Inverse trig functions: arcsin | Trigonometry | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe video script explains the concept of sine and arcsine (inverse sine) functions using the unit circle and right-angle triangles. It walks through solving for the sine of π/4 (or 45°), showing that it equals √2/2, and then discusses how to find the arcsine of a value, specifically √2/2 and -√3/2. The process involves solving triangles and using radians, explaining the need to restrict the range of the arcsine function to ensure it's valid. The script also highlights verifying results with a calculator.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The sine of pi over 4 radians (45 degrees) is the square root of 2 over 2.
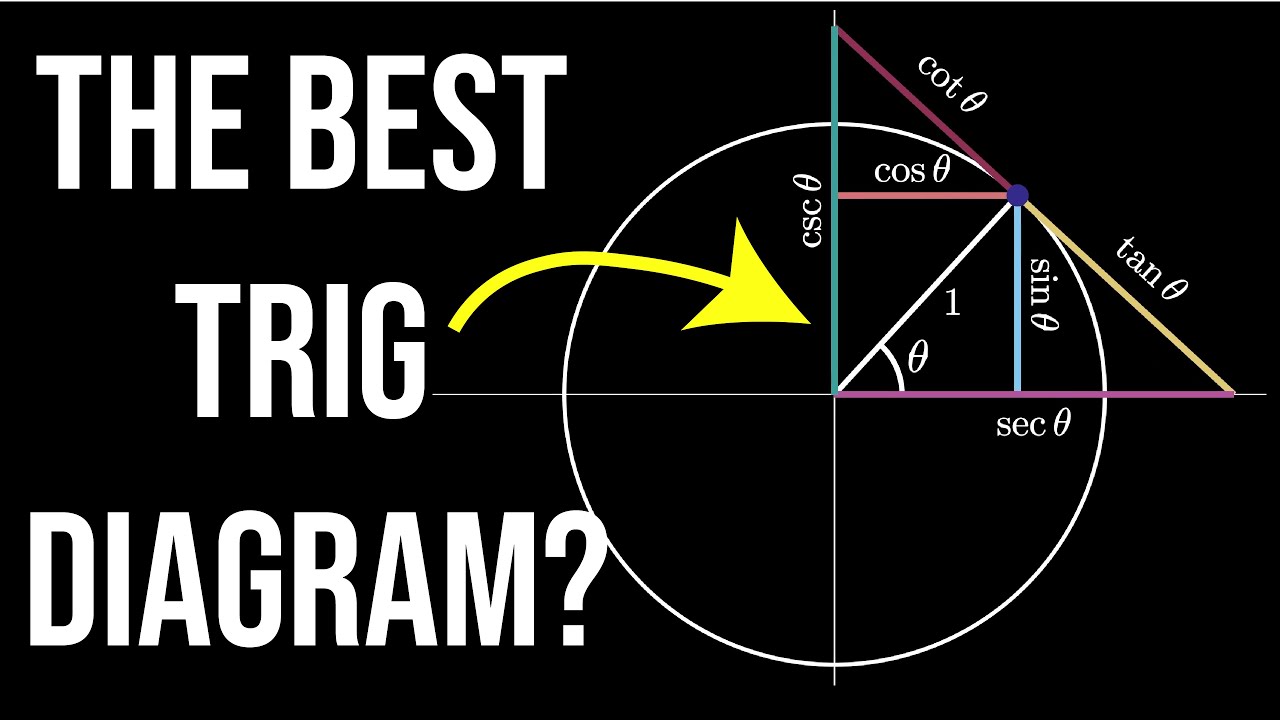
- 📐 The sine function refers to the y-coordinate on the unit circle for a given angle.
- 🔄 The arcsine function (or inverse sine) asks for the angle whose sine is a given value.
- ✖️ Multiple angles can give the same sine value, so the arcsine function must have a restricted range to be valid.
- 📏 The range for the arcsine function is restricted to angles between -pi/2 and pi/2 radians (first and fourth quadrants).
- ⬆️ The domain for the arcsine function is restricted to values between -1 and 1, as those are the possible outputs of the sine function.
