Proton Number, Nucleon Number & Isotope | SPKA
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the microscopic world, diving into the structure of atoms and their subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. It explains how atoms are mostly empty space and how their components are represented through isotope notation. The video also covers charged particles, isotopes, and their importance in fields such as archaeology and medicine, highlighting examples like carbon-14 and sodium-24. Viewers are invited to test their understanding of the concepts discussed, making the complex topic of atomic structure more accessible and engaging.
Takeaways
- 🔬 The tiniest particle that makes up everything in the universe is called an atom, derived from the Greek word 'atomos,' meaning 'cannot be cut.'
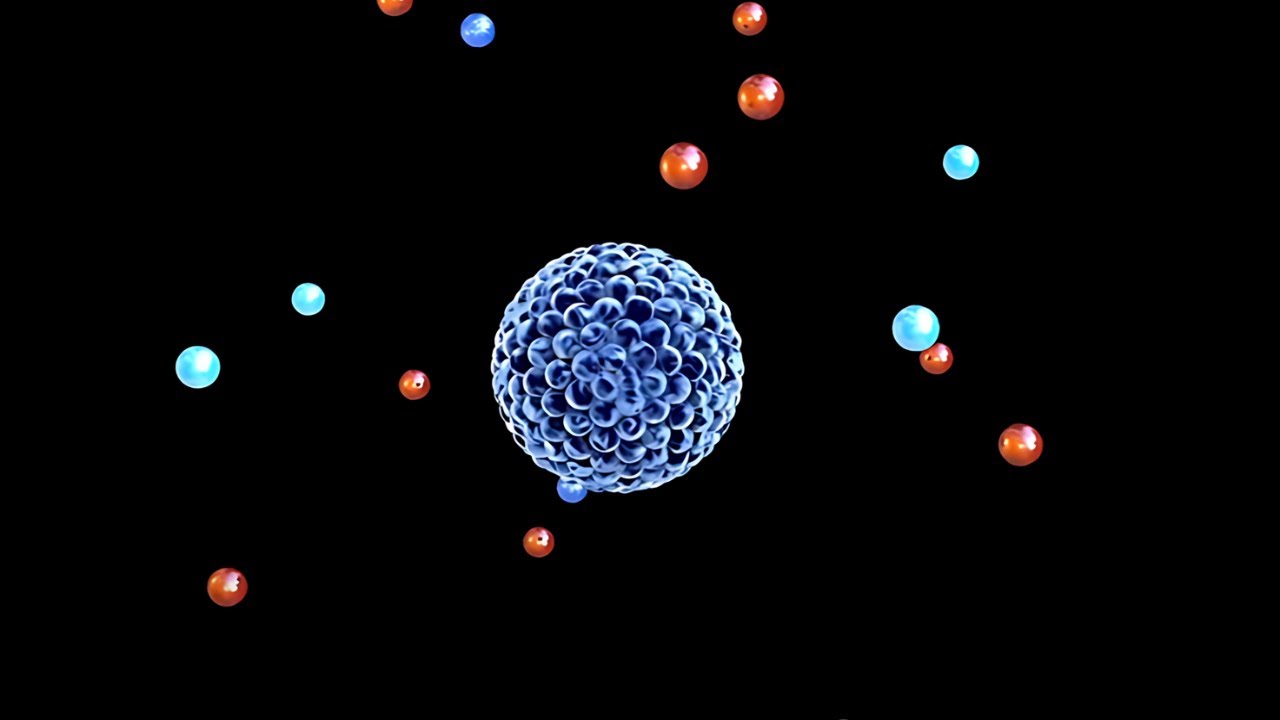
- 🌌 An atom is mostly empty space, with 99.999996% of its volume being empty. The remaining volume is occupied by subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- 🧪 Protons and neutrons are concentrated in the nucleus of an atom, which holds almost all of the atom's mass, while electrons orbit around the nucleus.
- ⚖️ Subatomic particles have extremely small masses: protons and neutrons have a mass of 1 amu each, while an electron has a mass of 1/1840 of that of a proton or neutron.
- 🧲 Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge. The balance of protons and electrons determines the atom's charge.
- 📝 Elements can be represented in isotope notation, where symbols represent the element, the nucleon number (mass number) is at the top left, and the proton number (atomic number) is at the bottom left.
- 🔄 Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This gives elements different nucleon numbers.
- 📊 A particle is neutral when protons equal electrons, positively charged when electrons are fewer than protons, and negatively charged when electrons exceed protons.
- 📉 Some isotopes are unstable and radioactive, making them useful in various fields like medicine and archaeology, such as carbon-14 for carbon dating.
- 🧮 Isotope notation helps in identifying the number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and the charge of an atom, providing valuable information for scientific applications.
Q & A
What is the smallest unit of a chemical element or compound?
-The smallest unit of a chemical element or compound is called an atom.
Where does the word 'atom' come from, and what does it mean?
-The word 'atom' comes from the Greek word 'atomos,' which means 'cannot be cut.' It describes the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of a chemical element.
What percentage of an atom is empty space?
-99.999996% of an atom's volume is empty space.
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
-An atom is made up of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Where are the protons and neutrons located in an atom?
-Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, which is at the center of the atom.
How does the mass of an electron compare to the mass of a proton or neutron?
-An electron has 1/1840 of the mass of a proton or neutron.
What is the charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
-Protons have a positive charge (+1), neutrons have no charge (neutral), and electrons have a negative charge (-1).
How is an isotope represented in atomic notation?
-An isotope is represented in the format where X is the element symbol, A is the nucleon (mass) number, and Z is the proton (atomic) number.
What distinguishes isotopes of the same element from each other?
-Isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
What are some common applications of isotopes in different fields?
-Isotopes are used in various fields such as archaeology (carbon-14 for carbon dating) and medicine (sodium-24 for leak detection in underground piping).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Struktur Atom | Elektron Proton Neutron | Notasi Atom | No Massa | Isotop Isobar Isoton Isoelektron

2 Subatomic Particles

Protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms | Atomic structure | High school chemistry | Khan Academy

GCSE Chemistry - Atoms & Ions #1
INILAH PARTIKEL DASAR PENYUSUN ATOM

What is an atom | Matter | Physics | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
