SOHCAHTOA using the TI-84 Plus
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial introduces right triangle trigonometry, focusing on SOA (Sine, Cosine, Tangent) and TOA (Tangent). Mr. Bourne, a math teacher from Minnesota, explains how to use trigonometric ratios to solve problems involving right triangles. He covers setting a calculator to degrees mode, understanding triangle side relationships (opposite, adjacent, hypotenuse), and emphasizes the importance of recognizing right triangles for these methods. The tutorial is part one of a four-part series, promising further examples in subsequent episodes.
Takeaways
- 📚 This tutorial covers SOA TOA, a mnemonic for right triangle trigonometry.
- 👨🏫 Mr. Bourne, a math teacher from Minnesota, introduces the concept and its applications.
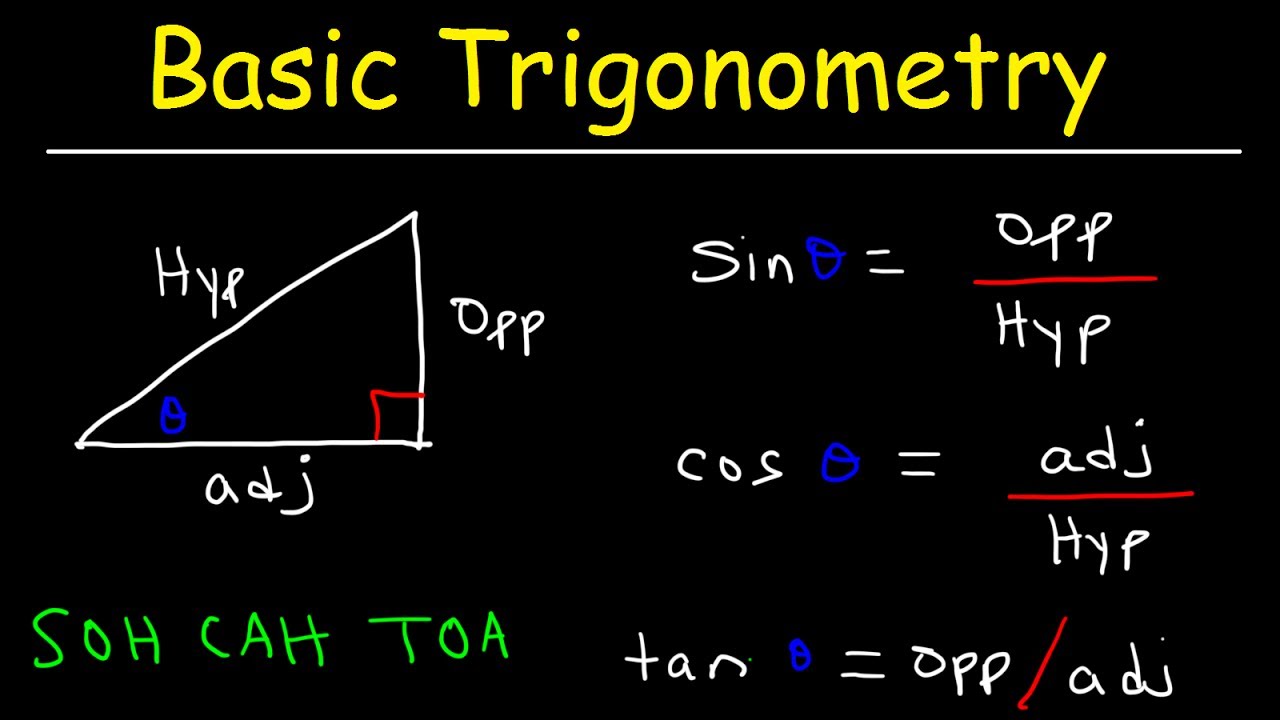
- 🔢 SOA stands for Sine = Opposite/Hypotenuse, Cosine = Adjacent/Hypotenuse, and Tangent = Opposite/Adjacent.
- 📐 The tutorial helps solve problems involving angles and sides of right triangles.
- 🛠️ It's crucial to set your calculator to degrees mode for these calculations.
- 📈 The tutorial will cover examples of using sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
- 🌐 Greek letters like Theta are sometimes used to represent angles, but they don't change the difficulty.
- 🚫 This method is only applicable to right triangles, not other types of triangles.
- 📉 The tutorial will show how to find angle measures given side lengths or how to find unknown sides given an angle measure.
- 🔄 The hypotenuse is always the longest side opposite the right angle, while opposite and adjacent sides change based on the angle in question.
- 📚 The tutorial is divided into four episodes, each focusing on different aspects of SOA TOA.
Q & A
What does SOA TOA stand for in trigonometry?
-SOA TOA is a mnemonic for remembering the trigonometric ratios in a right triangle. SOA stands for Sine, Opposite over Adjacent, and TOA stands for Tangent, Opposite over Adjacent.
What kind of problems can SOA TOA help solve?
-SOA TOA can help solve problems where you are given one side length and an angle of a right triangle and need to find another side length, or where you are given two side lengths and need to find an angle measure.
How do you set a calculator to degrees mode for trigonometry problems?
-For a TI-83 Plus or TI-84 Plus calculator, press the 'MODE' key, navigate to the third line down where it says 'Radian' and 'Degree', use the right arrow key to highlight 'Degree', and then press 'ENTER' to set the calculator to degrees mode.
What is the significance of the hypotenuse in a right triangle?
-The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle and is always opposite the right angle. It remains constant relative to the position of the angle being considered.
What is meant by the term 'adjacent' in the context of a right triangle?
-In a right triangle, the 'adjacent' side is the one that is next to the angle being considered and is not the hypotenuse.
How can you verify if your calculator is in degrees mode?
-You can verify if your calculator is in degrees mode by typing 'sin(90)'. If the calculator is in degrees mode, it should return 1.
Why is it important to know the difference between 'opposite' and 'adjacent' sides?
-Knowing the difference between 'opposite' and 'adjacent' sides is crucial for correctly applying trigonometric ratios like sine, cosine, and tangent to solve for unknown angles or side lengths in a right triangle.
What is the role of the mnemonic SOA TOA in solving trigonometry problems?
-The mnemonic SOA TOA helps in remembering the correct placement of sides relative to an angle in a right triangle when applying trigonometric functions, which is essential for solving problems involving unknown angles or sides.
Why might Greek letters be used in trigonometry problems?
-Greek letters like Theta (θ) might be used in trigonometry problems to represent unknown angles. This is a way to generalize the problem and does not make the problem more difficult, just a different way of referring to the angle.
What does the acronym SOA represent in the context of the sine function?
-In the context of the sine function, SOA stands for Sine, Opposite over Adjacent, which means the sine of an angle in a right triangle is equal to the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
How does the position of the angle affect the identification of 'opposite' and 'adjacent' sides?
-The position of the angle affects the identification of 'opposite' and 'adjacent' sides because these terms are relative to the angle being considered. The 'opposite' side is always the furthest from the angle, and the 'adjacent' side is the one next to the angle but not the hypotenuse.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
When Do I use Sin, Cos or Tan?

Menentukan Nilai Trigonometri Segitiga Siku Siku Perbandingan Trigonometri segitiga Siku Siku
Trigonometry For Beginners!

A-Level Maths: E5-01 [Trigonometric Identities: Proving tanθ = sinθ / cosθ]

Basic trigonometry II | Basic trigonometry | Trigonometry | Khan Academy

FÁCIL e RÁPIDO | ARCO DUPLO EM 9 MINUTOS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)