Maths Tutorial: Trigonometry SOH CAH TOA (trigonometric ratios)
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the use of trigonometric ratios—sine, cosine, and tangent—in solving right-angle triangle problems. It walks through how to correctly label triangle sides as hypotenuse, opposite, or adjacent based on the given angle. The mnemonic 'SOHCAHTOA' is used to recall the ratios: sine equals opposite over hypotenuse, cosine equals adjacent over hypotenuse, and tangent equals opposite over adjacent. The video also demonstrates examples where these ratios are applied to calculate unknown sides or angles using a calculator, emphasizing proper calculator settings.
Takeaways
- 📐 Trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan) are used to calculate unknown angles or sides in a right-angled triangle when enough information is provided.
- ⚠️ You must always ensure the triangle is a right-angled triangle before applying trigonometric ratios.
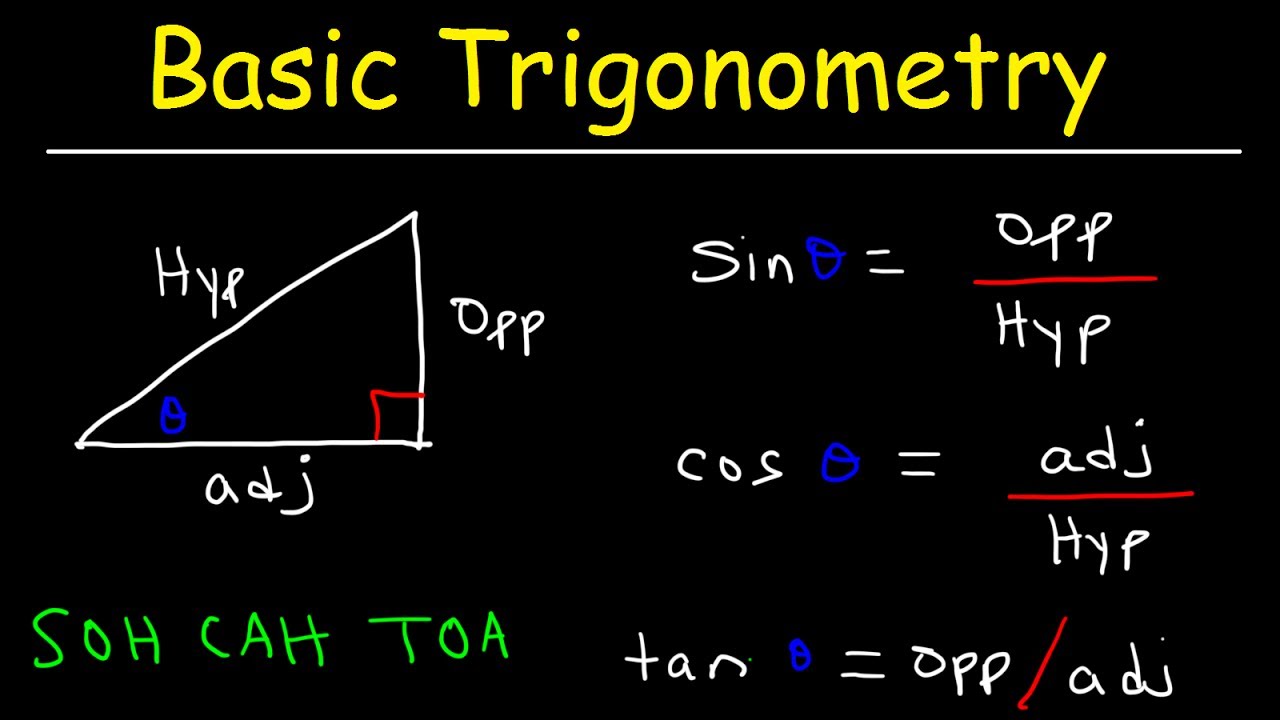
- ➕ The hypotenuse is always the longest side and opposite the right angle in a triangle.
- 🔄 Depending on the angle you are working with, the other two sides are labeled as opposite (opposite the angle) and adjacent (next to the angle).
- 🔢 SOHCAHTOA helps remember the trigonometric ratios: sin (opposite/hypotenuse), cos (adjacent/hypotenuse), and tan (opposite/adjacent).
- 🧮 To solve for unknown sides or angles, rearrange the trigonometric ratio formulas and use a calculator in degree mode.
- 📊 Example: Given an angle and hypotenuse, use the sine ratio to find the opposite side.
- 📏 Example: Use the cosine ratio when the adjacent and hypotenuse are involved in the calculation.
- 🔍 The inverse sine, cosine, or tangent function (sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹, tan⁻¹) is used to find the unknown angle when the sides are known.
- 📘 Real-world problem: Trigonometry can be applied to solve practical problems like calculating the angle and length of ropes anchoring a flagpole.
Q & A
What are the trigonometric ratios used for?
-Trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, and tangent) are used to calculate unknown angles or sides in a right-angle triangle, provided enough information about the triangle is given.
When can the trigonometric ratios not be applied?
-Trigonometric ratios cannot be applied if the triangle is not a right-angle triangle. You must have a right angle to use these ratios.
What is the hypotenuse in a triangle, and how do you identify it?
-The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angle triangle and is always opposite the right angle.
How do you label the opposite and adjacent sides in a right-angle triangle?
-The opposite side is the side directly opposite the angle of interest, while the adjacent side is the one next to the angle but not the hypotenuse.
What does the acronym SOHCAHTOA represent?
-SOHCAHTOA is a mnemonic to remember the trigonometric ratios: Sine (S) = Opposite/Hypotenuse, Cosine (C) = Adjacent/Hypotenuse, and Tangent (T) = Opposite/Adjacent.
How do you use the sine ratio to find a missing side of a triangle?
-To find a missing side using the sine ratio, use the formula Sin(θ) = Opposite/Hypotenuse. Rearrange to solve for the unknown side, then plug the known values into the equation.
How do you calculate a missing angle using the inverse trigonometric function?
-To find a missing angle, use the inverse sine, cosine, or tangent function. For example, if Sin(θ) = 3/5, use θ = Sin⁻¹(3/5) to calculate the angle.
What do you need to check before applying trigonometric ratios?
-Before applying trigonometric ratios, always check if the triangle has a right angle. Without a right angle, these ratios cannot be used.
How do you find the angle between a rope and the ground in a real-world scenario?
-To find the angle between a rope and the ground, you can treat the setup as a right-angle triangle and use the tangent ratio: Tan(θ) = Opposite/Adjacent. Use inverse tangent to find the angle.
How can the cosine ratio be used to solve for an unknown angle?
-To solve for an unknown angle using the cosine ratio, use Cos(θ) = Adjacent/Hypotenuse, rearrange to isolate θ, and then apply the inverse cosine function to find the angle.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Menentukan Nilai Trigonometri Segitiga Siku Siku Perbandingan Trigonometri segitiga Siku Siku

Identitas Trigonometri: Identitas Kebalikan, Perbandingan dan Pythagoras - SMA Kelas 10

TRIGONOMETRI - Ukuran Sudut dan Perbandingan Trigonometri

Perbandingan Trigonometri Pada Segitiga SIku-siku #Trigonometri

SOHCAHTOA using the TI-84 Plus
Trigonometry For Beginners!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
