Experience with Ethernet
Summary
TLDRThis session explores the advantages and disadvantages of Ethernet, the most prevalent wired LAN technology. It highlights Ethernet's cost-effectiveness, equal node privileges, simplicity in maintenance, reliability, and high data transfer quality, with modern versions like Gigabit Ethernet supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps. However, it also discusses its limitations, such as network capacity waste under heavy loads due to collisions, unsuitability for real-time applications, lack of client-server architecture, and the necessity for dummy data padding. The session concludes with an overview of various Ethernet cable categories, ranging from Category 3 to the latest Category 8, detailing their types, speeds, and whether they are shielded or unshielded.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Ethernet Dominance**: Ethernet is the most widely used wired LAN technology.
- 💰 **Cost-Effectiveness**: Ethernet is relatively inexpensive, contributing to its popularity.
- 🔄 **Equal Privileges**: Ethernet operates without a client-server architecture, giving all nodes the same privileges.
- 🛠️ **Simple Maintenance**: Ethernet is easy to maintain and administer.
- 🔒 **Noise Resistance**: Ethernet cables are robust against noise, ensuring reliability.
- 📈 **High Data Transfer Quality**: Ethernet provides consistent, high-quality data transfer.
- 🚀 **Fast Speeds**: With advancements like Gigabit Ethernet, speeds of up to 10 Gbps and more are achievable.
- 🚨 **Collision Issues**: Ethernet can waste network capacity due to collisions under heavy loads.
- ⏱️ **Unsuitable for Real-Time**: Ethernet's lack of priority setting makes it unsuitable for real-time applications.
- 📊 **Mandatory Frame Size**: Ethernet mandates a minimum frame size, requiring padding for small data transfers.
- 🔄 **No Acknowledgments**: Ethernet does not send acknowledgments after receiving packets, which can be a disadvantage.
- 📞 **Cable Categories**: Ethernet cables are categorized into different types, such as Cat3, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8, each with varying speeds and features.
- 🛡️ **Shielding Options**: Ethernet cables can be either shielded (STP) or unshielded (UTP), with shielded cables offering better performance against interference.
Q & A
What is the predominant wired LAN technology discussed in the session?
-Ethernet is the most widely used wired LAN technology discussed in the session.
Why is Ethernet popular according to the session?
-Ethernet is popular because it is relatively inexpensive, has simple maintenance and administration, and is robust to noise.
What is one of the pros of Ethernet mentioned in the session?
-Ethernet is considered a pro because all nodes have the same privileges, which is suitable for networks where every node should have equal access.
What are some disadvantages of Ethernet under heavy loads?
-Under heavy loads, Ethernet can waste network capacity due to collisions, which is a problem because it does not hold good for real-time applications.
Why is Ethernet not suitable for real-time applications?
-Ethernet is not suitable for real-time applications because it does not support setting priority for packets, which is necessary for ensuring timely data transfer.
What is the minimum frame size required for Ethernet?
-The minimum frame size in Ethernet should be of 64 bytes, with a payload of 46 bytes.
What does the term 'Ethernet cut cables' refer to?
-The term 'Ethernet cut cables' refers to various categories of Ethernet cables, which include different types of twisted pair cables such as UTP and STP.
What are the different categories of Ethernet cables mentioned in the session?
-The different categories of Ethernet cables mentioned are Category 3, 5, 5e, 6, 6a, 7, and 8.
What is the maximum speed of Category 5e Ethernet cables?
-Category 5e Ethernet cables have a maximum speed of 1 gigabit per second.
Which category of Ethernet cable is strictly shielded and operates at 10 gigabits per second?
-Category 6a Ethernet cables are strictly shielded and operate at a speed of 10 gigabits per second.
What is the maximum speed of Category 8 Ethernet cables?
-Category 8 Ethernet cables have a maximum speed of 40 gigabits per second.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

STS - Science and Technology and Nation Building - Science Education in the Philippines

TEKNOLOGI JARINGAN KABEL DAN NIRKABEL | 11 TKJ 2 | SMKN 2 TUREN #11tkjkeren
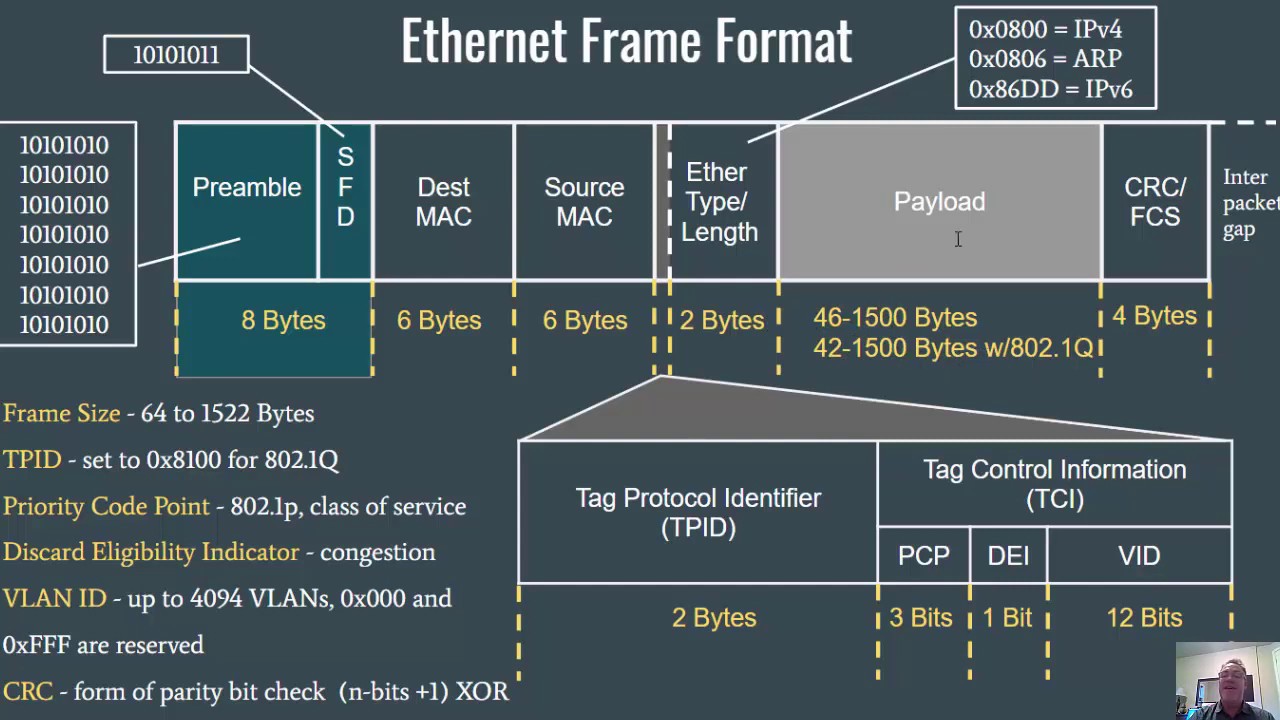
The Data Link Layer, MAC Addressing, and the Ethernet Frame

8 DC18 M10 NETWORKS

XI TKJ _ TEKNOLOGI JARINGAN BERBASIS LUAS Pemahaman Dasar Jaringan Berbasis Luas (WAN) Part 1

Materi Jaringan Komputer - Informatika
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
