Why Does Light Bend? | Concave & Convex Lenses | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explores the science of lenses, focusing on convex and concave lenses. It explains how lenses bend light through refraction and their effects: convergence for convex lenses, which focus light at a focal point, and divergence for concave lenses, which spread light away from a virtual focal point. The script also touches on focal length and its impact on image size, providing a fundamental understanding of these optical elements.
Takeaways
- 🔭 A lens is a transparent material, typically glass or plastic, with curved sides that can bend light as it passes through.
- 🌀 Refraction is the process by which light rays change direction as they pass from one medium to another, such as through a lens.
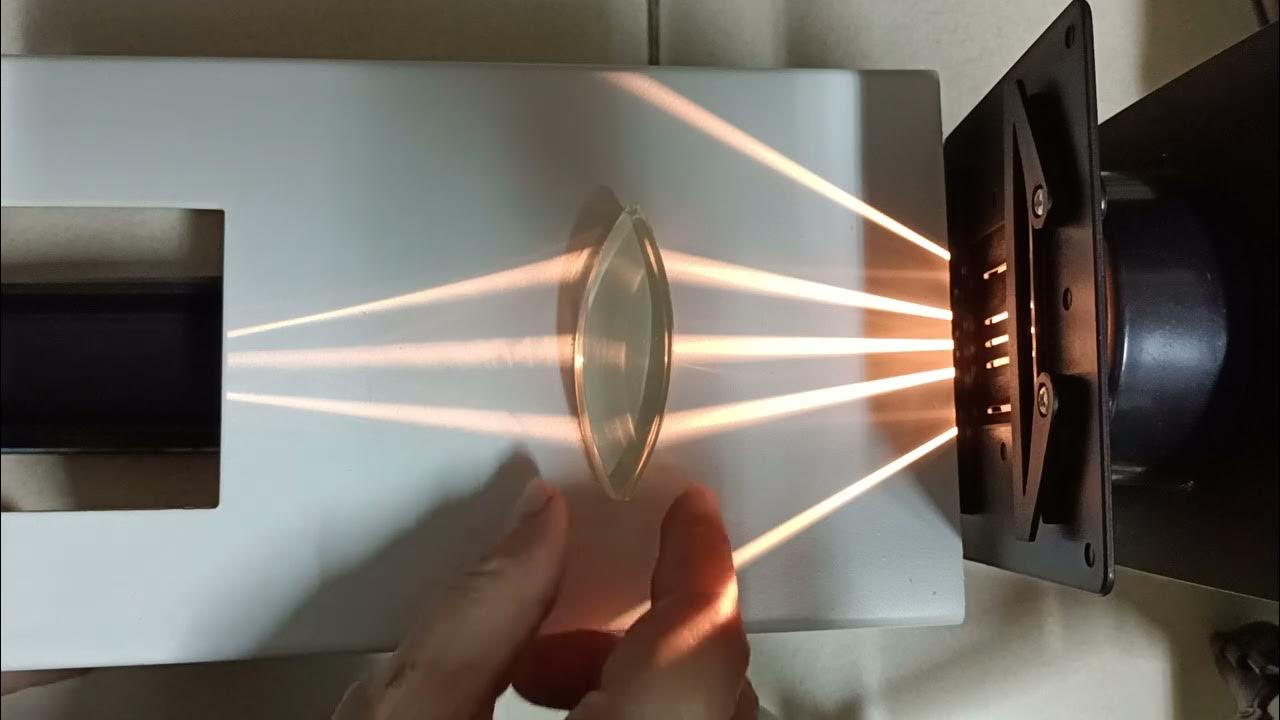
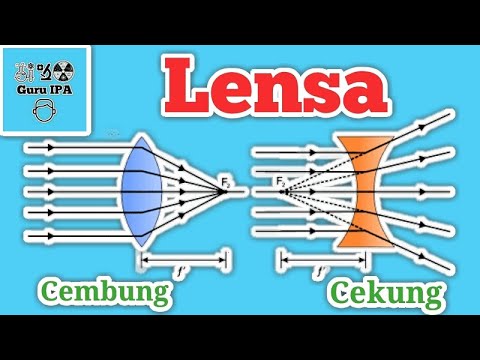
- 🔴 Convex lenses have two outwardly curved spherical surfaces and are thicker in the middle, causing light rays to converge at a focal point.
- 🔵 Concave lenses have surfaces that curve inwards and are thinner in the center, causing light rays to diverge after passing through.
- 🔼 The way light bends when passing through a lens depends on whether the lens is convex or concave, leading to convergence or divergence of light rays.
- 📏 The focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the focal point where light rays converge or appear to diverge.
- 🖼️ Convex lenses can focus light rays to form an image, which can be projected on a screen beyond the focal point.
- 🌐 Concave lenses do not form a real image but instead create a virtual image by making light rays appear to diverge from a point behind the lens.
- 🔎 The size of the image formed by a lens depends on the focal length of the lens and the distance between the lens and the object.
- 👓 Dr. Binox educates about lenses, emphasizing the importance of understanding how they work to appreciate the wonders of the universe.
Q & A
What is a lens?
-A lens is a transparent piece of glass or plastic with curved sides that can bend light rays as they pass through it, changing their direction. This process is known as refraction.
What are the two main types of lenses?
-The two main types of lenses are convex lenses and concave lenses.
How can you distinguish between a convex lens and a concave lens?
-In a convex lens, the two spherical surfaces are curved outwards and it is thicker in the middle with thinner edges. In contrast, a concave lens has surfaces curved inwards and is thinner in the center with thicker edges.
What is refraction and how does it relate to lenses?
-Refraction is the bending of light rays as they pass from one medium to another. In the context of lenses, it is the bending of light as it passes through the lens due to differences in the speed of light in different materials.
What happens to light when it passes through a convex lens?
-When light passes through a convex lens, it slows down and bends towards the normal line upon entering the lens, and then bends away from the normal line as it exits the lens, due to the change in medium density.
What is the term for the point where light rays converge after passing through a convex lens?
-The point where light rays converge after passing through a convex lens is called the focal point.
How does a concave lens affect light rays?
-A concave lens causes light rays to diverge, or spread out, rather than converging at a single point. Instead, the rays appear to come from a focal point behind the lens.
What is the focal length of a lens?
-The focal length of a lens is the distance from the center of the lens to the focal point.
How does the focal length affect the size of the image formed by a lens?
-The focal length, along with the distance between the lens and the object, determines whether the image formed will be smaller or larger than the original object.
What is the difference between a real image and a virtual image as formed by lenses?
-A real image is formed where actual light rays converge and can be projected onto a screen, typically formed by a convex lens. A virtual image is formed where the light rays appear to diverge from and cannot be projected onto a screen, typically formed by a concave lens.
Who is Dr. Binox and what is his role in the script?
-Dr. Binox is presumably the host or narrator of the educational video script, providing explanations and insights into the workings of lenses.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)