Understanding Time Zones
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the historical development of time zones, highlighting the 19th-century need for standardization due to rail travel. In 1884, 26 countries met in Washington DC and chose Greenwich, England as the Prime Meridian, establishing 24 time zones. The script explains how to calculate time zones, emphasizing the 15-degree intervals and the International Dateline's role in separating calendar days. It also touches on countries adjusting time zones for practical reasons, such as daylight savings or maintaining national unity.
Takeaways
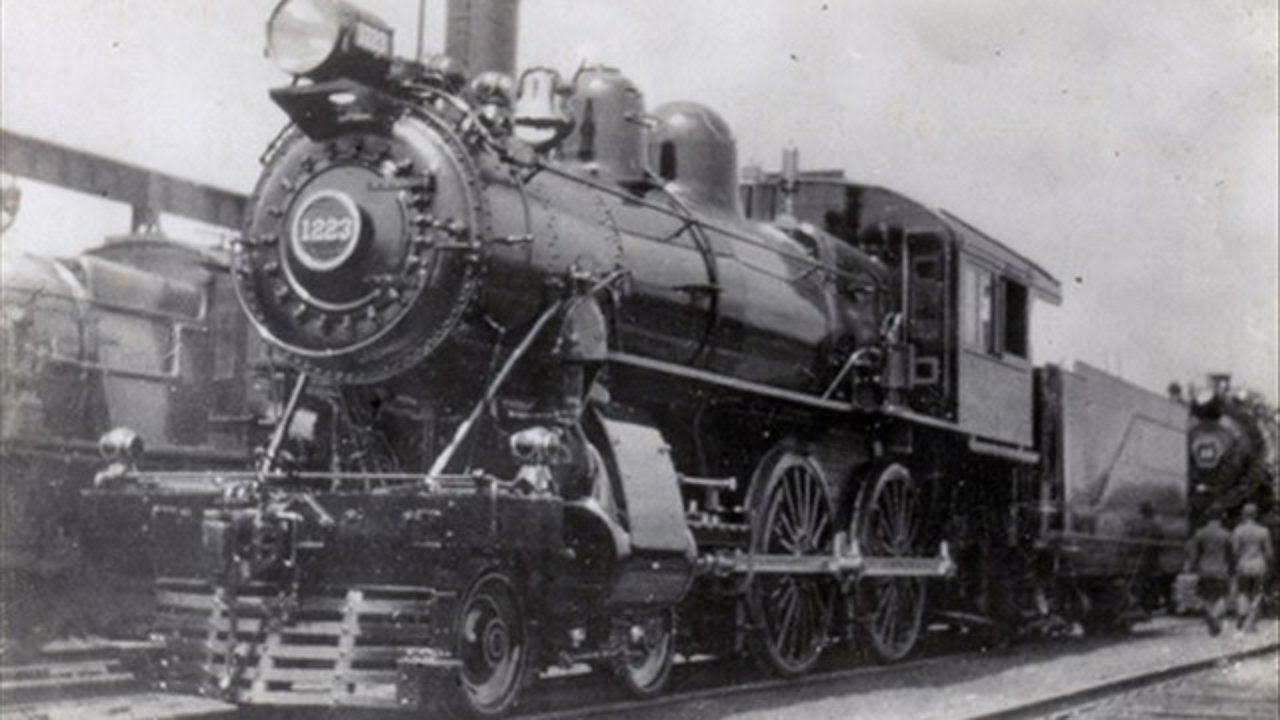
- ⏲️ In the past, towns set their own times based on local solar noon, leading to confusion with the advent of rail travel.
- 🚂 The need for standardized time arose in the late 19th century to streamline rail schedules across different towns.
- 🌐 In 1884, 26 countries met in Washington DC to agree on a Prime Meridian, settling on Greenwich, England as the reference for zero degrees longitude.
- 🌍 This meeting established the 24 time zones, each an hour apart, based on the Earth's rotation of 15 degrees longitude per hour.
- 🕰️ Time zones are counted from the Prime Meridian, extending 7.5 degrees on either side of central meridians at 15-degree intervals.
- 🌏 Sydney, Australia, for instance, is in the 150 degrees east central meridian, with its time zone spanning from 142.5 to 157.5 degrees east.
- 📍 To calculate time zones, determine if the location is east or west of the Prime Meridian and count the number of time zones away from Greenwich.
- ➖ For locations west of Greenwich, subtract the time zone difference from GMT, and ➕ for those east to find local time.
- 📅 The International Dateline, 180 degrees opposite the Prime Meridian, separates calendar days and has been adjusted to avoid land.
- 🗺️ Countries like Kiribati and Samoa have shifted their positions relative to the Dateline for practical reasons, such as aligning with trading partners.
Q & A
Why was it necessary to standardize time in the late 19th century?
-In the late 19th century, the standardization of time became necessary due to the advent of rail travel, which moved people across great distances. Schedules were confusing as each town operated on its own local time, leading to inefficiencies in rail operations.
What event in 1884 led to the standardization of time?
-In 1884, delegates from 26 countries met in Washington DC and agreed on a Prime Meridian as a common zero for longitude, which led to the standardization of time.
Which location was chosen as the international standard for zero degrees longitude?
-Greenwich, England was selected as the international standard for zero degrees longitude.
How many time zones were established as a result of the 1884 conference?
-As a result of the 1884 conference, 24 time zones were established.
Why do some countries not align their time zones perfectly with their longitudes?
-Some countries do not align their time zones perfectly with longitudes for reasons such as keeping the entire country in one time zone or altering times at certain times of the year, like during daylight savings time.
How does the earth's movement relate to the concept of time zones?
-The earth moves 15 degrees longitude each hour, and since there are 24 hours in a day, this results in 24 standard time zones.
What is the significance of the Prime Meridian in time zone calculations?
-The Prime Meridian, which is zero degrees longitude, is the starting point for time zone calculations. Time zones are counted from the Prime Meridian at 15-degree intervals.
How can one determine if a time zone is in the eastern or western hemisphere?
-A time zone is in the eastern hemisphere if it is east of the Prime Meridian and will be at an earlier time than Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). If it is west of the Prime Meridian, it will be in the western hemisphere and at a later time than GMT.
How does one calculate the local time for a location based on its time zone?
-To calculate the local time for a location, one must first determine if the location is east or west of the Prime Meridian, then count how many time zones away from Greenwich the location is, and finally, add or subtract the corresponding number of hours from Greenwich Mean Time.
What is the International Dateline, and why does it deviate in some places?
-The International Dateline is an imaginary line that lies 180 degrees in longitude on the opposite side of the earth from the Prime Meridian. It separates one calendar day from another. The line deviates in places to avoid crossing any land.
Why did Samoa and Tokelau change their position relative to the International Dateline in 2011?
-In 2011, Samoa and Tokelau moved westward to be in the eastern hemisphere so they could have the same date as their main trading partners, Australia and New Zealand.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)