍 Non-coding DNA plays a crucial role in gene regulation and DNA folding, affecting gene accessibility.
- 🌐 Whole genome sequencing covers the entire genome, while whole exome sequencing focuses on the coding parts, and genotyping checks a few hundred thousand locations.
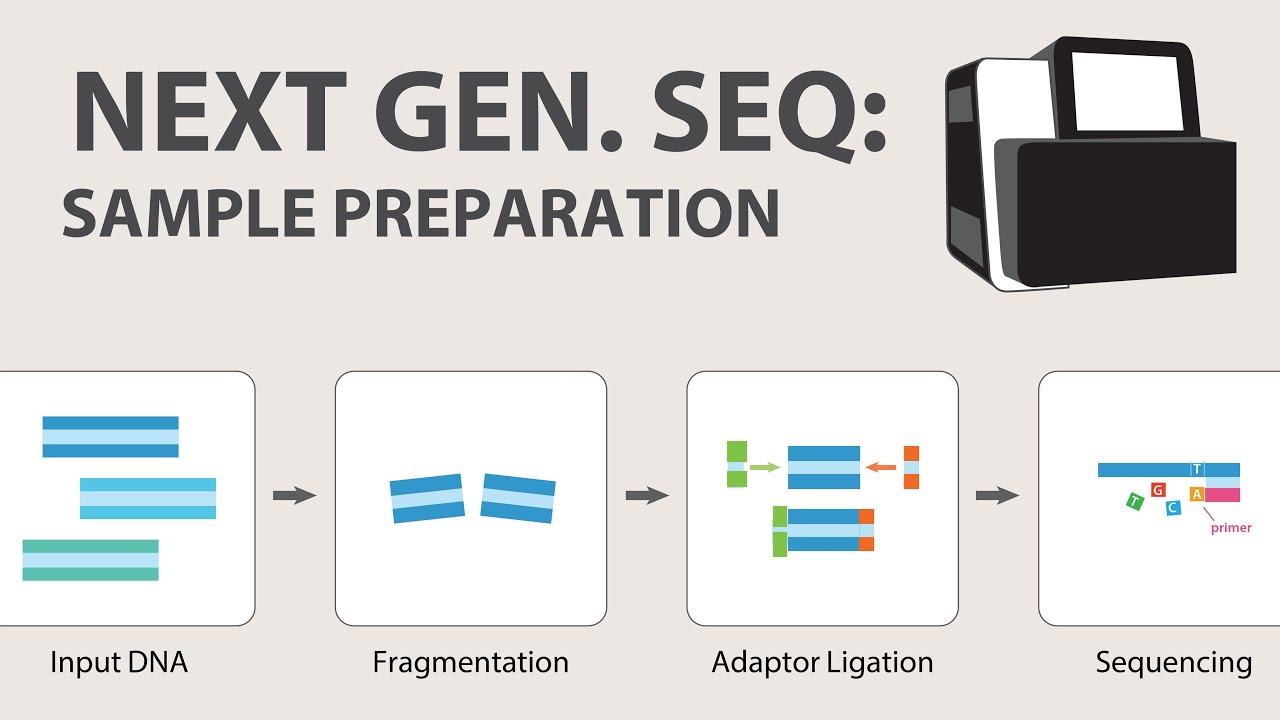
- 💡 Whole genome sequencing and whole exome sequencing have similar processes, involving DNA isolation and sequencing, whereas genotyping uses microarrays to detect specific DNA sequences.
- 🔑 Genotyping arrays are designed to test for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which are common genetic variations among individuals.
- 💰 The cost of these tests varies with whole genome sequencing being the most expensive, followed by whole exome sequencing, and genotyping being the least.
- 🌐 For ancestry tracing, whole genome sequencing provides the most data, making it the most accurate, followed by whole exome sequencing and then genotyping.
- 🧐 If you're looking for a specific mutation, genotyping could suffice if that mutation is included on the microarray.
- 🚫 Genotyping has limitations as it may not detect new mutations associated with conditions like breast cancer that are discovered after the test is taken.
- 🌟 Whole genome sequencing provides the most comprehensive data, including every variant compared to the average human (VCF file), the entire genome sequence (BAM file), and raw sequencing data for future analysis.
- 💼 The presenter recommends whole genome sequencing for its timelessness and the ability to leverage future genomic discoveries with the preserved data.
Q & A
What are the three methods for checking a person's DNA mentioned in the video?
-The three methods mentioned are whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, and genotyping.
What percentage of the human genome is coding DNA?
-Coding DNA makes up 1.2 percent of the human genome.
How much of the genome does whole genome sequencing cover?
-Whole genome sequencing covers the entire genome, which is 3.2 billion base pairs.
What is the difference between coding and non-coding DNA?
-Coding DNA sequences are responsible for protein production, while non-coding DNA sits between coding sequences and plays a role in gene regulation and DNA folding.
How does genotyping differ from whole genome sequencing and whole exome sequencing?
-Genotyping uses a microarray to test for specific single base variations (SNPs) rather than sequencing DNA base by base.
What is the approximate cost for whole genome sequencing?
-The cost for whole genome sequencing is around a thousand dollars.
How many base pairs does whole exome sequencing cover?
-Whole exome sequencing covers about 1.2% of the genome, or approximately 38 million base pairs.
What is a SNP and why are they important in genotyping?
-A SNP is a single base at a particular location in the genome that differs among people. They are important in genotyping because they can indicate genetic variations that may be associated with certain traits or diseases.
Why might genotyping for ancestry be inaccurate?
-Genotyping for ancestry can be inaccurate because it only considers a small number of variants, whereas ancestry is complex and involves many common variations across populations.
What is the advantage of whole genome sequencing over whole exome sequencing?
-Whole genome sequencing provides a complete list of every single variant in a person's genome, including both coding and non-coding DNA, which allows for the most comprehensive analysis and future discoveries.
Why is it recommended to keep the raw sequencing data from a whole genome sequencing test?
-It is recommended to keep the raw sequencing data because as new discoveries are made and software evolves, the data can be reanalyzed to provide new insights and applications throughout one's life.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)