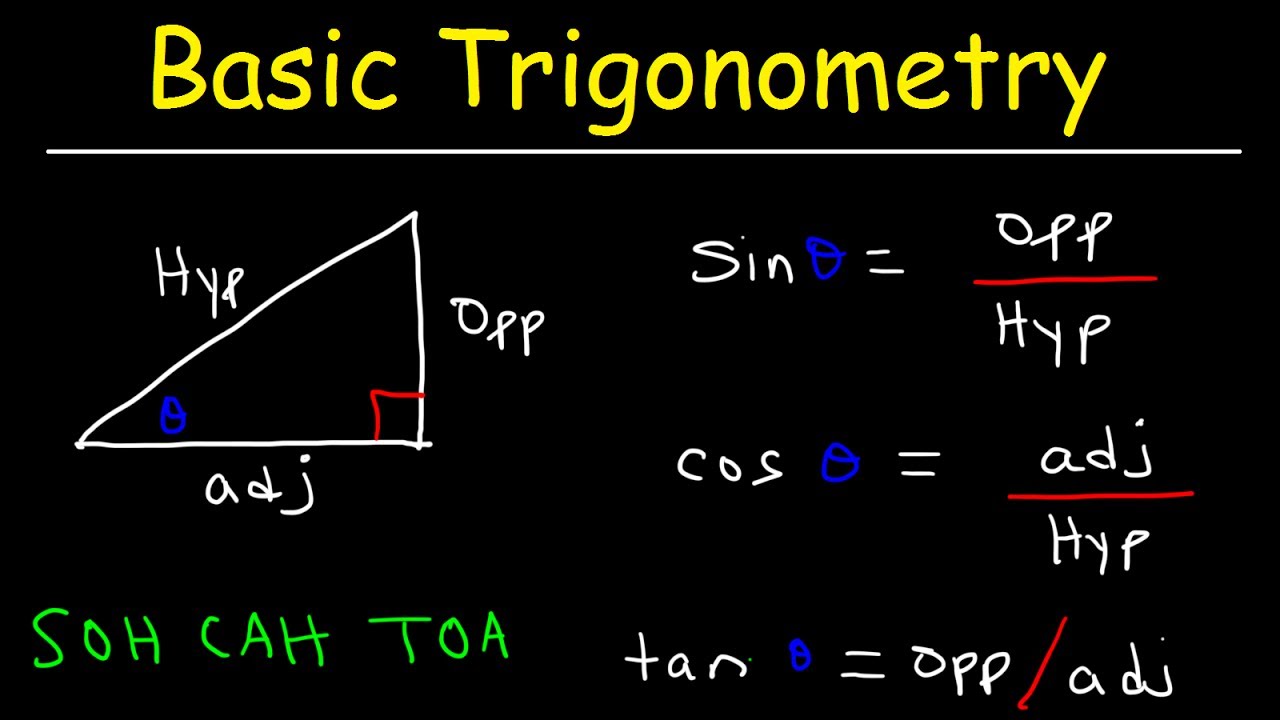
- 🔺 The triangle used for pi over 4 radians is an isosceles 45-45-90 triangle.
- 🔍 The sine of an angle provides the height (y-coordinate) on the unit circle, and arcsine finds the angle from this height.
- 📉 The arcsine of a negative value, like -sqrt(3)/2, results in a negative angle, which falls in the fourth quadrant.
- 📏 In a 30-60-90 triangle, the side opposite the 60-degree angle is sqrt(3)/2, which helps find the arcsine of -sqrt(3)/2 as -pi/3 radians.
Q & A
What is the sine of pi over 4 in radians?
-The sine of pi over 4 radians (which is equivalent to 45 degrees) is the square root of 2 over 2.
How is the sine of an angle determined on the unit circle?
-The sine of an angle is defined as the y-coordinate of the point on the unit circle corresponding to that angle.
What is the value of sine for a 45-degree angle in a 45-45-90 triangle?
-In a 45-45-90 triangle, the sine of the 45-degree angle is equal to the length of the opposite side, which is the square root of 2 over 2.
What does 'arcsine' or 'inverse sine' represent?
-The arcsine or inverse sine of a value is the angle whose sine is equal to that value. For example, arcsine of the square root of 2 over 2 equals pi over 4.
Why must the range of the arcsine function be restricted?
-To make the inverse sine a valid function, its range is restricted to avoid multiple angles producing the same sine value. The standard range for arcsine is between -pi/2 and pi/2 radians.
What is the domain of the arcsine function?
-The domain of the arcsine function is limited to values between -1 and 1 because sine of any angle only produces results within this range.
What is the arcsine of negative square root of 3 over 2?
-The arcsine of negative square root of 3 over 2 is equal to negative pi over 3 radians.
How do you calculate angles from sine values in radians?
-To calculate angles from sine values in radians, you use the inverse sine (arcsine) function. For example, the arcsine of negative square root of 3 over 2 gives negative pi over 3 radians.
Why does adding multiples of 2pi to an angle give the same sine value?
-Since sine is periodic with a period of 2pi, adding multiples of 2pi to an angle brings you to the same position on the unit circle, giving the same sine value.
What triangle type is involved when sine equals square root of 3 over 2?
-A 30-60-90 triangle is involved when sine equals the square root of 3 over 2. The angle opposite the side of length square root of 3 over 2 is 60 degrees, or pi over 3 radians.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)