Behaviorism: Part 2
Summary
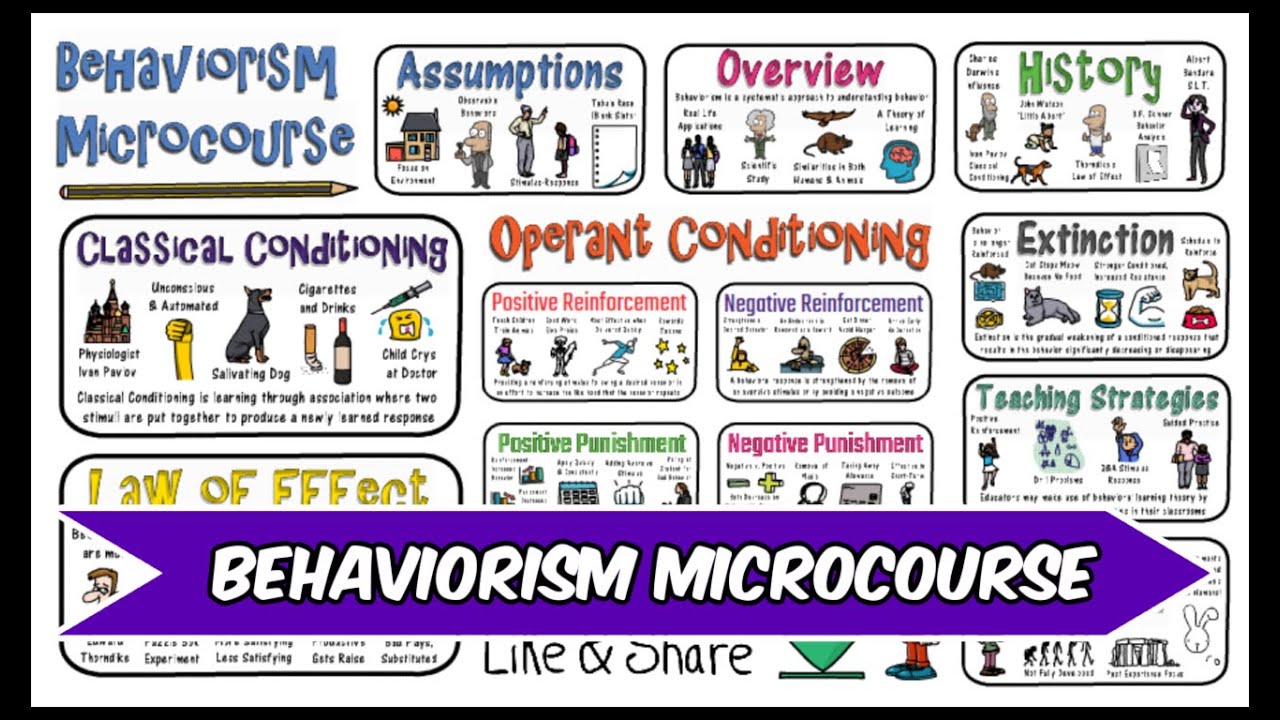
TLDRThis video discusses behaviorism, focusing on B.F. Skinner's experiments with animals, such as rats and pigeons. Skinner used positive reinforcement to encourage behavior, as seen when rats learned to press a lever for food. The video also explains negative reinforcement, punishment, shaping, and schedules of reinforcement, including fixed and variable intervals and ratios. These concepts illustrate how behavior can be modified through reinforcement and punishment, with examples like vending machines and gambling. The video emphasizes the role of environment in shaping behavior and the foundational contributions of behaviorists like Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner.
Takeaways
- 🐀 B.F. Skinner used animals, primarily rats and pigeons, to study behavior through experiments.
- 🍽️ Skinner trained rats using positive reinforcement by providing food whenever they pressed a lever, which increased the behavior.
- ⚡ Negative reinforcement involves removing a negative stimulus to increase behavior, like stopping an electric shock when a lever is pressed.
- 🚫 Punishment decreases behavior: positive punishment adds a consequence, while negative punishment removes something desirable.
- 🛠️ Shaping involves rewarding successive approximations toward a desired behavior, like rewarding rats for getting closer to the lever.
- 🔄 Schedules of reinforcement can be based on ratio (number of responses) or interval (time between rewards).
- 🍫 Continuous reinforcement provides a reward every time the desired behavior occurs, like getting candy from a vending machine with each payment.
- 🔢 Fixed ratio schedules provide rewards after a set number of responses, while variable ratio schedules are unpredictable.
- ⏳ Fixed interval schedules provide rewards after a specific amount of time, while variable interval schedules are unpredictable and vary in time.
- 🎲 Activities like gambling and fishing operate on variable reinforcement schedules, contributing to their popularity.
Q & A
What method did Skinner use to train rats in his experiment?
-Skinner used positive reinforcement by giving the rats food every time they pressed a lever, which increased the likelihood of the behavior.
What is negative reinforcement, according to Skinner?
-Negative reinforcement involves the removal of a negative consequence to increase the likelihood of a behavior. For example, Skinner could have used electric shocks and stopped them when the rat pressed the lever.
What is the difference between positive and negative punishment?
-Positive punishment adds an undesirable consequence (like chores for not doing homework), while negative punishment takes away something desirable (like taking away a phone) to decrease a behavior.
How did Skinner use shaping in his experiments with rats?
-Skinner used shaping by rewarding the rats each time they got closer to the lever. This gradual reinforcement led the rats to eventually press the lever for food.
What is the difference between ratio and interval schedules of reinforcement?
-Ratio schedules depend on the number of responses for reinforcement, while interval schedules depend on the amount of time that must pass before reinforcement is given.
What is continuous reinforcement, and how does it differ from fixed ratio reinforcement?
-Continuous reinforcement provides a reward every time the behavior is shown (like putting money into a vending machine), while fixed ratio reinforcement rewards behavior after a set number of responses.
What is variable ratio reinforcement, and how does it differ from fixed ratio reinforcement?
-Variable ratio reinforcement provides a reward after an unpredictable number of responses, unlike fixed ratio reinforcement where the reward comes after a set number of responses.
What are examples of variable interval reinforcement in real life?
-Variable interval reinforcement is seen in activities like fishing or gambling, where the time between rewards is unpredictable, making the activity highly engaging.
How does behaviorism view human and animal learning?
-Behaviorism sees learning in humans and animals as similar, where behavior is shaped by the environment through processes like classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
How has behaviorism influenced psychology?
-Behaviorism, through concepts like conditioning, shaped psychology by promoting the study of observable behavior and emphasizing the role of the environment in shaping actions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Behaviorism in Education (Explained in 4 Minutes)
Behaviorism: Skinner, Pavlov, Thorndike, etc.

Behaviorism: Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner

Big 3 Learning Theories: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism! Intro to ID Part 4 of 6

Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism & Learning and Instructional Theory

El Conductismo - Watson, Skinner y el Condicionamiento - ¿La mente nace o se hace?

Teori-Teori Belajar || Behaviorisme, Kognitivisme, Konstruktivisme, Humanisme, Sibernetik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
